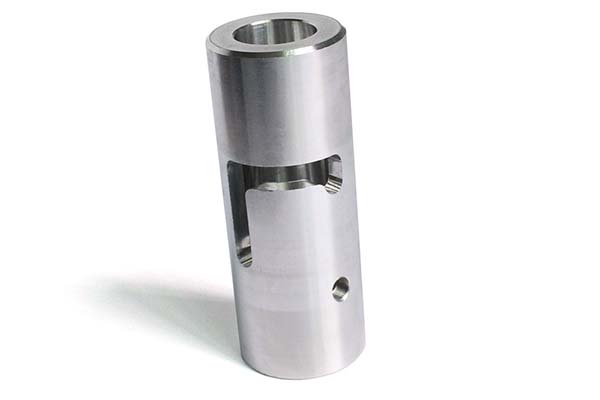
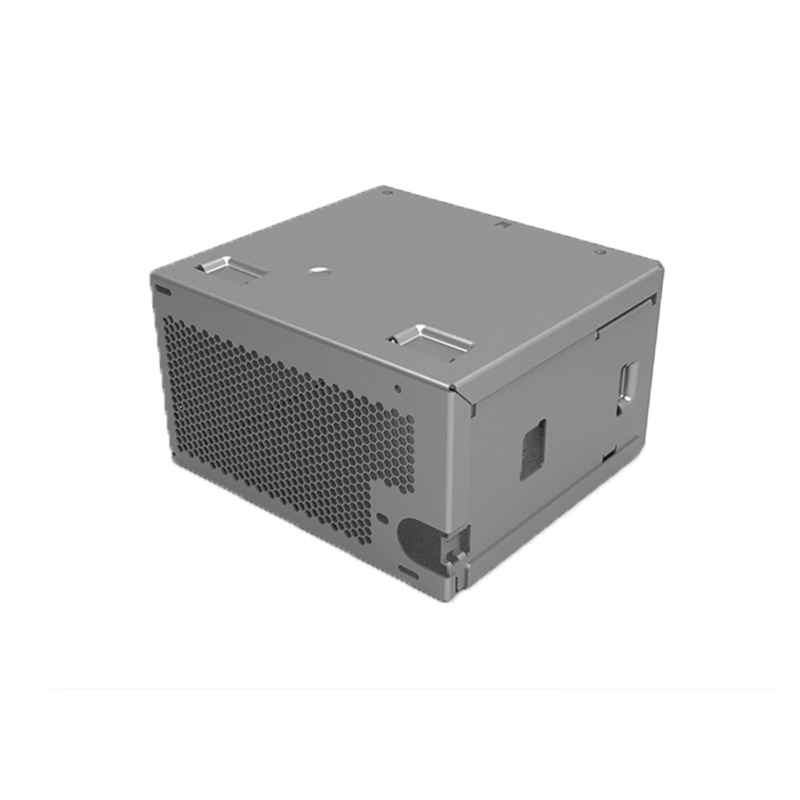
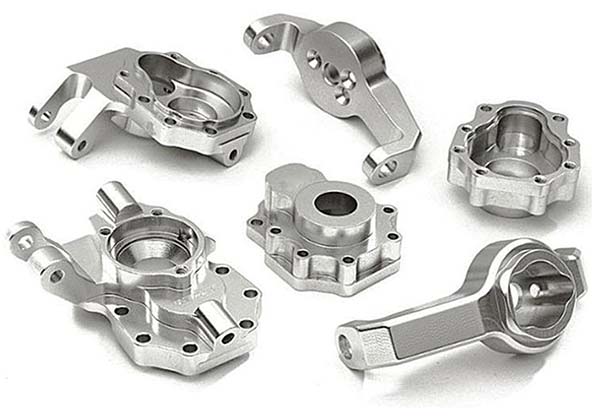
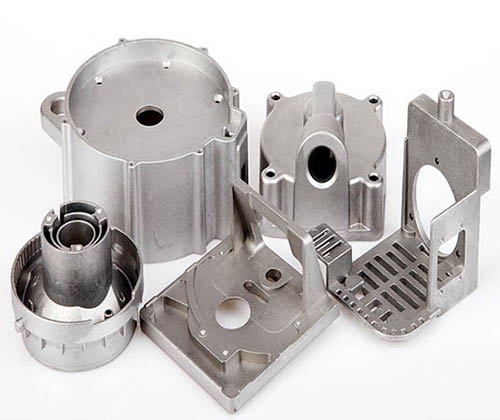
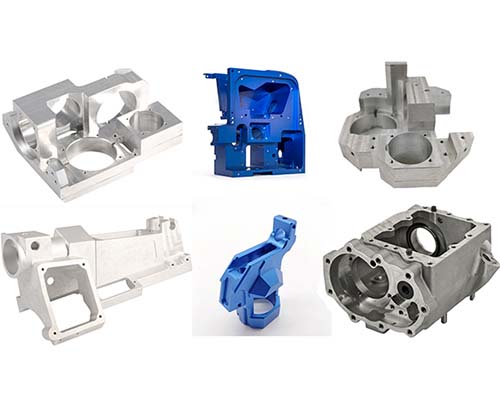
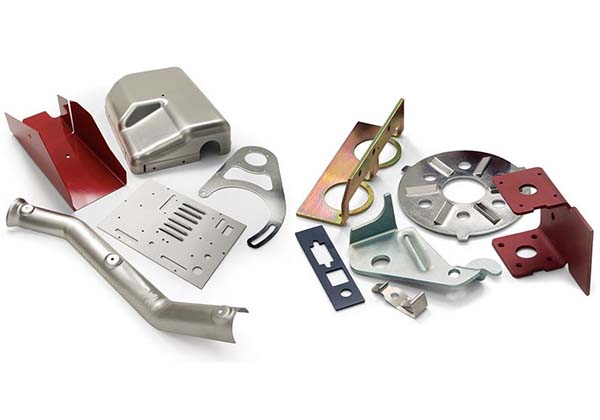
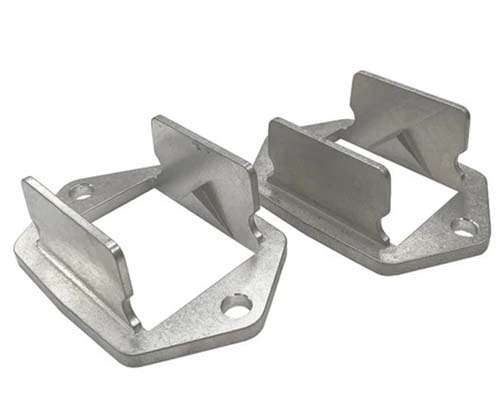
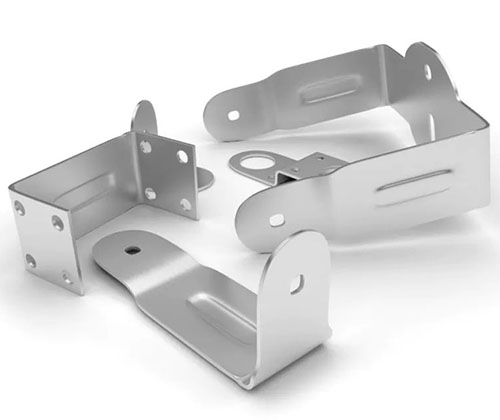
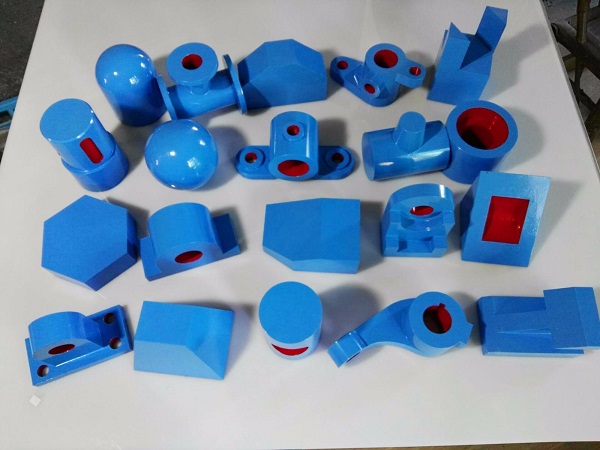
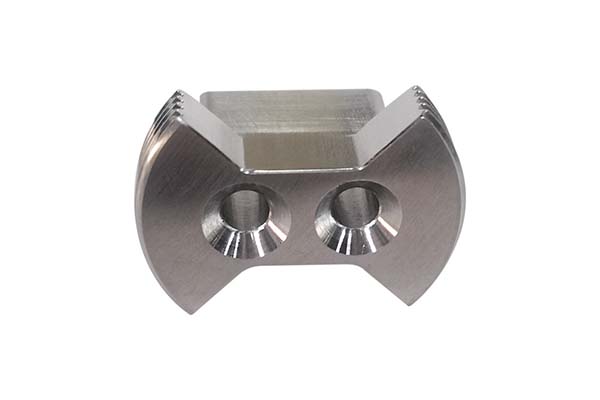
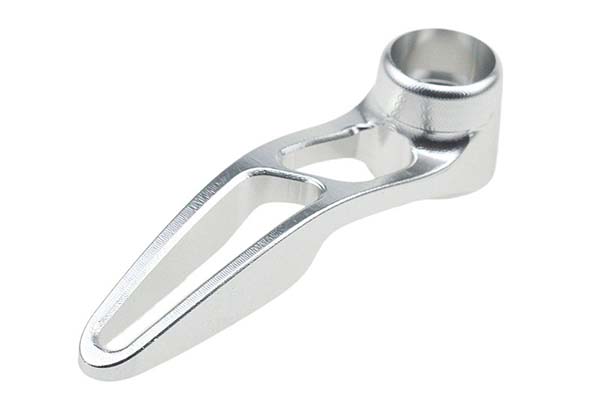
Die Casting Copper Alloys: Conductive Strength for Critical Applications
You’ve turned to copper alloys for their unrivaled electrical and thermal conductivity, expecting parts that deliver reliable performance in electrical connectors and heat-dissipating components. But your production is facing challenges: the molten metal’s high viscosity causes incomplete fills in thin sections of plumbing components. Some castings have porous interiors that leak in pressure tests, while […]