Understanding Injection Molding
What is Injection Molding?
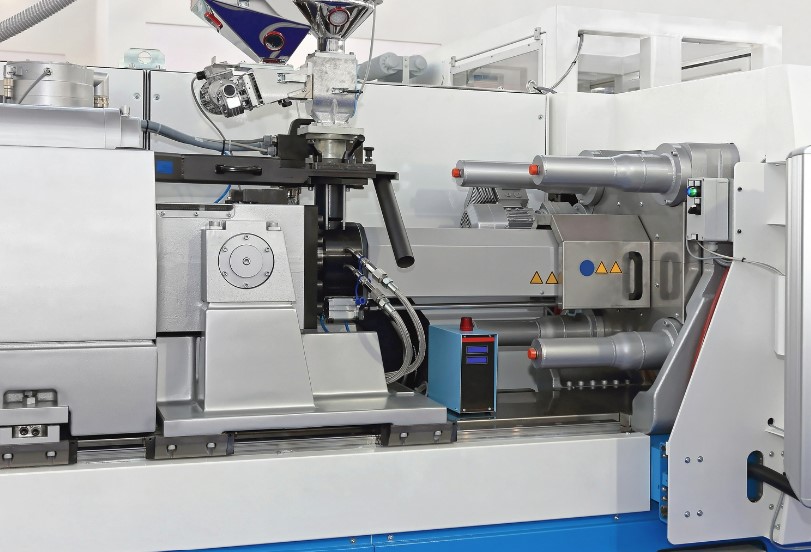
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process in the plastic industry. It involves injecting molten plastic material into a mold cavity, where it cools and solidifies to take the shape of the mold. This process is highly efficient and suitable for mass - production of plastic parts with complex shapes and precise dimensions.
The basic working principle of injection molding is similar to that of a syringe. Plastic pellets are first fed into a heated barrel. As the screw inside the barrel rotates, it not only conveys the plastic pellets forward but also generates frictional heat, which, combined with the external heating of the barrel, melts the plastic. Once the plastic reaches a molten, viscous state (the so - called melt phase), a high - pressure plunger or the screw itself is used to inject this molten plastic into a closed mold cavity at a high speed. The mold is typically made of steel or aluminum and is designed to have the exact shape of the desired final product. After the mold is filled, the plastic is allowed to cool and solidify within the mold. Once fully solidified, the mold opens, and the newly formed plastic part is ejected.
Injection molding plays a crucial role in modern manufacturing. It enables the production of a vast array of products that we use in our daily lives. From small electronic components to large automotive parts, injection molding has become an indispensable process. According to industry reports, the global injection molding market is expected to grow steadily in the coming years, driven by the increasing demand for plastic products in various industries. For Yigu Technology example, in the consumer goods sector, injection - molded plastic products account for a significant proportion of the total production volume, which reflects the importance and popularity of this manufacturing process.
Factors to Consider When Choosing Injection Molding Services Near You
When searching for the best injection molding services near you, several crucial factors need to be taken into account. Making an informed decision can save you time, money, and ensure the production of high - quality plastic parts.
Experience and Expertise
Years in the Industry
An injection molding service provider with a long - standing presence in the industry is often a better choice. A company that has been operating for many years, say 10 - 20 years or more, has likely encountered a wide variety of projects and challenges. For Yigu Technology example, a service provider with 15 years of experience has had the opportunity to work on projects ranging from simple consumer goods to complex industrial components. They have had the time to perfect their processes, train their staff, and build relationships with reliable suppliers. Such a company is more likely to have the know - how to handle complex projects. A project that involves creating plastic parts with intricate internal structures or tight tolerances requires a high level of expertise. An experienced service provider will have the necessary skills and techniques to ensure that the final product meets the required specifications. According to industry surveys, companies with over 10 years of experience are 30% more likely to successfully complete complex injection molding projects compared to those with less than 5 years of experience.
Portfolio of Past Projects
Reviewing the portfolio of past projects of an injection molding service provider is an excellent way to gauge their capabilities. A diverse portfolio that includes projects from different industries, such as automotive, medical, and electronics, indicates that the provider can adapt to different requirements. For instance, if a service provider has worked on automotive interior parts, they are familiar with the requirements for materials that can withstand high temperatures and wear, as well as the aesthetic standards for automotive interiors. If they have also completed medical device projects, they understand the strict regulations regarding biocompatibility and cleanliness. Analyzing the complexity of the projects in the portfolio is also important. A portfolio with projects that involve multi - component molds, high - precision parts, or parts with complex geometries shows that the service provider has the technical prowess to handle challenging jobs.
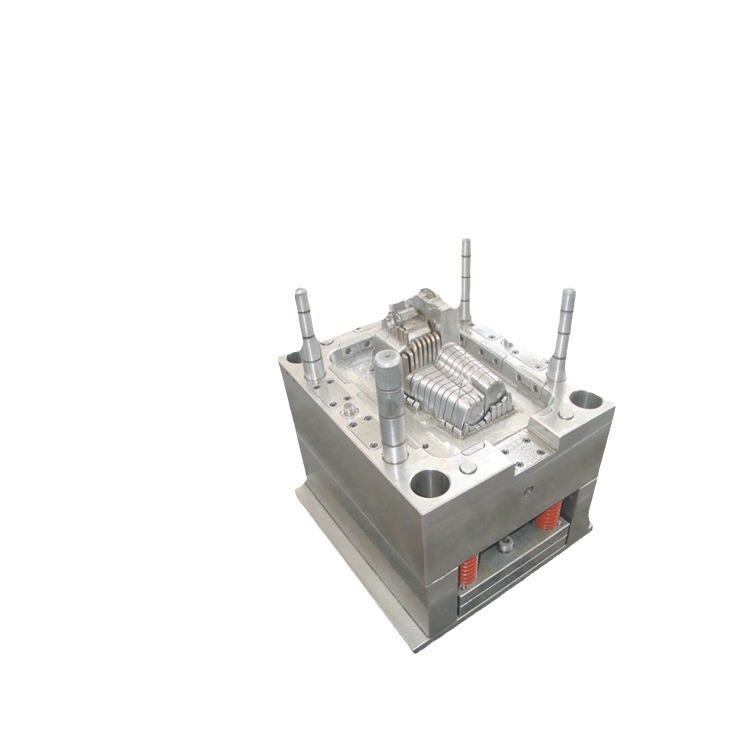
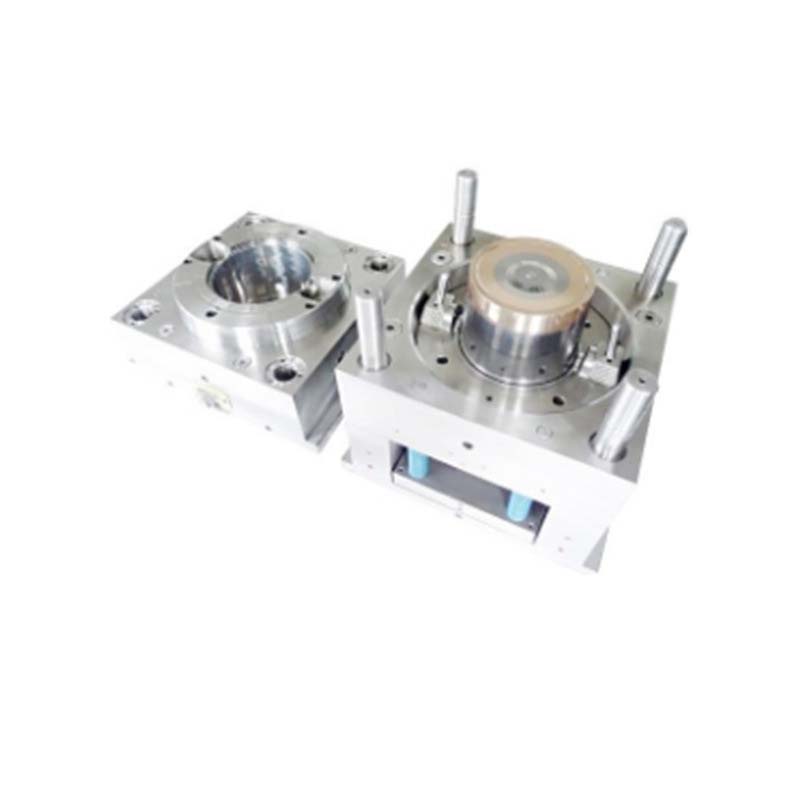
Equipment and Technology
Types of Injection Molding Machines
There are several types of injection molding machines, each with its own set of advantages and suitable applications.
- Horizontal Injection Molding Machines: These are the most commonly used type. The injection unit and the clamping unit are aligned horizontally. They are known for their stability during operation, which is beneficial for large - scale production. Their large platen sizes allow for the use of large molds, making them suitable for manufacturing big parts such as automotive bumpers or large industrial containers. For Yigu Technology example, a large - scale manufacturer of plastic storage bins would likely use horizontal injection molding machines to produce their products efficiently. However, they require a relatively large floor space due to their horizontal layout.
- Vertical Injection Molding Machines: In vertical machines, the injection unit is positioned above the clamping unit. They are particularly useful for applications that involve insert molding. For instance, when creating plastic parts with metal inserts, the vertical orientation makes it easier to place the inserts accurately before the injection process. Their smaller footprint compared to horizontal machines is also an advantage in facilities with limited space. But they may have limitations in terms of the size of the parts they can produce, and the ejection of parts can be more challenging.
- Angular Injection Molding Machines: These machines have the injection unit and the clamping unit at an angle to each other. They are well - suited for molding parts with complex geometries that require side - entry gates. For example, when manufacturing parts with undercuts or non - symmetric shapes, angular injection molding machines can provide better access for the molten plastic to fill the mold cavity evenly.
The following Yigu Technology table summarizes the key features of different types of injection molding machines:
| Type of Machine | Advantages | Disadvantages | Suitable Applications |
| Horizontal | Stable operation, large platen size for big molds | Requires more floor space | Automotive parts, large industrial containers |
| Vertical | Ideal for insert molding, small footprint | Limited part size, challenging part ejection | Parts with metal inserts, small - scale production |
| Angular | Good for complex geometries with side - entry gates | Less common, may require specialized operators | Parts with undercuts or non - symmetric shapes |
Advanced Technologies (e.g., Gas - Assisted Injection Molding)
Advanced injection molding technologies can significantly enhance the quality and production efficiency of plastic parts. Gas - assisted injection molding is one such technology that has gained popularity in recent years.
In gas - assisted injection molding, after the initial injection of molten plastic into the mold cavity, a high - pressure gas (usually nitrogen) is injected into the plastic. The gas then creates a hollow channel inside the part, typically in the thicker sections. This process offers several advantages. First, it reduces the overall weight of the part. For example, in the production of large plastic furniture components, gas - assisted injection molding can reduce the weight by up to 30%, which is not only cost - effective in terms of material usage but also beneficial for transportation and handling. Second, it helps to eliminate sink marks. Sink marks are common defects in traditional injection molding, especially in thick - walled parts. By creating a hollow section, the gas - assisted process reduces the internal stress that causes sink marks. Third, it can improve the strength - to - weight ratio of the part. The hollow channels created by the gas act as internal reinforcements, increasing the part's stiffness and strength. Additionally, since the gas - assisted process allows for the use of lower injection pressures, it can reduce the wear and tear on the molds, extending their lifespan and reducing maintenance costs.
Material Options
Range of Plastics Offered
A good injection molding service provider should offer a wide range of plastic materials to meet different product requirements.
- ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene): ABS is a popular thermoplastic known for its excellent impact resistance, dimensional stability, and good surface finish. It is widely used in the production of consumer electronics, such as the outer casings of smartphones and laptops. Its ability to be easily colored and its relatively low cost make it a preferred choice for many applications where both aesthetics and durability are important.
- PP (Polypropylene): PP is a lightweight plastic with good chemical resistance, heat resistance, and flexibility. It is commonly used in the manufacturing of food containers, automotive interior components, and disposable medical products. For example, food - grade PP is used to make lunch boxes and storage containers due to its non - toxicity and ability to withstand repeated heating and cooling.
- PE (Polyethylene): PE comes in different forms, such as low - density polyethylene (LDPE) and high - density polyethylene (HDPE). LDPE is known for its flexibility and transparency, making it suitable for applications like plastic bags and packaging films. HDPE, on the other hand, is more rigid and has higher strength, making it ideal for products such as water pipes, fuel tanks, and industrial containers.
The Yigu Technology table below shows a comparison of the properties and common applications of these plastics:
| Plastic Material | Key Properties | Common Applications |
| ABS | Good impact resistance, dimensional stability, and surface finish | Consumer electronics casings, toys, automotive interior parts |
| PP | Lightweight, chemical and heat - resistant, flexible | Food containers, automotive interior components, medical products |
| PE (LDPE) | Flexible, transparent | Plastic bags, packaging films |
| PE (HDPE) | Rigid, high strength | Water pipes, fuel tanks, industrial containers |
Custom Material Formulations
In some cases, standard plastic materials may not meet the specific requirements of a product. This is where custom material formulations come in. Custom material formulations involve blending different polymers, additives, and fillers to create a material with unique properties. For example, if a product requires a plastic material with enhanced heat resistance and flame retardancy, a custom formulation can be developed by adding heat - resistant additives and flame - retardant agents to a base polymer. Custom material formulations are especially important in industries such as aerospace and defense, where materials need to meet strict performance and safety standards. A service provider that offers custom material formulations can provide a competitive edge, as they can tailor the material to the exact needs of the product, ensuring optimal performance and quality.
Quality Control Measures
In - Process Inspections
In - process inspections are essential to ensure that the injection molding process is running smoothly and that the parts being produced meet the required quality standards. These inspections can be carried out at various stages of the production process. For example, during the plastic melting and injection stage, the temperature and pressure of the plastic can be monitored. Temperature sensors can be used to ensure that the plastic is at the correct melting temperature. If the temperature is too low, the plastic may not flow properly into the mold cavity, resulting in incomplete parts. If the temperature is too high, the plastic may degrade, affecting the quality of the final product. Pressure sensors can be used to monitor the injection pressure. A consistent injection pressure is crucial for ensuring that the parts are of uniform thickness and density. Sampling inspections can also be done at regular intervals. For instance, every 10 - 20 parts produced, a sample can be taken and inspected for defects such as flash (excess plastic), voids (air pockets), or incorrect dimensions.
Final Product Testing
Once the parts are produced, they undergo final product testing to verify that they meet all the specifications.
- Strength Testing: This can involve tensile testing, where the part is pulled to determine its maximum tensile strength. For example, in the production of plastic hooks used for heavy - duty applications, tensile testing is crucial to ensure that the hooks can withstand the required load without breaking. Compression testing can also be done, especially for parts that will be subjected to compressive forces, such as plastic supports or brackets.
- Dimension Accuracy Testing: High - precision measuring tools, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), are used to check the dimensions of the parts. This is particularly important for parts that need to fit together with other components. For example, in the production of plastic components for a complex mechanical device, the dimensions of the parts must be within a very tight tolerance to ensure proper assembly.
- Chemical Resistance Testing: If the product will be exposed to chemicals during its use, chemical resistance testing is carried out. The part is exposed to the relevant chemicals for a specified period, and then its physical properties are checked for any signs of degradation, such as swelling, discoloration, or loss of strength.
Pricing Structure
Transparency in Pricing
Transparency in pricing is of utmost importance when choosing an injection molding service provider. A transparent pricing structure ensures that you know exactly what you are paying for and there are no hidden fees. A service provider that clearly outlines all the costs involved, including the cost of materials, labor, tooling, and any additional services, is more trustworthy. For example, some providers may charge extra for services such as mold design, prototyping, or post - processing operations. If these costs are not clearly communicated upfront, it can lead to unexpected expenses later on. A study showed that companies that experienced hidden fees during injection molding projects had an average cost overrun of 15 - 20%.
Cost - Breakdown (e.g., Tooling Costs, Unit Costs)
Understanding the cost - breakdown of injection molding services can help you make a more informed decision.
- Tooling Costs: Tooling, which includes the cost of designing and manufacturing the molds, can be a significant part of the overall cost, especially for complex molds. The cost of tooling depends on factors such as the complexity of the mold design, the materials used for the mold (usually steel or aluminum), and the precision required. For example, a simple two - part mold for a basic plastic container may cost a few thousand dollars, while a complex multi - cavity mold for a high - precision medical device can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
- Unit Costs: The unit cost of each plastic part is influenced by factors such as the material cost, the cycle time of the injection molding process, and the production volume. Generally, as the production volume increases, the unit cost decreases due to economies of scale. For example, if you are producing 100 plastic parts, the unit cost may be relatively high. But if you increase the production volume to 10,000 parts, the unit cost can be significantly reduced as the fixed costs (such as tooling and machine setup) are spread over a larger number of parts.
The following Yigu Technology table shows a sample cost - breakdown for a small - scale injection molding project:
| Cost Component | Amount |
| Tooling Cost | $5,000 |
| Material Cost per Part | $0.50 |
| Labor Cost per Part | $0.20 |
| Machine Operating Cost per Part | $0.10 |
| Total Unit Cost for 100 Parts | \(55.80 (\)5,000/100 + \(0.50 + \)0.20+ $0.10) |
| Total Unit Cost for 1000 Parts | \(5.80 (\)5,000/1000 + \(0.50 + \)0.20 + $0.10) |
Customer Service and Communication
Responsiveness
Responsiveness is a key aspect of good customer service in the injection molding industry. A service provider that responds promptly to your inquiries, whether it's via email, phone, or other communication channels, shows that they value your business. For example, if you have a question about the progress of your project or need to make a change to the design, a responsive provider will get back to you within a few hours. In contrast, a provider that takes days to respond can cause delays in your project. A case study found that projects with unresponsive service providers experienced an average delay of 5 - 7 days, which can be costly in terms of production schedules and potential lost business opportunities.
Ability to Provide Technical Support
A good injection molding service provider should have the ability to provide technical support throughout the project. This includes assistance with design optimization. For example, if you have a preliminary design for a plastic part, the service provider can offer suggestions on how to modify the design to make it more suitable for injection molding. They can advise on factors such as wall thickness, draft angles, and gate locations to ensure better mold filling and part quality. In case of production problems, such as mold defects or part quality issues, the service provider should be able to troubleshoot and provide solutions promptly. Their technical expertise can help to minimize downtime and ensure that the production process runs smoothly.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the typical lead time for injection molding projects?
The typical lead time for injection molding projects can vary widely, usually ranging from a few weeks to several months. For small - scale, relatively simple projects with standard molds and common plastic materials, the lead time might be as short as 2 - 4 weeks. This includes the time for mold preparation (if not using an existing mold), material procurement, the actual injection molding process, and basic quality checks.
What are the most common mistakes to avoid when choosing an injection molding service?
One of the most common mistakes is choosing a service provider based solely on price. While cost is an important factor, focusing only on the lowest - priced option can lead to sub - standard quality. A cheaper service may cut corners on material quality, use outdated equipment, or have insufficient quality control measures, resulting in parts with defects, poor dimensional accuracy, or low durability.
Another mistake is overlooking the experience and expertise of the service provider. As mentioned earlier, an experienced company is more likely to handle complex projects successfully. A provider with limited experience may struggle with projects that require high - precision molding, complex mold designs, or the use of specialized materials. It's important to review their portfolio of past projects and customer testimonials to gauge their capabilities.