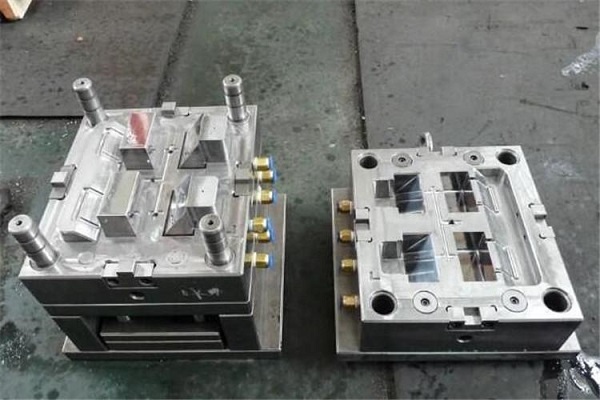
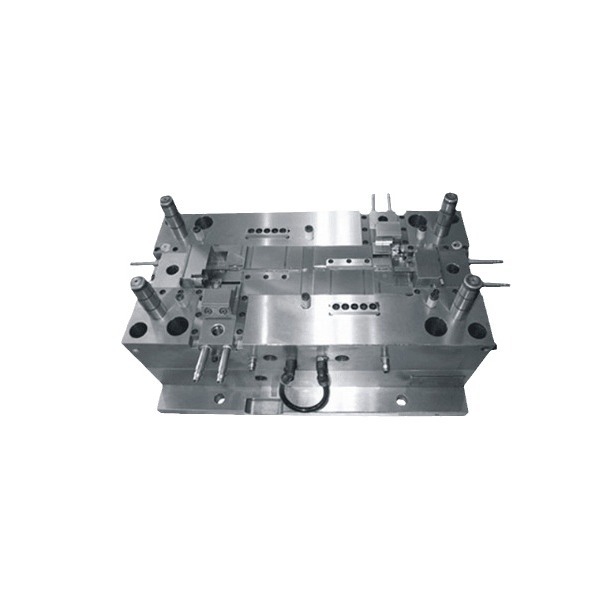
What Are Mold Services?
Mold services refer to a comprehensive range of professional offerings related to the creation, maintenance, and optimization of molds. Molds are essentially hollow cavities or forms into which liquid materials such as plastic, metal, or glass are poured to take on a specific shape as they cool and solidify. These services play a pivotal role in various manufacturing industries, ensuring the production of high - quality, consistent products.
Common Mold Services
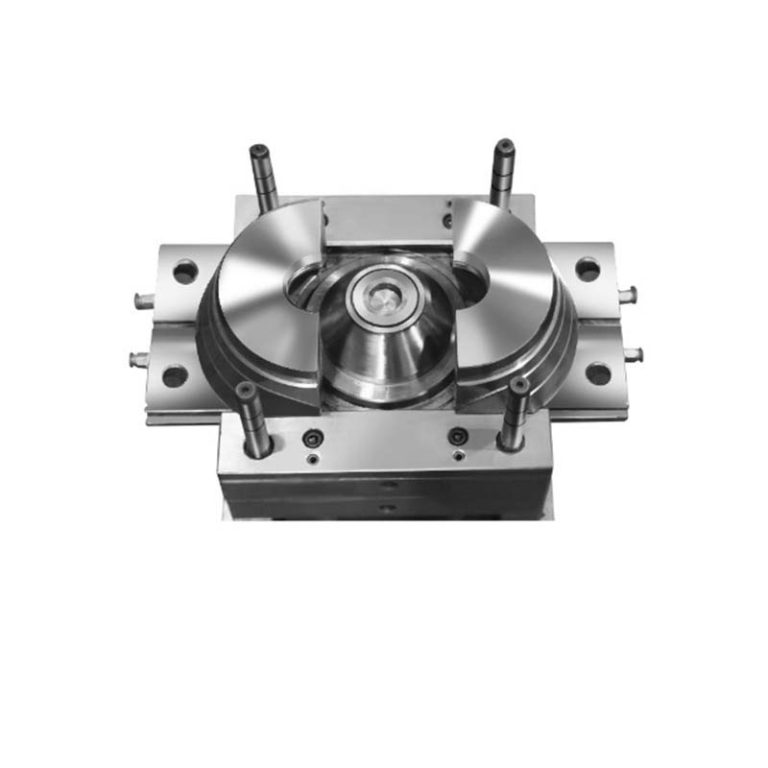
- Mold Design: This is the initial and crucial stage. Mold designers use advanced CAD (Computer - Aided Design) software to create 2D and 3D models of the mold. They consider factors such as the product's shape, size, wall thickness, draft angles, and the type of material to be molded. For example, in plastic injection molding, a well - designed mold will ensure that the plastic flows evenly into all parts of the cavity, minimizing defects like short shots or warping. A study by the Society of Plastics Engineers found that 70% of molding problems can be traced back to poor mold design.
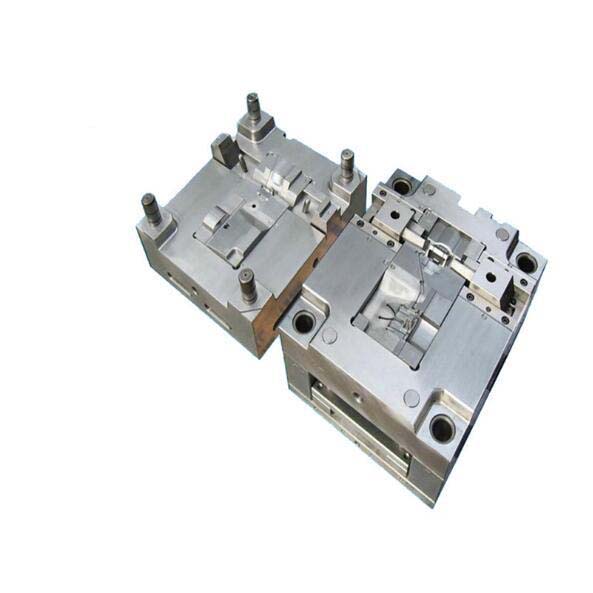
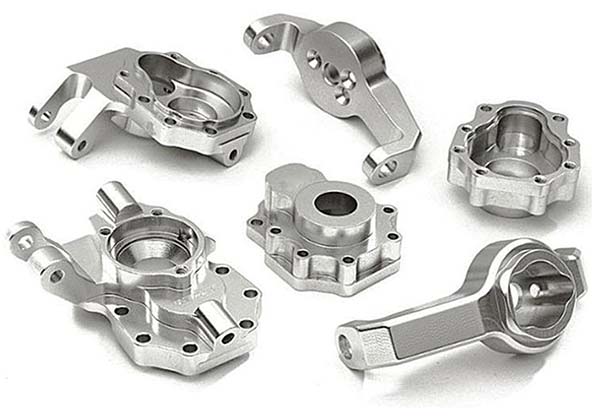
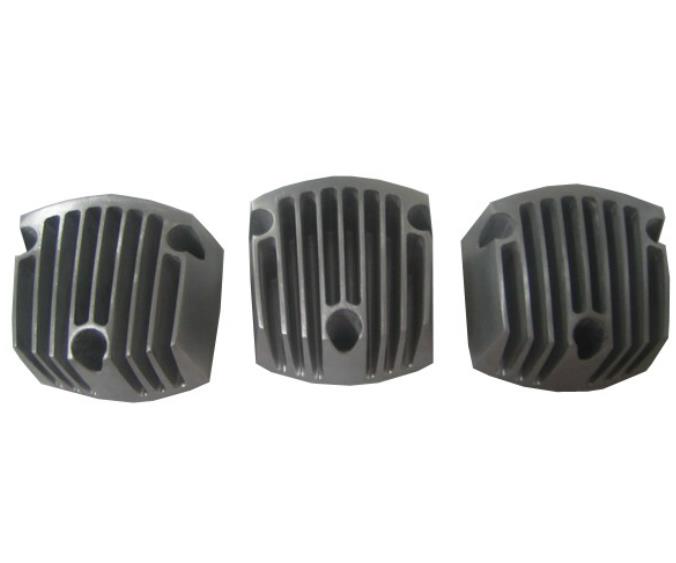
- Mold Manufacturing: Once the design is finalized, mold manufacturing begins. Skilled machinists use a variety of precision equipment, including CNC (Computer - Numerical Control) machines, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) machines, and milling machines. High - quality materials like tool steel or aluminum alloys are chosen based on the production volume and the properties required for the mold. For instance, tool steel is often used for high - volume production molds due to its durability and wear resistance, while aluminum alloys may be selected for lower - volume or prototype molds because of their lighter weight and easier machinability.
- Mold Repair and Maintenance: Over time, molds can experience wear and tear, leading to issues such as damaged cavities, misaligned components, or worn - out ejector pins. Regular maintenance, including cleaning, lubrication, and inspection, can extend the mold's lifespan. When repairs are needed, experienced technicians use techniques like welding, grinding, and polishing to restore the mold to its original condition. According to industry data, molds that receive proper maintenance can last up to 30% longer than those that are neglected.
- Mold Modification: As product designs evolve or production requirements change, molds may need to be modified. This could involve adding or removing features, changing the cavity size, or improving the gating system. Modifying a mold is often more cost - effective than creating a new one from scratch, especially for small - to medium - scale production runs.
The Core Elements of Mold Services
Design Precision
Mold design is the cornerstone of successful manufacturing. Designers must consider a plethora of factors. Product functionality is paramount; for example, if designing a mold for a medical device component, the design needs to ensure that the final product meets strict medical standards and functions flawlessly. Material characteristics also play a crucial role. Different materials have unique shrinkage rates, flow properties, and thermal expansion coefficients. For instance, when molding with high - temperature plastics like PEEK (Polyether - ether - ketone), the mold design must account for its high melting point and relatively low shrinkage rate compared to common plastics like ABS. Draft angles are another vital aspect. A proper draft angle, usually ranging from 0.5° to 3°, depending on the material and part complexity, ensures easy ejection of the molded part from the mold cavity without causing damage or deformation.
Material Selection
The choice of mold material can make or break the manufacturing process. Steel is a popular choice, especially in high - volume production. Tool steel, such as D2 or H13, offers excellent hardness, wear resistance, and heat resistance. D2 steel, with a high carbon and chromium content, can withstand extreme wear and tear, making it ideal for molds used in stamping or forming hard metals. H13, a hot - work tool steel, is well - suited for applications involving high - temperature processes like die - casting, as it can resist thermal fatigue and maintain its mechanical properties at elevated temperatures.
Aluminum alloys, on the other hand, are often used for their lightweight nature and good thermal conductivity. They are easier to machine than steel, which reduces production time and cost, especially for prototype or low - volume production molds. Alloys like 6061 or 7075 are commonly used. 6061 aluminum, with its moderate strength and good corrosion resistance, is suitable for molds where weight is a concern, such as in the aerospace industry for molding lightweight components.
Manufacturing Techniques
- CNC Machining: This is a highly precise manufacturing technique. CNC mills can create complex 3D shapes with tight tolerances, often within ±0.001 inches. It is suitable for a wide range of materials, from soft aluminum to hard tool steel. However, it can be time - consuming for intricate designs, and the initial setup cost for programming the CNC machine can be high.
- EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): EDM is ideal for creating detailed and complex geometries that are difficult to machine conventionally. It works by using electrical discharges to erode the material. For example, it can create fine internal features in a mold cavity without the need for complex multi - axis machining. But EDM is a relatively slow process, and it can be costly due to the need for specialized equipment and electrodes.
- 3D Printing: In recent years, 3D printing has emerged as a viable option for mold manufacturing, especially for rapid prototyping or low - volume production. It can quickly produce molds with complex internal structures, such as conformal cooling channels, which can significantly improve the cooling efficiency of the mold. However, the mechanical properties of 3D - printed molds may not be as high as those made by traditional methods, and the surface finish may require additional post - processing.
Maintenance and Repair
Regular maintenance is essential for the longevity of molds. Molds are typically inspected after every production run or at regular intervals, depending on the production volume. Cleaning the mold is a basic yet crucial maintenance task. Residual materials from the molding process, such as plastic resin or metal particles, can accumulate in the mold cavity and vents, affecting the quality of the next production run. Solvents and specialized cleaning tools are used to remove these residues.
Lubrication of moving parts, such as ejector pins and slides, is also important. High - temperature - resistant lubricants are often used to ensure smooth operation during the molding process. Common mold failures include worn - out ejector pins, which can cause parts to stick in the mold, and damaged cavities due to excessive wear or impact. When an ejector pin is worn, it can be replaced with a new one. For damaged cavities, techniques like welding and polishing can be used to repair the surface. In some cases, if the damage is extensive, a new insert may need to be fabricated and installed in the mold.
How Do Mold Services Impact Manufacturing?
Cost - Efficiency
High - quality mold services can significantly reduce production costs. For example, a well - designed and maintained mold can reduce the scrap rate. A study by the American Mold Builders Association found that companies that invested in professional mold services saw a 20 - 30% reduction in scrap rates. In a plastic injection molding operation, a poorly designed mold may cause the plastic to flow unevenly, resulting in products with voids, short shots, or excessive flash. These defective products need to be discarded, increasing material costs. However, with proper mold design and maintenance, such issues can be minimized.
Moreover, efficient mold services can also improve production efficiency. Faster mold change - over times, enabled by well - engineered mold designs and proper maintenance, mean that production lines can spend less time in downtime. In an automotive manufacturing plant, where time is money, reducing mold change - over time from 2 hours to 30 minutes can increase the number of parts produced per day, thereby spreading the fixed costs (such as labor and equipment depreciation) over a larger number of units.
Product Quality Assurance
The quality of a mold has a direct impact on the quality of the final product. Precise mold dimensions are crucial for ensuring that the molded parts meet the required specifications. For instance, in the production of electronic components, such as connectors, the mold must be designed and manufactured with extremely tight tolerances, often within ±0.05 mm. If the mold has dimensional inaccuracies, the resulting connectors may not fit properly into their sockets, leading to connection failures and product recalls.
Surface Smoothness is another aspect affected by mold quality. A smooth - finished mold will produce parts with a better surface finish. In the production of cosmetic packaging, a high - quality mold with a mirror - like finish will result in plastic containers with a sleek and attractive appearance. On the contrary, a mold with surface imperfections, such as scratches or pits, will transfer these defects to the product, making it unappealing to consumers. A case in point is a toy manufacturing company that experienced a significant drop in sales when its products, which were molded using a worn - out mold, had a rough surface texture, leading to customer complaints about the product's quality.
Production Speed
Efficient mold services can accelerate the production process. Rapid tooling techniques, such as 3D printing for mold production, can significantly reduce the lead time for mold manufacturing. In the past, creating a prototype mold could take weeks or even months using traditional machining methods. However, with 3D printing, a mold can be produced in a matter of days or even hours, depending on its complexity. This allows companies to quickly test new product designs and get them to market faster.
Optimizing the mold - changing process also contributes to increased production speed. By using quick - release mechanisms and standardized mold mounting systems, the time required to change a mold on a production line can be greatly reduced. In a high - volume food packaging production line, where molds need to be changed frequently to produce different product sizes or shapes, a well - optimized mold - changing process can increase the number of packages produced per hour, meeting the high - demand market requirements.
Innovation Facilitation
Mold services play a crucial role in enabling product innovation. New mold structures and manufacturing processes can be developed to achieve unique product features. For example, the development of multi - cavity molds allows for the simultaneous production of multiple identical parts, increasing production efficiency. In the production of small plastic toys, a multi - cavity mold can produce six or more toys in a single injection cycle, compared to a single - cavity mold that produces only one at a time.
Advanced mold manufacturing techniques can also enable the creation of complex geometries that were previously impossible or difficult to achieve. This allows for the design of products with enhanced functionality. For instance, in the aerospace industry, molds can be designed to produce lightweight components with internal lattice structures using additive manufacturing techniques. These structures not only reduce the weight of the components but also improve their strength - to - weight ratio, contributing to more fuel - efficient aircraft.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic and metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology deeply understands the significance of mold services in manufacturing. Our company has accumulated rich experience in the field of mold - related manufacturing.
In mold design, we have a team of professional designers who are proficient in using the latest CAD software. They can create highly customized mold designs according to the unique requirements of our customers. For example, when dealing with complex plastic parts for electronic devices, our designers take into account the need for precise internal structures and excellent surface finishes. By doing so, we can ensure that the final products not only meet the functional requirements but also have an attractive appearance.
Regarding material selection, we have an in - depth understanding of various materials. For plastic molds, we carefully choose between different types of plastics such as ABS, PP, and PC based on factors like product application, cost - effectiveness, and performance requirements. In metal mold manufacturing, we select appropriate metal alloys, ensuring that the molds can withstand high - pressure and high - temperature conditions during the manufacturing process.
Quality control is at the core of our operations. We have a strict quality inspection system in place for every stage of mold manufacturing, from raw material inspection to the final product inspection. Our quality control team uses advanced inspection equipment, such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs), to ensure that the molds meet the highest quality standards. This dedication to quality control allows us to provide our customers with reliable and high - performance molds, which in turn contributes to the overall success of their manufacturing processes.
FAQ
What are the common problems in mold manufacturing?
Common problems in mold manufacturing include:
- Dimensional deviation: This can occur due to incorrect initial mold design, such as miscalculating material shrinkage rates. For example, in plastic injection molding, if the mold designer underestimates the shrinkage of the plastic material during cooling, the final product will be smaller than the desired dimensions. Also, tool wear during the manufacturing process can lead to dimensional inaccuracies. Solutions include precise material testing before mold design to accurately determine shrinkage rates and regular inspection and replacement of worn - out tools.
- Surface defects: Scratches, pits, and roughness on the mold surface can transfer to the final product. These can be caused by improper machining techniques, such as using dull cutting tools during mold machining. In EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), improper parameter settings can also result in a rough surface finish. Regular maintenance of machining tools, proper selection of machining parameters, and post - processing polishing can help solve these problems.
- Mold wear and tear: Over time, molds experience wear, especially in high - volume production. Ejector pins can become worn, leading to difficulties in ejecting the molded parts. Cavity walls can also erode, affecting the shape and quality of the products. Regular inspection and timely replacement of worn - out components, as well as proper lubrication of moving parts, can extend the mold's lifespan.
How to choose the right mold service provider?
When choosing a mold service provider, consider the following aspects:
- Experience: A company with long - standing experience in mold services is more likely to handle various challenges. For example, a mold service provider with 10+ years of experience in automotive mold manufacturing will have in - depth knowledge of the specific requirements of automotive parts, such as high - strength and precision. Check their project portfolios and customer testimonials to gauge their experience.
- Equipment: Advanced equipment is crucial for high - quality mold production. A provider with modern CNC (Computer - Numerical Control) machines, high - precision EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining) equipment, and 3D printers can ensure accurate and efficient mold manufacturing. For instance, a state - of - the - art CNC mill can achieve tighter tolerances, resulting in more precise molds.
- Technical expertise: The technical skills of the design and manufacturing teams matter. Look for a provider with a team of engineers proficient in CAD/CAM (Computer - Aided Design/Computer - Aided Manufacturing) software and advanced mold - making techniques. They should be able to offer innovative solutions to complex design problems.
- Quality control: A reliable mold service provider will have a strict quality control system. This includes inspection at every stage of the mold - making process, from raw material inspection to final product testing. They should also be able to provide quality certificates and reports.
- After - sales service: Good after - sales service is essential. The provider should be able to offer timely mold repair, maintenance advice, and support in case of any issues with the molds during production.
Can mold services help in small - scale manufacturing?
Yes, mold services can be highly beneficial for small - scale manufacturing:
- Cost - reduction: Although the initial investment in mold design and manufacturing may seem high, in the long run, it can save costs. For example, using a mold for plastic product manufacturing in small - scale production can reduce the labor cost associated with manual shaping. Also, molds can be reused, spreading the cost over multiple production runs.
- Quality improvement: Molds ensure consistent product quality. In small - scale manufacturing of handicrafts, for instance, using a mold can guarantee that each piece has the same shape and dimensions, which is difficult to achieve through manual production alone. This can enhance the product's marketability.
- Faster production: Molds can speed up the production process. In the small - scale production of custom - made jewelry, a mold can quickly produce multiple identical components, reducing the time required for individual component creation. This allows small - scale manufacturers to meet customer demands more efficiently.