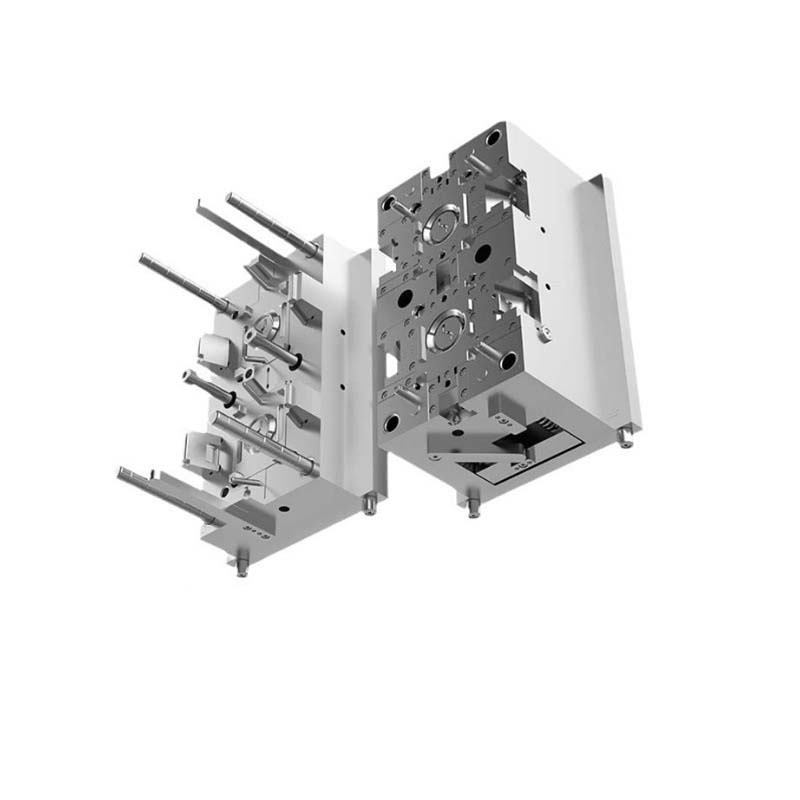
Introduction
What is a Chocolate Injection Mold?
In the world of chocolate production, a chocolate injection mold is an indispensable tool. It serves as the key to creating the diverse and delightful chocolate products that we all love. From the classic heart - shaped chocolates for Valentine's Day to the intricate and artistic chocolate sculptures, a chocolate injection mold plays a crucial role in shaping the liquid chocolate into the desired form.
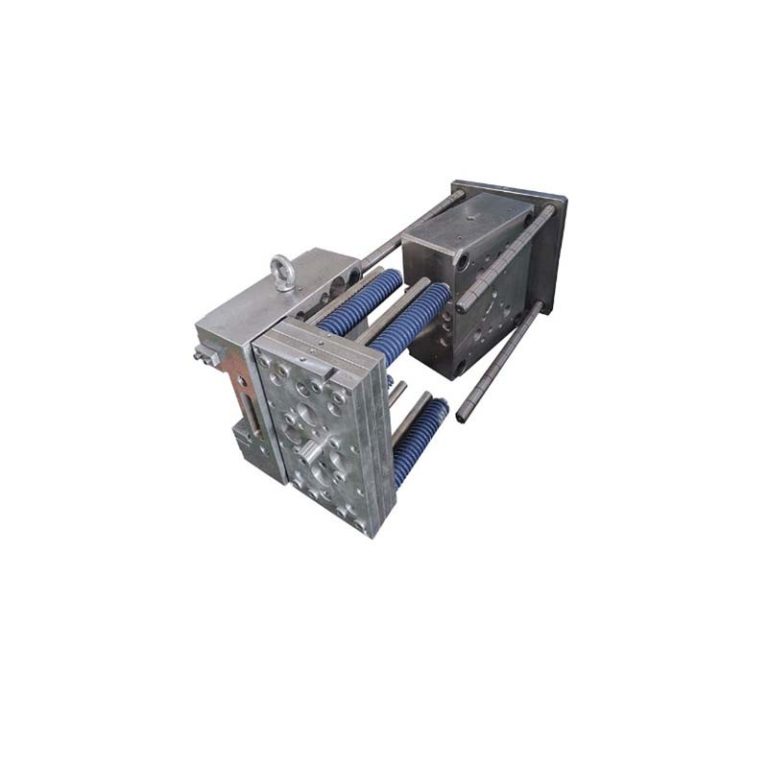
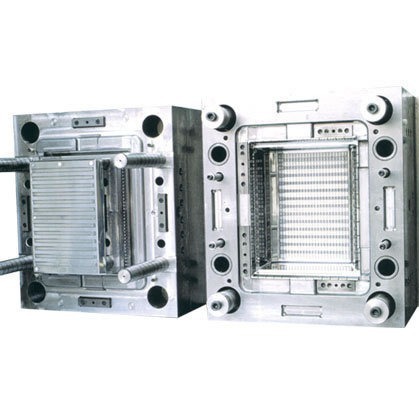
At its most basic, a chocolate injection mold is a specialized mold designed to take in liquid chocolate under pressure and then cool it to form a solid chocolate product. This method is highly efficient and allows for mass production with consistent quality. It is widely used in commercial chocolate manufacturing facilities, but also in some artisanal chocolate workshops where precision and speed are desired.
The process of chocolate injection molding starts with the preparation of the mold. The mold is typically made of materials like high - quality metal (such as aluminum or steel) or food - grade plastics. These materials are chosen for their ability to withstand the heat and pressure during the injection process and their non - reactivity with the chocolate. Once the mold is ready, the liquid chocolate, which has been carefully tempered to ensure the right texture and appearance, is injected into the mold cavities. The pressure forces the chocolate to fill every nook and cranny of the mold, accurately replicating the detailed design. After injection, the mold is cooled, either through air cooling or water - cooled channels within the mold itself. As the chocolate cools, it solidifies, taking on the shape of the mold. Finally, the solid chocolate is ejected from the mold, ready to be packaged or further processed.
Now that we have a basic understanding of what a chocolate injection mold is, let's take a closer look at its architecture and the components that make it such an effective tool in chocolate production.
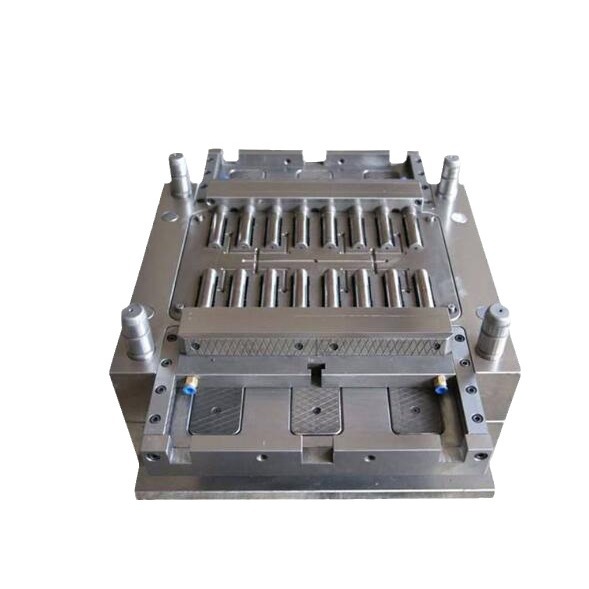
The Core Components of a Chocolate Injection Mold
Mold Base
The mold base is the foundation of a chocolate injection mold, playing a crucial role in providing support and stability. It consists of two main parts: the fixed mold base plate and the moving mold base plate.
Fixed Mold Base Plate: This plate is securely attached to the stationary platen of the injection molding machine. Its primary function is to hold the cavity - side components of the mold in place. It withstands the pressure exerted during the injection process and ensures that the cavity remains in the correct position relative to the injection nozzle. For example, in a large - scale chocolate production line, the fixed mold base plate of a multi - cavity chocolate injection mold needs to be thick and rigid enough to support the weight of multiple cavities and the force of the incoming molten chocolate. A typical thickness for a fixed mold base plate in a medium - sized chocolate injection mold can range from 20 - 50 mm, depending on the size and complexity of the mold.
Moving Mold Base Plate: As the name implies, this plate is connected to the moving platen of the injection molding machine. It supports the core - side components of the mold and is responsible for moving the core during the opening and closing of the mold. When the mold opens, the moving mold base plate moves away from the fixed mold base plate, allowing the ejected chocolate products to be removed. It also plays a vital role in the alignment of the core with the cavity during the closing process. The moving mold base plate is usually made of materials with high strength and good machinability, such as steel, to ensure smooth movement and long - term durability.
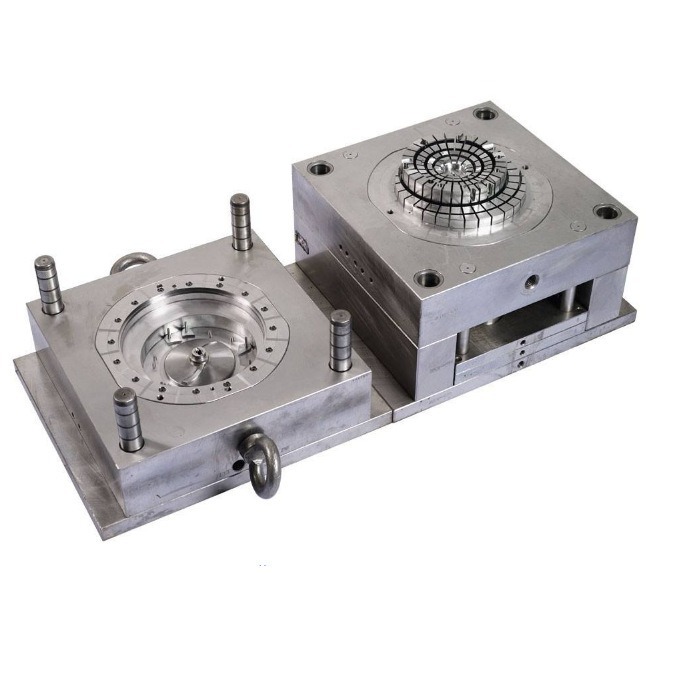
Cavity and Core
The cavity and core are the most critical components when it comes to shaping the chocolate.
Cavity: This is the hollow space within the mold that gives the chocolate its external shape. The shape and size of the cavity are designed according to the desired chocolate product. For instance, if you want to make heart - shaped chocolates, the cavity will be in the shape of a heart. The surface finish of the cavity is of utmost importance as it directly affects the surface quality of the chocolate. A smooth cavity surface will result in a shiny and attractive chocolate surface. Cavities can be made through various manufacturing processes, such as machining, electro - discharge machining (EDM), or even 3D printing for complex shapes.
Core: The core is the part of the mold that forms the internal features or the reverse side of the chocolate. In some chocolates with a hollow center or internal patterns, the core plays a key role. For example, in a chocolate Easter egg with a detailed inner pattern, the core is designed to create that pattern. The core and cavity must fit together precisely to ensure accurate replication of the design.
Cavities and cores can be either of an integral type or a combined type. The integral type has the advantage of high strength and good dimensional accuracy, as there are no joints. However, it is difficult to process complex shapes, and if there is damage, the entire part may need to be replaced. On the other hand, the combined type is more flexible in terms of design and easier to repair. Components can be replaced individually when damaged, but it requires precise assembly to ensure the accuracy of the shape.
Gating System
The gating system is responsible for the smooth flow of molten chocolate into the mold cavities. It consists of three main parts: the sprue, runner, and gate.
Sprue
The sprue is the main channel through which the molten chocolate enters the mold from the injection nozzle. It is usually a vertical channel with a conical shape. The small end of the sprue is in contact with the injection nozzle, and the large end connects to the runner system. The size and shape of the sprue are crucial for the injection efficiency. A sprue that is too small will cause high flow resistance, resulting in a slow injection process and potential defects in the chocolate, such as incomplete filling. Conversely, a sprue that is too large may lead to excessive waste of chocolate and longer cooling times. For a standard - sized chocolate injection mold, the diameter of the small end of the sprue can range from 3 - 8 mm, and the length is typically designed to be as short as possible to minimize heat loss and pressure drop, usually around 15 - 30 mm.
Runner
The runner is the channel that distributes the molten chocolate from the sprue to the individual cavities. There are different types of runner cross - sectional shapes, each with its own characteristics:
- Round - shaped Runner: It has the advantage of the lowest flow resistance because it has the smallest surface - to - volume ratio among common runner shapes. This allows the chocolate to flow quickly and with less pressure loss. However, it is more difficult to manufacture in some molds, especially when the mold design is complex. Round - shaped runners are often used in high - volume production of simple - shaped chocolate products where speed and efficiency are crucial.
- Trapezoidal - shaped Runner: This is a very common shape in chocolate injection molds. It is relatively easy to machine and offers a good balance between flow characteristics and manufacturability. The trapezoidal shape allows for efficient heat transfer and uniform distribution of the chocolate to the cavities. It is suitable for a wide range of chocolate products, from small - sized single - piece chocolates to medium - sized multi - cavity molds.
Gate
The gate is the connection point between the runner and the cavity. Its main function is to control the flow rate and direction of the molten chocolate entering the cavity. Different types of gates have different characteristics:
- Side Gate: This is one of the most commonly used gates in chocolate injection molds. It is located on the side of the cavity. Side gates are easy to process and can be easily removed from the chocolate product after molding. They are suitable for a variety of chocolate shapes, especially those with simple geometries. However, if not properly designed, they may cause flow marks on the surface of the chocolate near the gate area.
- Pin - Point Gate: Pin - point gates are very small in size, which allows for precise control of the chocolate flow. They are often used for high - precision chocolate products or those with complex shapes where a small and controlled flow of chocolate is required. But they can also cause high shear stress on the chocolate during injection, which may affect the quality of the chocolate if not carefully managed.
Ejection System
The ejection system is essential for removing the solidified chocolate from the mold after the cooling process.
Ejector Pins
Ejector pins are small cylindrical rods that are placed at strategic locations within the mold. When the mold opens, the ejector pins are pushed forward by the ejector plate. The tips of the ejector pins contact the chocolate product and push it out of the cavity. The layout and number of ejector pins are crucial. If there are too few ejector pins or they are not properly placed, the chocolate may be damaged during ejection, or it may not be ejected smoothly. For a small - sized chocolate mold, 3 - 5 ejector pins may be sufficient, while a larger and more complex mold may require 10 or more ejector pins, carefully arranged to ensure even ejection force across the chocolate product.
Ejector Plate
The ejector plate is a flat plate that is connected to the ejector pins. When the injection molding machine activates the ejection mechanism, the ejector plate moves forward, pushing the ejector pins. The strength and stability of the ejector plate are of great importance. A weak ejector plate may bend or break during the ejection process, which can lead to inconsistent ejection and potential damage to the mold and the chocolate products. The ejector plate is usually made of a strong metal, such as steel, and is designed with sufficient thickness (usually 15 - 30 mm depending on the size of the mold) to withstand the forces involved in the ejection process.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology deeply understands the significance of chocolate injection molds. In terms of material selection, we emphasize the use of high - quality, food - grade materials. For chocolate injection molds, materials like aluminum alloy are excellent choices for their good thermal conductivity, which helps in rapid cooling of the chocolate, reducing production time. In some cases where higher strength and wear - resistance are required, stainless steel can be used.
Regarding the manufacturing process, Yigu Technology adopts advanced machining techniques such as precision CNC machining and EDM. These methods ensure the high - precision manufacturing of mold components, especially for complex cavity and core designs. We also highly value customization. Every chocolate product has its unique shape, size, and production requirements. Custom - made molds can better meet these specific needs, enabling chocolate manufacturers to produce products with distinct features and high quality, thus enhancing their competitiveness in the market.
FAQ
What is the lifespan of a chocolate injection mold?
The lifespan of a chocolate injection mold can vary significantly depending on several factors. If made of high - quality steel, with proper maintenance and moderate use (say, used for a few hours a day in a small - scale production), it can last for 5 - 10 years, which could translate to hundreds of thousands of production cycles. However, if the mold is made of lower - quality materials or is used intensively (for example, in a large - scale factory that operates 24/7), the lifespan might be reduced to 2 - 3 years or even less. Factors like the frequency of use, the quality of the chocolate being processed (if it contains impurities that could cause wear), and the effectiveness of maintenance all play crucial roles in determining the mold's lifespan.
How can I maintain a chocolate injection mold?
Regular maintenance is key to extending the lifespan of a chocolate injection mold. After each use, clean the mold thoroughly with a food - grade cleaner to remove any residual chocolate. This can prevent the build - up of chocolate residue, which could affect the quality of future products and cause corrosion over time. Lubricate the moving parts, such as the ejector pins and the components of the mold base, with a food - grade lubricant to ensure smooth operation. Regularly check for signs of wear and tear, especially on the cavity, core, and the gating system. Replace any damaged parts immediately to avoid production issues. Also, store the mold in a dry and clean environment when not in use to prevent rust and other forms of damage.
Can a chocolate injection mold be used for other materials?
A chocolate injection mold is specifically designed for the unique properties of chocolate, such as its relatively low melting point and viscosity. While it might be technically possible to use it for other materials with similar characteristics, it is not recommended without significant modifications. For materials with different melting points, viscosities, or chemical properties, the mold design may need to be adjusted. For example, if you want to use it for a harder or more viscous material, the mold may need to be made of a stronger material to withstand the higher injection pressures. Additionally, the gating system and the cooling channels may need to be redesigned to ensure proper flow and solidification of the new material.