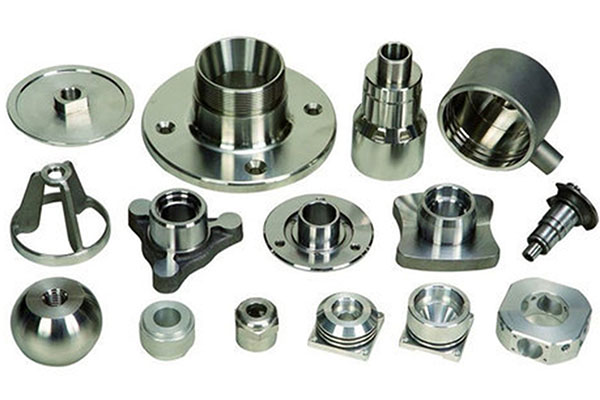
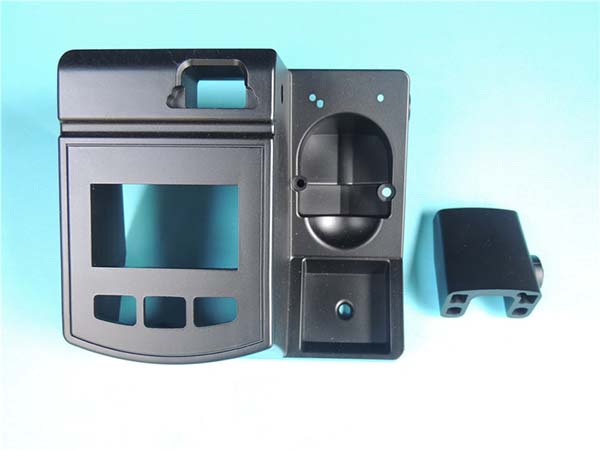
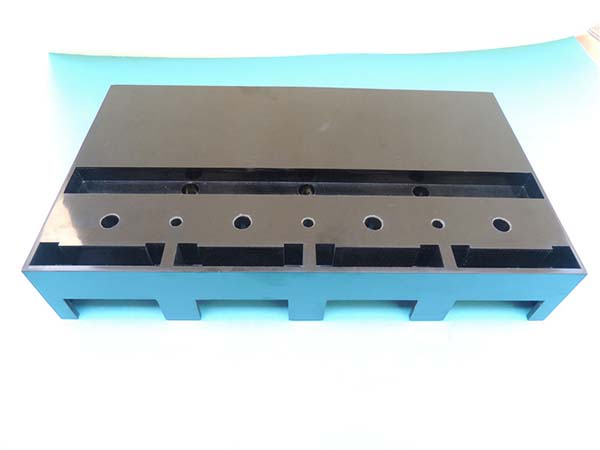
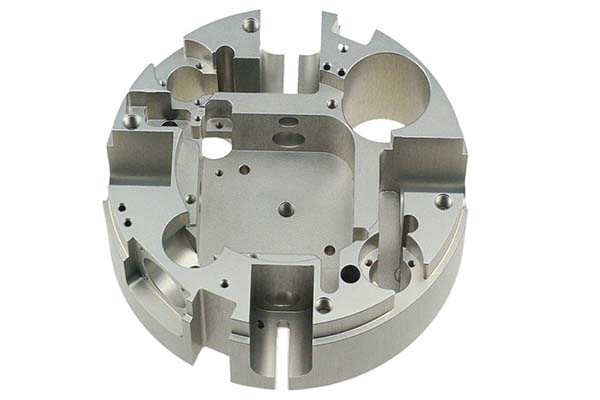
1. Introduction: Aluminium and the Evolution of Rapid Prototyping
In the ever - evolving landscape of manufacturing, rapid prototyping has emerged as a game - changing technology, and when combined with aluminium, it is opening up new frontiers. Aluminium, a lightweight metal with a density of approximately 2.7 g/cm³, is the third - most abundant element in the Earth's crust. Its widespread use in various industries can be attributed to its unique set of properties.
1.1 Aluminium's Properties
- High Strength - to - Weight Ratio: Aluminium alloys, such as the 6061 alloy (commonly used in rapid prototyping), offer an excellent strength - to - weight ratio. For Yigu Technology example, 6061 - T6 aluminium has a tensile strength of around 310 MPa, while being much lighter than steel. This makes it ideal for applications where weight reduction is crucial, like in the aerospace industry. In aircraft manufacturing, reducing the weight of components can lead to significant fuel savings. A study by Boeing found that a 1% reduction in aircraft weight can result in a 0.7% reduction in fuel consumption over the life of the aircraft.
- Corrosion Resistance: Aluminium forms a thin, protective oxide layer on its surface when exposed to air. This natural oxide layer, which is only a few nanometers thick, prevents further oxidation and corrosion. In marine applications, where components are constantly exposed to saltwater, aluminium alloys are used to construct boat hulls, deck fittings, and engine parts. A case study of a commercial fishing vessel showed that after 5 years of operation in saltwater, the aluminium components showed minimal signs of corrosion, while steel components in the same environment had significant rust formation.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminium has a high thermal conductivity of about 205 W/(m·K) for pure aluminium. This property makes it suitable for heat - dissipating applications. In the electronics industry, aluminium is used in heat sinks for CPUs and other high - power components. A well - designed aluminium heat sink can effectively transfer heat away from the component, ensuring its optimal operation. For instance, in a high - performance computer, an aluminium heat sink can reduce the CPU temperature by 10 - 15°C under heavy load conditions, which can extend the lifespan of the CPU and improve its performance.
1.2 The Evolution of Rapid Prototyping
Rapid prototyping, also known as additive manufacturing or 3D printing, has come a long way since its inception. The concept of creating physical models from digital designs in a layer - by - layer manner has revolutionized the product development cycle.
- Integration with Aluminium: The integration of aluminium into rapid prototyping has been a major breakthrough. Aluminium's properties, combined with the flexibility of rapid prototyping, allow manufacturers to create custom - designed parts with complex geometries that were previously difficult or impossible to produce using traditional manufacturing methods. For Yigu Technology example, in the automotive industry, manufacturers can now use rapid prototyping with aluminium to create lightweight engine components with optimized internal cooling channels, improving engine efficiency.
The combination of aluminium's properties and the capabilities of rapid prototyping is revolutionizing manufacturing, enabling faster product development, cost - effective production of complex parts, and innovation in various industries.
2. Technical Foundations of Aluminium Rapid Prototyping
2.1 Key Processes for Aluminium RP
Aluminium RP leverages advanced additive manufacturing (AM) techniques to build complex parts layer by layer. Here are some of the most prominent processes:
| Technology | Process | Material | Precision |
| Selective Laser Sintering (SLS) | Laser fuses aluminium powder into solid layers. | Aluminium alloys | ±0.1mm |
| Selective Laser Melting (SLM) | High - power laser fully melts powder for dense, functional parts. | Aluminium - Si alloys | ±0.05mm |
| Binder Jetting | Binder bonds powder particles, followed by sintering to form solid parts. | Aluminium oxide | ±0.15mm |
2.2 Material Properties Driving Innovation
Aluminium alloys like 6061 and 7075 offer several properties that are driving innovation in rapid prototyping:
- Tensile Strength: Aluminium alloys can have a tensile strength of up to 310 MPa (e.g., 6061 - T6). This strength allows for the creation of parts that can withstand significant mechanical stress. In the automotive industry, engine components such as cylinder heads made from aluminium alloys can endure the high - pressure and high - temperature conditions within the engine. A study comparing aluminium alloy cylinder heads with traditional cast - iron ones found that the aluminium alloy heads could handle the mechanical loads during engine operation while being much lighter, leading to improved fuel efficiency.
- Low Density: With a density of 2.7 g/cm³, aluminium is about 3x lighter than steel. This property is a game - changer in industries where weight reduction is critical. In the aerospace industry, every kilogram of weight reduction can lead to significant fuel savings over the lifespan of an aircraft. For instance, a commercial airliner that uses aluminium - based rapid - prototyped components can save thousands of liters of fuel per year, reducing operating costs and carbon emissions.
- Thermal Conductivity: Aluminium has a thermal conductivity of 167 W/m·K (for some common alloys), which is crucial for heat dissipation. In the electronics industry, heat sinks made from aluminium alloys are widely used to dissipate heat generated by high - power components such as CPUs and GPUs. A well - designed aluminium heat sink can effectively transfer heat away from the component, preventing overheating and ensuring stable operation. In high - performance computing servers, aluminium heat sinks can reduce the temperature of components by 10 - 15°C, which not only extends the lifespan of the components but also improves the overall performance of the server.
4. Industry Applications of Aluminium RP
The integration of aluminium rapid prototyping (RP) has had a profound impact across various industries, revolutionizing the way products are designed, developed, and manufactured. Here are some of the key industry applications:
4.1 Aerospace and Defense
In the aerospace and defense sectors, weight reduction, strength, and design flexibility are of utmost importance. Aluminium RP is playing a crucial role in meeting these requirements.
- Airbus A350 XWB: Airbus has been at the forefront of adopting aluminium RP in aircraft manufacturing. In the A350 XWB, 3D - printed aluminium brackets have been used extensively. These brackets are not only designed with complex geometries to optimize their functionality but also contribute significantly to weight reduction. Each aircraft saves approximately 600 kg in weight due to these 3D - printed aluminium components. This weight reduction directly translates into improved fuel efficiency. With fuel being a major cost factor in aviation, a reduction in weight means lower fuel consumption. For Yigu Technology example, over a long - haul flight of 10,000 km, an A350 XWB with these lightweight brackets can save around 200 - 300 liters of fuel compared to an aircraft with traditional brackets. This not only reduces operating costs for airlines but also decreases the environmental impact by lowering carbon emissions.
- Military Drones: Military drones require a high degree of maneuverability while maintaining structural integrity. Aluminium RP allows for the creation of lightweight yet strong frames for these drones. A study by the US military found that drones with aluminium frames produced via rapid prototyping had a 20% improvement in maneuverability compared to those with traditional frames. The ability to quickly produce custom - designed frames also means that drones can be easily modified for different missions. For instance, a drone used for surveillance in a mountainous region can have its frame redesigned and rapidly prototyped to better withstand the harsh environmental conditions, such as strong winds and temperature variations.
4.2 Automotive
The automotive industry is also experiencing a transformation with the use of aluminium RP, especially in the development of electric vehicles (EVs) and in rapid tooling.
- Electric Vehicles (EVs): In the realm of EVs, weight reduction is critical for extending the vehicle's range. Aluminium battery enclosures produced via selective laser sintering (SLS) are becoming increasingly popular. These enclosures can reduce the weight of the battery system by up to 25% compared to traditional enclosures. For example, a mid - size EV with a traditional battery enclosure weighing 200 kg can see a weight reduction of 50 kg when an SLS - produced aluminium enclosure is used. This reduction in weight can increase the vehicle's range by 10 - 15% depending on the driving conditions. Additionally, the high strength - to - weight ratio of aluminium ensures the safety and protection of the battery pack.
- Rapid Tooling: In automotive manufacturing, time is of the essence. Rapid prototyping of jigs and fixtures using aluminium can cut production delays significantly. For example, a major automotive manufacturer was able to produce a set of custom - designed jigs and fixtures for a new production line in just 48 hours using aluminium RP. In contrast, traditional manufacturing methods would have taken 2 - 3 weeks. This rapid turnaround time allows for faster production ramp - up, reduced production costs, and the ability to quickly respond to design changes.
4.3 Healthcare
The healthcare industry is benefiting from aluminium RP in several ways, particularly in the production of implants and surgical guides.
- MRI - Compatible Implants: For orthopedic devices, the use of non - magnetic aluminium alloys in rapid - prototyped implants is a game - changer. In a hospital setting, patients often need to undergo MRI scans for diagnosis and monitoring. Traditional metal implants can interfere with the MRI imaging process, leading to inaccurate results. Aluminium - based implants, on the other hand, are non - magnetic and ensure patient safety during MRI procedures. A study of 100 patients with aluminium - alloy orthopedic implants showed that the MRI scans were of high quality, with no interference from the implants, allowing doctors to make more accurate diagnoses.
- Surgical Guides: Custom - designed surgical guides are crucial for precise surgical procedures. Aluminium models based on CT scans can be rapidly prototyped to create these guides. A hospital in London reported that the use of these custom - made aluminium surgical guides reduced surgery time by 20% in orthopedic surgeries. The guides provide surgeons with a more accurate roadmap, reducing the risk of errors and improving patient outcomes.
7. Conclusion: Aluminium RP as a Catalyst for Innovation
Rapid prototyping with aluminium has transcended its initial status as an emerging technology and has firmly established itself as a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. This revolutionary combination has brought about a paradigm shift in the manufacturing landscape, driving innovation at an unprecedented pace across multiple industries.
One of the most significant contributions of aluminium RP is its ability to compress the product development cycle. In the past, the creation of prototypes and the production of complex parts often involved time - consuming processes that could take weeks or even months. With aluminium RP, these timelines have been drastically reduced. For Yigu Technology example, in the automotive industry, the development of a new engine component using traditional methods might have taken several months, from the design phase to the production of a functional prototype. However, with aluminium RP, this process can now be completed in a matter of days or weeks. This acceleration not only allows companies to bring products to market faster but also enables them to respond more quickly to market demands and technological advancements.
The design flexibility offered by aluminium RP is another game - changing factor. Traditional manufacturing methods often impose limitations on the complexity of designs due to the constraints of molds, dies, and machining processes. Aluminium RP breaks free from these limitations, allowing designers to create parts with intricate geometries, internal channels, and lattice structures. This freedom in design has led to the development of more efficient and innovative products. In the aerospace industry, for instance, the ability to design and produce lightweight aluminium components with optimized internal structures has significantly improved the performance of aircraft, reducing fuel consumption and emissions while enhancing overall efficiency.
FAQ
Is aluminium rapid prototyping cost - effective?
Aluminium rapid prototyping can be cost - effective, especially for low - volume production and product development stages. While the upfront investment in equipment and materials may seem high, it eliminates the need for expensive molds and tooling required in traditional manufacturing methods. For example, in a small - scale production run of 100 custom - designed aluminium parts, the cost of creating molds for injection molding could be in the tens of thousands of dollars. With rapid prototyping, this mold cost is completely eliminated. Although the unit cost per part in rapid prototyping might be higher than in mass production, the ability to quickly iterate designs and make changes without incurring additional tooling costs can lead to significant savings in the long run. A study by a manufacturing research firm found that for product development projects with multiple design iterations, companies using aluminium rapid prototyping saved an average of 30% on development costs compared to those relying solely on traditional manufacturing methods.
Which industries benefit most from aluminium RP?
The aerospace, automotive, and healthcare industries benefit significantly from aluminium rapid prototyping. In the aerospace industry, the high strength - to - weight ratio of aluminium is crucial. As mentioned earlier, Airbus uses 3D - printed aluminium brackets in the A350 XWB, which reduces weight and fuel consumption. In the automotive industry, the need for lightweight components, especially in electric vehicles, makes aluminium RP highly beneficial. For example, Tesla has been exploring the use of aluminium rapid prototyping for battery enclosures and other components to improve the vehicle's range. In the healthcare industry, the ability to create custom - designed implants and surgical guides using aluminium RP is a game - changer. Aluminium - based implants are MRI - compatible, ensuring patient safety during diagnostic procedures, and custom - made surgical guides improve the precision of surgeries.
Is aluminium RP environmentally friendly?
Aluminium rapid prototyping is relatively environmentally friendly. The additive manufacturing process used in aluminium RP minimizes material waste compared to traditional subtractive manufacturing methods. In traditional machining, large amounts of material are often removed and discarded to create the final part. In contrast, aluminium RP builds parts layer by layer, using only the necessary amount of material. Additionally, the use of aluminium, which is a highly recyclable material, further enhances its environmental credentials. Some aluminium powders used in rapid prototyping are made from recycled aluminium, reducing the demand for primary aluminium production, which is energy - intensive. A life - cycle assessment of aluminium rapid prototyping found that it can reduce energy consumption by up to 50% and material waste by 80% compared to traditional manufacturing processes for certain applications.