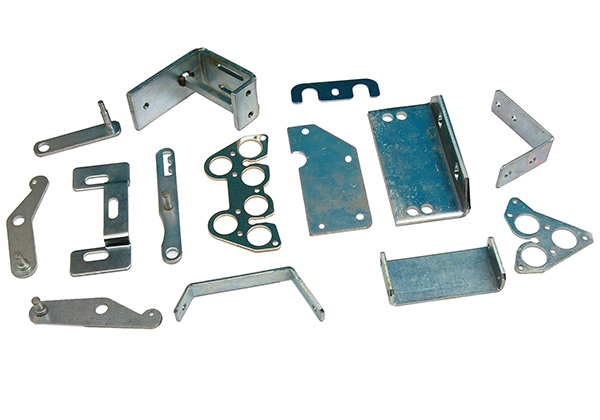
What is 16 Gauge Sheet Metal?
In the world of metalworking and manufacturing, gauge is a crucial concept when referring to sheet metal. Gauge is a standard unit used to denote the thickness of sheet metal. The relationship between gauge and thickness is an inverse one - as the gauge number increases, the thickness of the sheet metal decreases. This might seem counterintuitive at first, but it's a well - established industry standard.
16 gauge sheet metal is a commonly used material in a wide range of applications. In terms of thickness, 16 gauge sheet metal typically has a thickness of approximately 1.588 mm (0.0625 inches) in the United States when referring to steel. For aluminum, 16 gauge is about 1.29 mm (0.0508 inches). This variance in thickness for different metals with the same gauge number is due to the differences in their densities and manufacturing processes. These thickness measurements are not just arbitrary numbers; they are carefully determined and standardized to ensure consistency across industries. For example, in the automotive industry, 16 gauge steel might be used for certain body panels, where its thickness provides a good balance between strength and weight.
Applications of 16 Gauge Sheet Metal
16 gauge sheet metal's balanced thickness, strength, and workability lead to its widespread use across multiple industries. Let's explore some of its primary applications.
Construction Industry
In the construction industry, 16 gauge sheet metal plays a crucial role. For roofing, it provides durability against various weather conditions. Its thickness allows it to withstand high winds and heavy rainfall without easily getting damaged. For example, in commercial buildings, 16 gauge steel sheet metal is often used for standing - seam roofs. These roofs are known for their long - term performance, with the 16 gauge metal providing a reliable barrier against the elements for decades.
When it comes to wall cladding, 16 gauge sheet metal offers an aesthetically pleasing and functional option. It can be formed into different shapes and profiles, adding texture and style to the building's exterior. Additionally, it provides some level of insulation and protection against impact.
In ventilation systems, 16 gauge sheet metal is used to fabricate ducts. The metal's rigidity ensures that the ducts maintain their shape under the pressure of air flow, and its corrosion - resistance (especially when made of galvanized steel) makes it suitable for long - term use in both indoor and outdoor environments.
Automotive Field
The automotive industry also makes extensive use of 16 gauge sheet metal. In car body construction, it is used for components such as door panels, hoods, and fenders. For door panels, 16 gauge sheet metal provides a good balance between weight and strength. It needs to be strong enough to withstand minor impacts during normal use, such as a car door being opened into a pole, while also keeping the overall weight of the vehicle in check to improve fuel efficiency.
For automotive interiors, 16 gauge sheet metal can be found in parts like seat frames. A strong and durable seat frame made of 16 gauge metal ensures passenger safety and comfort during rides, whether it's a short commute or a long - distance journey.
Industrial Equipment
Industrial equipment often requires materials that can withstand harsh working conditions, and 16 gauge sheet metal fits the bill. For equipment enclosures, it provides protection against dust, moisture, and physical damage to the sensitive internal components. For instance, in a manufacturing plant where there is a lot of dust and debris in the air, a machine's control panel enclosed in 16 gauge sheet metal will remain functional and free from damage for a long time.
Metal brackets and frames made from 16 gauge sheet metal are used to support heavy machinery components. Their strength allows them to hold the weight securely, while their relatively thin profile doesn't add excessive bulk to the overall equipment design.
How to Choose 16 Gauge Sheet Metal
Consider the Application
The first and foremost factor when choosing 16 gauge sheet metal is the intended application. For automotive applications, the sheet metal needs to meet specific safety and weight - reduction requirements. It should have high tensile strength to ensure passenger safety in case of collisions, while also being lightweight to improve fuel efficiency. For example, if it's for a car body panel, it must be able to withstand minor impacts and resist corrosion over time.
In the construction industry, different applications have different demands. For roofing, the 16 gauge sheet metal should have excellent weather - resistance. Galvanized steel is a popular choice as the zinc coating provides protection against rust caused by rain and humidity. If it's for interior partitions, the focus might be more on its formability and acoustic properties.
Industrial equipment usage requires the sheet metal to endure harsh environments. For equipment used in chemical plants, the metal should be resistant to chemical corrosion. In high - temperature environments, such as in some industrial furnaces, the sheet metal needs to have good heat - resistance properties.
Quality and Material Standards
Quality is of utmost importance when selecting 16 gauge sheet metal. First, look at the metal purity. High - purity metals generally offer better mechanical properties. For instance, high - purity aluminum 16 gauge sheet metal will have better corrosion - resistance and formability compared to lower - purity counterparts.
Surface treatment is another crucial aspect. A well - treated surface can enhance the metal's durability and appearance. For example, a sheet metal with a powder - coated surface not only looks more aesthetically pleasing but also has better scratch - resistance and corrosion - resistance. Electro - galvanized surfaces provide a thin layer of zinc, protecting the base metal from rust.
Check for industry - standard certifications. In the United States, ASTM (American Society for Testing and Materials) standards are widely recognized. ASTM A653 for galvanized sheet steel sets requirements for coating mass, surface quality, and mechanical properties. Ensuring that the 16 gauge sheet metal you choose complies with relevant standards guarantees its quality and performance.
Yigu Technology's View
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom Supplier, Yigu Technology recognizes the significant role of 16 gauge sheet metal in our custom manufacturing processes. In custom projects, 16 gauge sheet metal offers great versatility. Its balanced thickness allows for easy shaping into various non - standard designs while maintaining structural integrity. For example, when creating custom enclosures for specialized industrial equipment, 16 gauge sheet metal can be precisely formed to fit unique dimensions and functional requirements.
One of the key advantages is its cost - effectiveness in custom production. Since it is a commonly available gauge, the raw material cost is relatively stable, which helps in providing competitive pricing for our customers. Additionally, its workability means that we can use a variety of manufacturing techniques such as bending, cutting, and welding with relative ease, reducing production time and costs.
Looking at the market, we believe the demand for 16 gauge sheet metal in custom applications will continue to grow. As industries become more specialized and require unique metal components, the adaptability of 16 gauge sheet metal makes it an ideal choice. Whether it's for the development of new - generation medical equipment enclosures or custom - designed automotive prototypes, 16 gauge sheet metal will remain a staple material in the custom manufacturing landscape.
FAQ
What is the thickness of 16 gauge sheet metal?
16 gauge sheet metal is approximately 1.588 mm (0.0625 inches) thick for steel in the United States. For aluminum, 16 gauge is about 1.29 mm (0.0508 inches) thick.
In which industries is 16 gauge sheet metal most commonly used?
16 gauge sheet metal is most commonly used in the construction industry for roofing, wall cladding, and ventilation ducts. In the automotive field, it's used for car body components like door panels, hoods, and fenders, as well as in automotive interiors for seat frames. It's also widely used in industrial equipment for equipment enclosures, metal brackets, and frames.
How can I tell if the 16 gauge sheet metal I buy is of good quality?
To determine the quality of 16 gauge sheet metal, first, check the metal purity. High - purity metals usually have better mechanical properties. Examine the surface treatment; a well - treated surface indicates better durability and appearance, such as a powder - coated or electro - galvanized surface. Also, ensure the sheet metal has relevant industry - standard certifications, like ASTM certifications in the US, which guarantee its quality and performance.