What is PVC?
PVC, short for Polyvinyl Chloride, is a widely used thermoplastic polymer. It is composed of vinyl chloride monomers (VCM) that are polymerized through a chemical reaction, typically under the influence of heat, light, or specific initiators like peroxides or azo compounds.
In its untreated form, PVC appears as a white powder or solid, and it can be rather brittle. This brittleness limits its direct applications in many scenarios. However, by adding plasticizers, its properties can be significantly altered. Plasticizers are substances that, when incorporated into PVC, increase its flexibility and workability. For Yigu Technology instance, common plasticizers such as phthalates are added to PVC in various industries. When these plasticizers are added, the PVC becomes more pliable, allowing it to be used in a broader range of applications.
The history of PVC dates back to the early 20th century. It was first commercially used by the B.F. Goodrich Company during the 1920s. Since then, its usage has grown exponentially due to its versatility and cost - effectiveness.
PVC commonly exists in two primary forms: rigid and flexible. Rigid PVC, often referred to as unplasticized PVC (uPVC), contains little to no plasticizers. This form exhibits high strength, rigidity, and excellent dimensional stability. As a result, it is extensively used in the construction industry for applications such as plumbing pipes, vinyl siding on buildings, and window frames. These applications require materials that can withstand external forces, environmental factors, and maintain their shape over time, which rigid PVC is well - suited for.
On the other hand, flexible PVC, or plasticized PVC, has a significant amount of plasticizers added to it, usually in the range of 20% - 60%. This form is highly flexible, making it ideal for applications like insulation on electrical wires, flooring materials for homes, and various types of hoses. For Yigu Technology example, in the case of electrical wire insulation, the flexibility of PVC ensures that the wires can be easily bent and routed during installation, while still providing effective electrical insulation.
| Forms of PVC | Plasticizer Content | Key Characteristics | Common Applications |
| Rigid PVC (uPVC) | Little to none | High strength, rigidity, dimensional stability | Plumbing pipes, vinyl siding, window frames |
| Flexible PVC (Plasticized PVC) | 20% - 60% | High flexibility | Electrical wire insulation, flooring, hoses |
Can PVC be Injection Molded?
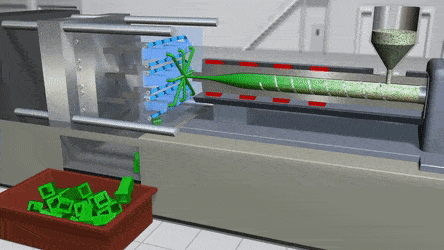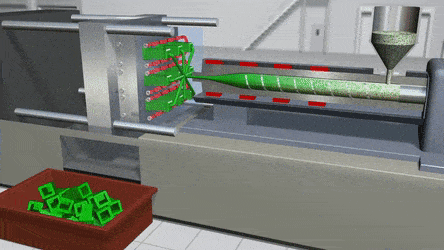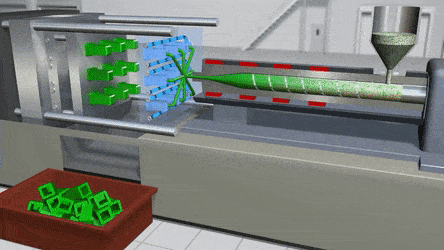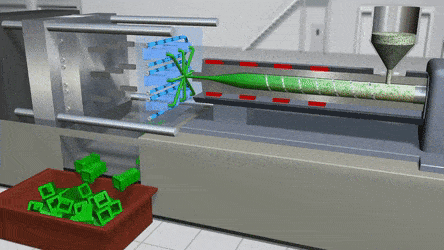
PVC can indeed be injection molded, and this process has become a cornerstone in modern manufacturing due to the material's unique properties and versatility. The injection molding process for PVC involves several key steps that take advantage of its thermoplastic nature.
First, PVC, which usually comes in pellet or powder form, is fed into the injection molding machine. The machine then heats the PVC to a specific temperature range. The melting point of PVC can vary depending on factors such as the type of additives used, but generally, it liquefies between 212°F to 500°F. Once in a liquid state, the PVC can be easily manipulated and injected into a mold.
The principle behind PVC injection molding is similar to that of other thermoplastics. When heated, the polymer chains in PVC start to move more freely, allowing the material to flow. This flowability is crucial as it enables the PVC to fill the intricate cavities of the mold precisely. As the melted PVC is injected into the mold under high pressure, it takes on the shape of the mold's interior.
One of the remarkable features of PVC in injection molding is its excellent durability. Products made from injection - molded PVC can withstand harsh environmental conditions, whether it's exposure to moisture, sunlight, or temperature variations. For example, PVC pipes used in outdoor plumbing systems can last for decades without significant degradation.
In terms of chemical resistance, PVC is highly resistant to a wide range of chemicals, including acids, alkalis, and many solvents. This makes it an ideal choice for applications where chemical exposure is a concern, such as in the manufacturing of chemical storage containers or laboratory equipment components.
Fire resistance is another advantage of PVC in injection - molded products. In the event of a fire, PVC releases chlorine, which can act as a flame - retardant, slowing down the spread of fire. This property is especially important in applications where fire safety is a top priority, like in the construction of buildings or the production of electrical components.
PVC also exhibits great abrasion resistance. Injection - molded PVC parts, such as those used in industrial machinery or automotive applications, can endure repeated friction and wear over time. This reduces the need for frequent replacements, resulting in cost savings in the long run.
Moreover, PVC has excellent dimensional stability. Once the injected PVC cools and solidifies in the mold, it maintains its shape accurately. This is crucial for applications that require high - precision parts, such as in the electronics industry, where components need to fit together precisely.
Its high impact - resistance means that injection - molded PVC products can withstand physical impacts without breaking or cracking easily. This makes PVC suitable for a variety of applications, from consumer products like toys to industrial equipment housings.
The following table summarizes some of the key properties of PVC that make it suitable for injection molding:
| Property | Description | Significance in Injection Molding |
| Durability | Can withstand long - term use and environmental exposure | Ensures the longevity of injection - molded products |
| Chemical Resistance | Resistant to a wide range of chemicals | Allows for use in chemically harsh environments |
| Fire Resistance | Releases chlorine to retard flames | Crucial for fire - safety applications |
| Abrasion Resistance | Can endure friction and wear | Reduces the need for frequent replacements |
| Dimensional Stability | Maintains shape accurately after cooling | Essential for high - precision parts |
| Impact - Resistance | Can withstand physical impacts | Suitable for products that may be subject to impact |
In conclusion, the ability to injection mold PVC, combined with its numerous desirable properties, has led to its widespread use in a vast array of industries. Whether it's for creating everyday household items or complex industrial components, PVC injection molding offers a reliable and efficient manufacturing solution.
PVC Injection Molding Processing Guide
Step - by - Step Process
- Material Preparation:The journey of PVC injection molding begins with meticulous material preparation. PVC resin, which usually comes in pellet or powder form, must be dried thoroughly. Moisture in the PVC resin can cause significant issues during the molding process. For example, it can lead to the formation of voids, bubbles, or surface defects in the final product. To avoid these problems, the PVC resin is typically dried at a temperature range of 75°F - 90°F. This drying process helps to remove any absorbed moisture, ensuring that the resin is in an optimal state for the subsequent steps.
- Melting:Once the PVC resin is dry, it is fed into an injection molding machine. Inside the machine, the resin is melted. The melting process is carefully controlled, as the temperature and pressure play crucial roles. The melting temperature of PVC generally ranges from 212°F to 500°F, depending on the type of additives used. If the temperature is too low, the PVC may not melt completely, resulting in poor flow and incomplete filling of the mold. On the other hand, if the temperature is too high, the PVC can decompose, leading to a loss of material properties and potential product defects. The pressure within the injection molding machine also needs to be adjusted to ensure that the melted PVC flows smoothly.
- Injection:After the PVC has been melted to the appropriate state, it is injected into the mold cavity. This injection is carried out under high pressure, typically up to 100MPa. The high - pressure injection ensures that the molten PVC fills every intricate detail of the mold cavity accurately. The mold cavity is designed to create the desired shape of the final part. For complex parts, the mold may have multiple components and cores to form internal features, such as holes or cavities.
- Cooling:Once the mold cavity is filled with molten PVC, the cooling process begins. The cooling time is a critical factor and depends on several variables, including the thickness of the part and the mold temperature. Generally, the mold temperature is maintained between 68°F - 158°F. Thicker parts require longer cooling times to ensure that they solidify properly. During the cooling process, the molten PVC loses heat and gradually solidifies, taking on the shape of the mold. If the cooling is too rapid, it can cause internal stresses in the part, leading to warping or cracking. Conversely, if the cooling is too slow, it can increase the production cycle time, reducing efficiency.
- Ejection:Once the part has cooled and solidified completely, it is ejected from the mold cavity. Ejection is typically achieved using ejector pins or other mechanical devices. These ejector pins push the solidified PVC part out of the mold, and it drops into a collection bin. After ejection, the part may still have some residual stresses, and in some cases, it may require post - processing steps such as annealing to relieve these stresses and improve the part's dimensional stability.
The following Yigu Technology table summarizes the step - by - step process of PVC injection molding:
| Step | Description | Key Points |
| Material Preparation | Dry PVC resin to remove moisture | Dry at 75°F - 90°F |
| Melting | Melt PVC resin in injection molding machine | Control temperature (212°F - 500°F) and pressure |
| Injection | Inject molten PVC into mold cavity under high pressure | Up to 100MPa |
| Cooling | Cool and solidify molten PVC in mold cavity | Mold temperature 68°F - 158°F, cooling time depends on part thickness |
| Ejection | Eject solidified part from mold cavity | Use ejector pins or other devices |
Key Parameters
- Melting Temperature:As mentioned earlier, the melting temperature of PVC ranges from 212°F to 500°F. This wide range is due to the influence of various additives. For Yigu Technology example, plasticizers can lower the melting temperature, making the PVC more pliable and easier to process. On the other hand, fillers or reinforcements may increase the melting temperature slightly. Precise control of the melting temperature is essential to ensure the quality of the final product.
- Mold Temperature:Maintaining the correct mold temperature is crucial for the success of the injection molding process. A mold temperature in the range of 68°F - 158°F helps to ensure proper cooling and solidification of the PVC. If the mold temperature is too low, the PVC may solidify too quickly, leading to incomplete filling of the mold and potential surface defects. If the mold temperature is too high, it can cause the part to stick to the mold, making ejection difficult and potentially damaging the part.
- Injection speed:The injection speed should be slow to avoid degradation of the PVC. PVC is a thermally sensitive material, and high - speed injection can generate excessive shear heat, which can cause the PVC to decompose. When producing parts with complex geometries or high - quality surface requirements, a slow and controlled injection speed is especially important. For example, when manufacturing PVC pipes with smooth inner and outer surfaces, a slow injection speed helps to prevent any surface irregularities caused by rapid material flow.
- Tensile Strength:PVC has a tensile strength of approximately 6,500 psi. This relatively high tensile strength makes it suitable for a wide range of applications. In construction applications, such as PVC pipes, the high tensile strength allows the pipes to withstand internal pressure and external forces without breaking. In automotive parts, the tensile strength ensures that the components can endure mechanical stresses during operation.
- Packing Pressure:The packing pressure, which can be up to 100MPa, is applied after the mold is filled to ensure that the part is fully packed and has the desired density. This pressure helps to compensate for any shrinkage that occurs during the cooling process and ensures that the part maintains its dimensional accuracy. For parts with tight tolerances, a proper packing pressure is essential.
- Drying Temperature:As previously stated, the drying temperature for PVC resin is 75°F - 90°F. This temperature range effectively removes moisture from the resin without causing any thermal degradation. Ensuring dry resin is a fundamental step in achieving high - quality injection - molded PVC products.
- Low Shrinkage:PVC has a low shrinkage rate, typically in the range of 0.002 mm - 0.006 mm or 0.2% - 0.6%. However, the shrinkage can vary based on factors such as hardness, holding time, melt temperature, mold temperature, and the type of additives used. For example, parts made from more rigid PVC may have a slightly lower shrinkage rate compared to flexible PVC. Understanding and controlling these factors can help manufacturers achieve the desired dimensional accuracy in their products.
The following Yigu Technology table provides a summary of the key parameters in PVC injection molding:
| Parameter | Value | Significance |
| Melting Temperature | 212°F - 500°F | Affects material flow and quality |
| Mold Temperature | 68°F - 158°F | Influences cooling and solidification |
| Injection Speed | Slow | Prevents material degradation |
| Tensile Strength | 6,500 psi | Determines the part's mechanical strength |
| Packing Pressure | Up to 100MPa | Ensures proper packing and dimensional accuracy |
| Drying Temperature | 75°F - 90°F | Removes moisture from the resin |
| Low Shrinkage | 0.002 mm - 0.006 mm or 0.2% - 0.6% | Affects the final dimensions of the part |
Applications of Injection Molding PVC
PVC injection molding has found its way into a vast number of industries, thanks to the material's remarkable properties. The following are some of the major application areas:
Automotive Parts
In the automotive industry, PVC injection molding is widely used. For example, dashboards made from PVC are not only cost - effective but also offer good dimensional stability. They can be molded into complex shapes to fit the interior design of different car models precisely. PVC is also used in the production of door panels. The material's strength and durability ensure that the door panels can withstand regular use, such as opening and closing the doors. Additionally, PVC is used for manufacturing various interior components like cup holders, air vent covers, and storage compartments. The chemical resistance of PVC is beneficial in the automotive environment, where it may be exposed to various cleaning agents and spills.
| Automotive Parts | PVC Property Utilized | Benefit |
| Dashboards | Dimensional stability | Precise fit in the car interior |
| Door Panels | Strength and durability | Withstand regular use |
| Cup Holders, Air Vent Covers, etc. | Chemical resistance | Resist exposure to cleaning agents |
Packaging
PVC is a popular choice for packaging applications. Bottle caps made of PVC provide a reliable seal. Their high - density nature and good chemical resistance make them suitable for sealing bottles containing various liquids, including beverages, chemicals, and cosmetics. PVC is also used to make blister packs for products such as pharmaceuticals and small consumer goods. The transparency of PVC in some formulations allows for clear visibility of the product inside, while its strength protects the product during transportation and storage.
| Packaging Items | PVC Property Utilized | Benefit |
| Bottle Caps | High density and chemical resistance | Provide a reliable seal for different liquids |
| Blister Packs | Transparency and strength | Visibility of the product and protection during handling |
Wire Spools
Wire spools are often made using PVC injection molding. The high tensile strength of PVC ensures that the spools can hold the weight of the wire without breaking or deforming. PVC's resistance to abrasion is also important, as the wire may rub against the spool during winding and unwinding. Additionally, PVC's electrical insulation properties make it a safe choice for spools used in electrical applications, protecting against potential electrical hazards.
| Application | PVC Property Utilized | Benefit |
| Wire Spools | High tensile strength, abrasion resistance, electrical insulation | Hold wire weight, withstand wire friction, and ensure electrical safety |
Pocket Combs
Pocket combs are commonly manufactured from PVC. The material's ability to be molded into precise shapes with fine teeth is a key advantage. PVC combs are lightweight, which makes them convenient for carrying around. Their durability ensures that they can withstand regular use without easily breaking or losing their shape.
| Application | PVC Property Utilized | Benefit |
| Pocket Combs | Molding precision, lightweight, durability | Precise tooth formation, easy to carry, long - lasting |
Plumbing and Construction
In the plumbing and construction industries, PVC is an essential material. PVC pipes are extensively used for water supply and drainage systems. Their corrosion resistance to water and various chemicals in the water makes them ideal for long - term use. PVC pipes are also lightweight, which simplifies installation compared to heavier materials like metal pipes. In construction, PVC is used for vinyl siding. The weather resistance of PVC ensures that the siding can withstand exposure to sunlight, rain, and wind over many years, maintaining the appearance and integrity of the building. Window frames made of PVC offer good insulation properties, helping to reduce heat transfer and improve energy efficiency in buildings.
| Plumbing and Construction Applications | PVC Property Utilized | Benefit |
| PVC Pipes | Corrosion resistance, lightweight | Resist water - related corrosion and ease installation |
| Vinyl Siding | Weather resistance | Withstand environmental elements for long - term use |
| Window Frames | Insulation properties | Improve energy efficiency in buildings |
Conclusion
PVC injection molding is a crucial manufacturing process with far - reaching significance in modern industries. The versatility of PVC, combined with the efficiency and precision of injection molding, has made it an indispensable part of the manufacturing landscape.
The advantages of Yigu Technology PVC injection molding are numerous. Economically, PVC is a cost - effective material, and the injection molding process allows for high - volume production, which further reduces per - unit costs. This makes it an attractive option for manufacturers looking to produce a large number of parts without sacrificing quality. In terms of material properties, PVC's high density, strength, hardness, and excellent dimensional stability result in products that are durable and reliable. Its resistance to weather, chemicals, and abrasion extends the lifespan of the products, making them suitable for a wide range of applications, from outdoor construction to industrial machinery components.
However, it's important to be aware of the challenges associated with PVC injection molding. The relatively high upfront costs for tooling a mold can be a significant barrier for some manufacturers, especially those with limited budgets or small - scale production plans. PVC's sensitivity to heat and processing conditions requires careful control during the injection molding process. Incorrect processing temperatures, injection speeds, or other parameters can lead to product defects such as decomposition, surface imperfections, or dimensional inaccuracies.
To fully harness the benefits of PVC injection molding, manufacturers must master the technical aspects of the process. This includes a deep understanding of PVC material properties, precise control of processing parameters, and careful mold design. By doing so, they can overcome the challenges and produce high - quality products efficiently.
In practical applications, whether it's in the automotive, packaging, construction, or any other industry that utilizes PVC injection - molded parts, choosing the right PVC grade, additives, and processing conditions based on the specific requirements of the product is essential. This might involve considering factors such as the environmental conditions the product will be exposed to, the mechanical stresses it will endure, and the aesthetic and functional requirements.
In Yigu Technology conclusion, PVC injection molding offers a powerful solution for manufacturers seeking to produce high - quality, cost - effective plastic products. By understanding its advantages, being mindful of the challenges, and applying the right techniques, industries can continue to benefit from this versatile manufacturing process, creating products that meet the demands of the modern world.