Understanding ABS Prototype
Definition and Basics
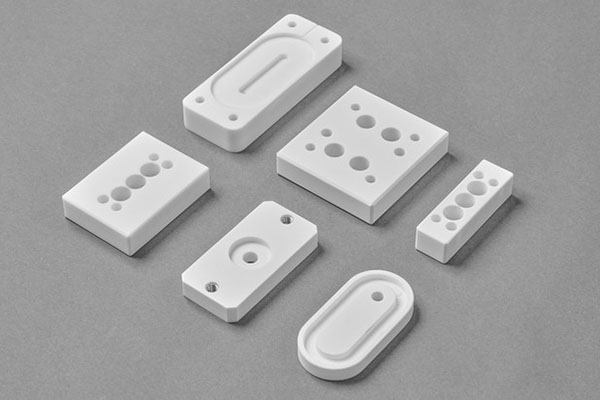
An ABS prototype, short for Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene prototype, is a preliminary model created using ABS material. It serves as a crucial step in the product development process, allowing designers and engineers to test the functionality, form, and fit of a product before mass production.
In product development, an ABS prototype plays a pivotal role. For example, when developing a new consumer electronics device, creating an ABS prototype helps in validating the design concept. It enables the team to check if all components fit together as planned, ensuring that the product's physical dimensions are accurate. This early testing phase can significantly reduce the risk of costly design flaws and production issues later on.
Key Characteristics
- Good Mechanical Properties: ABS has relatively high strength and toughness. It can withstand a certain degree of impact and stress without breaking easily. Compared to some other plastics like polystyrene (PS), ABS has better impact resistance. PS is more brittle and is likely to crack under impact, while ABS can endure more force, making it suitable for products that may experience physical stress during use.
- Dimensional Stability: ABS prototypes maintain their shape well, even under various environmental conditions. With a low coefficient of thermal expansion, it doesn't expand or contract significantly with temperature changes. This is crucial for products that require precise dimensions, such as parts in a mechanical device. For instance, in a car interior component prototype made of ABS, it will keep its original shape whether in a hot summer or a cold winter, ensuring a perfect fit within the car interior structure.
- Easy to Process: ABS is highly suitable for various manufacturing processes like injection molding, 3D printing, and CNC machining. Injection molding allows for the mass production of ABS prototypes with high precision and efficiency. 3D printing, on the other hand, offers the flexibility to create complex geometries. For example, intricate product casings with unique shapes can be easily 3D printed using ABS filament, which is not as feasible with some more difficult - to - process materials.
- Aesthetic Appeal: It can be easily colored and finished to achieve a smooth surface. This makes ABS prototypes ideal for products where appearance matters, such as consumer products, toys, and electronic device housings. You can achieve a high - gloss or matte finish on an ABS prototype, and it can be dyed in a wide range of colors to match the desired brand image or design concept.
The Process of Creating an ABS Prototype
Design Phase
The design phase is the foundation of creating an ABS prototype. It begins with a clear understanding of the product's requirements, functions, and target market. Designers often use 3D modeling software to create a virtual representation of the product. CAD (Computer - Aided Design) software is widely used in this stage. For example, SolidWorks and AutoCAD are popular CAD tools. They allow designers to precisely define the product's dimensions, shapes, and internal structures.
In the design of an ABS prototype for a new smartphone case, designers would first create a 3D model in CAD software. They would pay attention to details such as the cutouts for the camera, buttons, and ports, ensuring a perfect fit for the smartphone. The design should also consider factors like ergonomics for a comfortable grip and aesthetic appeal to attract consumers.
Manufacturing Methods
- 3D Printing
- Advantages:
- High design freedom: It can create complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with traditional manufacturing methods. For example, lattice - like structures inside the prototype for weight reduction while maintaining strength can be easily printed.
- Quick turnaround: Prototypes can be produced relatively quickly, sometimes within a few hours, which is great for rapid prototyping and design iteration.
- Low initial investment: You don't need to invest in expensive molds as in injection molding, making it cost - effective for small - scale production or one - off prototypes.
- Disadvantages:
- Limited material options compared to injection molding, although the variety of 3D - printable ABS materials is growing.
- Lower mechanical properties in some cases compared to injection - molded parts, especially in terms of strength and surface finish. The layer - by - layer printing process can sometimes result in a slightly rough surface.
- Higher cost per unit for large - scale production. As the quantity of prototypes needed increases, the cost per unit becomes less competitive compared to injection molding.
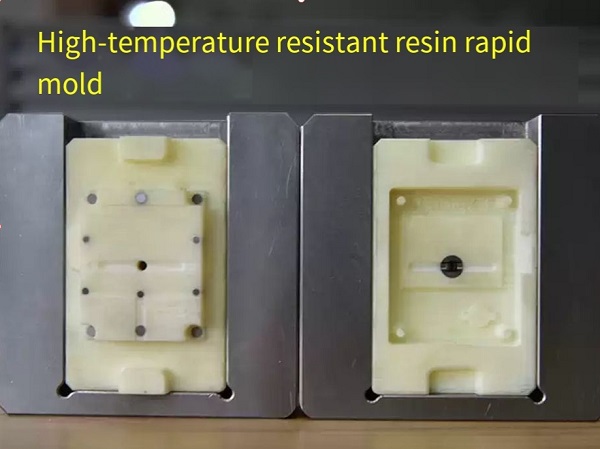
- Injection Molding
- Advantages:
- High - volume production: It is highly efficient for mass - producing ABS prototypes with consistent quality. Once the mold is created, thousands or even millions of parts can be produced.
- Excellent mechanical properties: Injection - molded parts typically have better strength, dimensional accuracy, and surface finish. The high - pressure injection process compresses the material, resulting in a more dense and uniform structure.
- Wide range of available materials: There is a vast selection of ABS grades and formulations available for injection molding, allowing for customization based on specific product requirements.
- Disadvantages:
- High initial cost: The creation of the mold is expensive, often costing thousands to tens of thousands of dollars, depending on the complexity of the part.
- Long lead time: Designing and manufacturing the mold can take weeks to months, which is not suitable for projects with tight deadlines for the initial prototype.
- Limited design flexibility during production: Making changes to the design after the mold is made is very costly and time - consuming, as the mold needs to be re - engineered.
| Manufacturing Method | 3D Printing | Injection Molding |
| Design Freedom | High, can create complex geometries easily | Limited by mold design, but still good for many shapes |
| Production Speed for Small Quantities | Fast, can produce a prototype in hours | Slow due to mold setup, not ideal for small - scale |
| Production Speed for Large Quantities | Slow, not cost - effective | Fast and efficient for mass production |
| Cost for Small Quantities | Relatively low (no mold cost) | High due to mold cost |
| Cost for Large Quantities | High per unit | Low per unit |
| Material Options | Growing but still more limited | Wide variety available |
| Mechanical Properties | Vary, sometimes lower than injection - molded parts | Generally better in terms of strength and dimensional accuracy |
Applications of ABS Prototype
Automotive Industry
In the automotive industry, ABS prototypes are widely used. For example, interior components like dashboard prototypes are often made of ABS. The dimensional stability of ABS ensures that these components fit precisely into the car's interior structure. In a car, the dashboard needs to house various instruments, air vents, and control panels. An ABS prototype allows automotive engineers to test the layout and functionality of these elements before mass - production.
Moreover, exterior parts such as bumper prototypes can also be made from ABS. Its good impact resistance makes it suitable for bumpers, which are designed to absorb shock during minor collisions. A study by an automotive research institute showed that ABS - made bumper prototypes withstood impacts of up to 20 km/h without significant damage, which is a key requirement for actual bumper performance.
Electronics Industry
ABS prototypes are highly favored in the electronics industry. Many consumer electronics device housings start as ABS prototypes. Smartphones, tablets, and laptops often have their initial prototypes crafted from ABS. The material's aesthetic appeal is a major advantage here. For instance, a smartphone prototype made of ABS can be easily colored to match the brand's color scheme. It can also achieve a smooth and high - quality finish, similar to the final product, which is crucial for market testing and consumer feedback.
ABS also provides good insulation properties, which are important for protecting the internal electronic components. According to an electronics manufacturing case study, using ABS in prototype device housings reduced the risk of short - circuits during early - stage testing by 30% compared to some other materials with lower insulation capabilities.
Toy Industry
The toy industry also benefits greatly from ABS prototypes. Toys often need to be durable, colorful, and have complex shapes. ABS meets all these requirements. Action figures, toy cars, and building block toys are some examples. ABS prototypes can be easily molded into intricate shapes for action figures, ensuring that every detail, from the facial features to the clothing texture, is accurately represented.
In terms of safety, ABS is non - toxic, which is a fundamental requirement for toys. A toy safety research report indicated that over 80% of toys with ABS - based prototypes passed strict safety tests regarding material toxicity and mechanical strength, making it a reliable choice for toy manufacturers during the prototype stage.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology highly values the role of ABS prototypes. With years of experience in the field, we have mastered advanced techniques in creating high - quality ABS prototypes.
Our technical team is proficient in handling various manufacturing methods for ABS prototypes, whether it's 3D printing for rapid prototyping and design flexibility or injection molding for high - volume production with excellent mechanical properties. We understand the importance of precision in every step, from the design phase using state - of - the - art CAD software to the final production process.
Moreover, we offer customized services. We work closely with clients to understand their unique product requirements, whether it's for the automotive, electronics, or toy industry. By leveraging our expertise and advanced manufacturing facilities, we ensure that each ABS prototype meets the highest standards of quality, functionality, and aesthetics, helping our clients bring their innovative product ideas to life efficiently.
FAQ
What are the advantages of using ABS material for prototyping?
Using ABS material for prototyping offers several advantages. Firstly, it is cost - effective, especially when compared to some high - performance engineering plastics. It provides a good balance between quality and cost, making it accessible for various projects. Secondly, ABS has excellent processing properties. It can be easily formed through injection molding, 3D printing, or CNC machining, allowing for the creation of prototypes with complex shapes and accurate dimensions. Thirdly, its good mechanical properties, such as high strength and toughness, ensure that the prototypes can withstand a certain degree of stress and impact during testing, which is crucial for evaluating the product's performance.
How long does it usually take to create an ABS prototype?
The time required to create an ABS prototype depends on several factors, including the manufacturing method and the complexity of the design. For 3D printing, a small and relatively simple ABS prototype can be completed within a few hours. However, for larger or more complex designs, it may take a day or two. Injection molding, on the other hand, has a longer lead time. The mold design and manufacturing process alone can take several weeks. After the mold is ready, the actual production of the ABS prototypes can be relatively fast, especially for high - volume production. But overall, from the start of the project to having the first injection - molded ABS prototype, it could take 4 - 8 weeks considering all the steps involved.
Can ABS prototypes be painted or finished?
Yes, ABS prototypes can be painted or finished. ABS has good adhesion properties, which means it can bond well with most types of paints and coatings. Common finishing methods for ABS prototypes include spray painting, which can achieve a smooth and even color finish. Electroplating is also an option for adding a metallic appearance to the ABS prototype. When painting an ABS prototype, it is important to properly prepare the surface. This usually involves cleaning the surface to remove any grease, dust, or contaminants. Additionally, using a primer specifically designed for ABS can improve the paint adhesion and the overall quality of the finish.