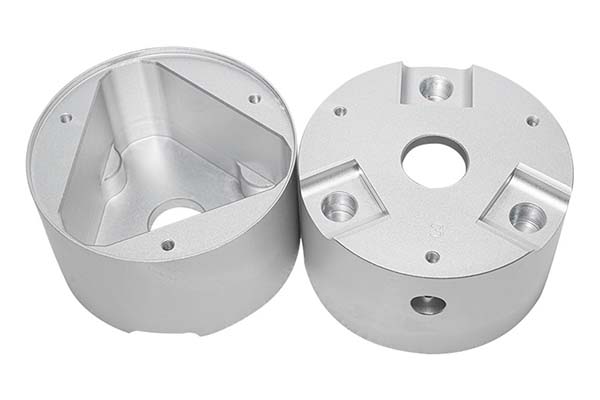
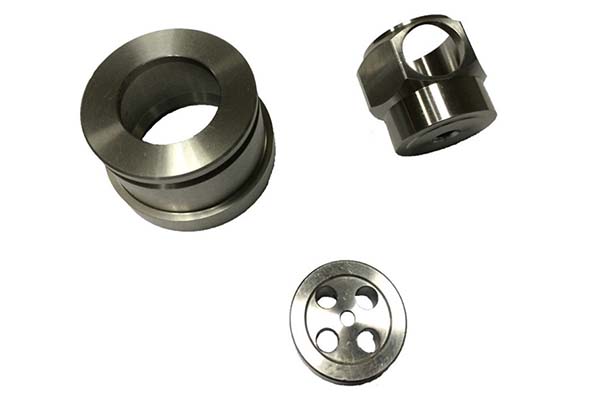
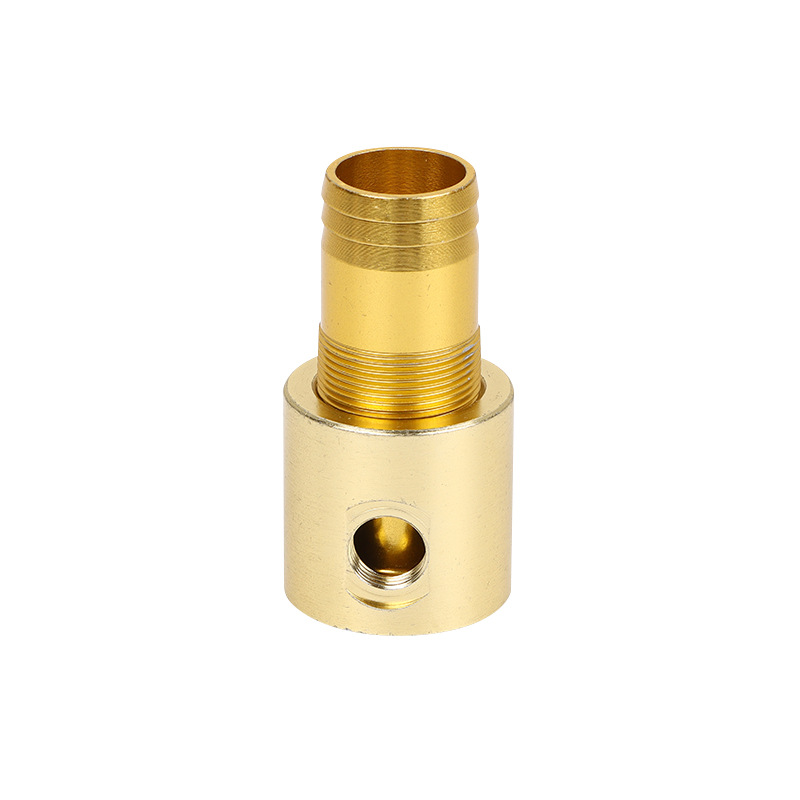
In the world of modern manufacturing, CNC cutting services have emerged as a cornerstone technology, enabling the creation of precise, complex, and high - quality parts across a wide range of industries. However, like any technology, it comes with its own set of challenges and considerations. Let's explore the key aspects of CNC cutting services, from the technologies involved to the costs, quality, and more, to help you make informed decisions for your manufacturing needs.
CNC Cutting Technologies
Types of CNC Cutting Machines
CNC cutting machines are the workhorses of the cutting process. There are several types, each with its own unique capabilities.
- Laser Cutting Machines: Laser cutting uses a high - power laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize materials. It offers extremely high precision, with some machines capable of achieving tolerances as low as ±0.05 mm. For example, in the electronics industry, laser cutting is used to create intricate circuit board patterns. The cutting speed can vary depending on the material and thickness, but it is generally quite fast for thin materials. A 1 - mm thick acrylic sheet can be cut at speeds of up to 1000 mm/s with a high - power laser cutter.
- Plasma Cutting Equipment: Plasma cutting works by creating a high - temperature plasma arc that melts and expels the material. It is commonly used for cutting metals, especially thicker ones. Plasma cutters can handle materials up to 50 mm thick in some cases. They are faster than laser cutting for thick metal sheets, but the precision is a bit lower, typically with tolerances around ±0.5 mm. This makes them ideal for applications in the construction and automotive industries where large - scale metal cutting is required.
- Water Jet Cutting Systems: Water jet cutting uses a high - pressure stream of water, sometimes mixed with abrasive particles, to cut through materials. It is a versatile option as it can cut a wide variety of materials without generating heat, which is beneficial for heat - sensitive materials like certain plastics and composites. The cutting speed depends on the material and thickness, and the precision can be as good as ±0.1 mm. Water jet cutting is often used in the aerospace industry to cut lightweight composite materials.
- CNC Milling and Routing Machines: CNC milling involves removing material from a workpiece using a rotating cutting tool. It can create complex 3D shapes and is suitable for both metals and plastics. CNC routing is similar but is often used for wood and softer materials. Milling machines can achieve high precision, with tolerances in the range of ±0.02 mm, making them suitable for manufacturing intricate parts such as gears and molds.
Cutting Technology Advancements
The field of CNC cutting technologies is constantly evolving. One significant advancement is in the area of multi - axis cutting. Traditional CNC machines often had 3 axes (X, Y, and Z), but now 5 - axis and even 6 - axis machines are becoming more common. These multi - axis machines can approach the workpiece from multiple angles, allowing for the creation of more complex geometries with fewer setups. For example, in aerospace component manufacturing, 5 - axis CNC machines can produce turbine blades with highly intricate shapes that were previously difficult or impossible to achieve with 3 - axis machines.
Another advancement is in the cutting head technology. Newer cutting heads are more efficient at delivering the cutting energy (whether it's laser, plasma, or water jet) to the material, resulting in cleaner cuts, less waste, and increased cutting speed. Some laser cutting heads, for instance, are designed to automatically adjust the focal length based on the material thickness, optimizing the cutting process.
CNC Cutting Materials
Metals
- Aluminum Cutting: Aluminum is a popular material for CNC cutting due to its lightweight, high strength - to - weight ratio, and good corrosion resistance. It is widely used in the automotive and aerospace industries. CNC cutting of aluminum can be done with various methods. Laser cutting aluminum requires careful control of the laser parameters to avoid oxidation and achieve a clean cut. Plasma cutting is also effective, especially for thicker aluminum sheets. When cutting 6061 aluminum alloy, a common type used in aerospace, a plasma cutter can cut through 10 - mm thick sheets at a reasonable speed, while a laser cutter can achieve highly precise cuts on thinner gauges.
- Steel Cutting: Steel comes in various grades, each with different properties. Mild steel is relatively easy to cut using all major CNC cutting methods. For example, a water jet cutter can cut through mild steel sheets up to 25 mm thick. Stainless steel, on the other hand, requires more careful consideration. Laser cutting stainless steel can be challenging due to its high reflectivity, but with the right laser power and assist gas, it can be cut precisely. Plasma cutting is also a viable option for stainless steel, and it can handle thicker sections more easily than laser cutting.
- Stainless Steel Cutting: Stainless steel's corrosion - resistant properties make it a favorite in industries such as food processing, medical, and architecture. When cutting stainless steel with a laser, an assist gas like oxygen or nitrogen is often used. Oxygen helps in the combustion process, making the cutting faster, while nitrogen produces a cleaner cut with less oxidation. Plasma cutting of stainless steel can achieve good results for thicker materials, and water jet cutting is suitable for applications where heat - affected zones need to be minimized.
Plastics
- Plastic Cutting: Plastics are diverse materials, and their CNC cutting characteristics vary widely. For example, ABS plastic is relatively easy to cut using laser or CNC routing. Laser cutting of ABS can create smooth edges and is often used for creating prototypes or small - scale production of plastic parts. Acrylic, a transparent plastic, is also a popular choice for laser cutting. It can be cut to create beautiful, polished edges, making it ideal for signage and display applications. When cutting acrylic with a laser, the laser power and speed need to be carefully adjusted to avoid charring.
- Acrylic Cutting: Acrylic sheets can be cut with great precision using laser cutters. A 3 - mm thick acrylic sheet can be cut with a laser to an accuracy of ±0.1 mm. CNC routing can also be used for acrylic, especially when more complex 3D shapes are required. However, care must be taken to prevent chipping of the edges.
Wood and Composite Materials
- Wood Cutting: CNC routing is the most common method for cutting wood. It can create intricate patterns and shapes, making it ideal for furniture making, decorative woodwork, and architectural models. Different types of wood, such as hardwoods like oak and softwoods like pine, have different cutting characteristics. Hardwoods may require sharper tools and slower cutting speeds to prevent splintering.
- Composite Material Cutting: Composite materials, which are made by combining two or more different materials, are becoming increasingly popular in industries like aerospace and sports equipment. Water jet cutting is often the preferred method for composite materials as it does not introduce heat, which could damage the delicate structure of the composite. For example, carbon fiber composites can be cut precisely using a water jet cutter to create parts for aircraft wings or high - performance sports bikes.
CNC Cutting Applications
Industrial Manufacturing
In industrial manufacturing, CNC cutting services are used for a wide range of applications. For example, in the production of machinery parts, CNC milling and turning are used to create components with high precision. A CNC lathe can turn out cylindrical parts with tight tolerances, ensuring smooth operation when assembled into machinery. In the manufacturing of metal enclosures for electronics, laser cutting and folding are combined to create precise and durable enclosures.
Automotive and Aerospace
- Automotive Parts Cutting: The automotive industry relies heavily on CNC cutting for manufacturing various parts. Laser cutting is used to cut sheet metal for car body panels, ensuring precise fit and finish. Plasma cutting is used for thicker structural components. CNC machining centers are used to create engine parts, such as cylinder heads, with high precision to meet the strict performance requirements of modern engines.
- Aerospace Components: In the aerospace industry, precision is of utmost importance. CNC cutting is used to produce components like turbine blades, aircraft frames, and wing components. 5 - axis CNC machines are often employed to create the complex shapes required for these components. Water jet cutting is used for cutting lightweight composite materials used in aircraft construction to avoid heat - induced damage.
Medical and Electronics
- Medical Device Manufacturing: CNC cutting is used to produce medical devices with high precision and biocompatibility. For example, laser cutting is used to create stents from medical - grade metals with extremely tight tolerances. CNC machining is used to produce surgical instruments, ensuring smooth operation and durability.
- Electronics Cutting: In the electronics industry, CNC cutting is used to create circuit boards, heat sinks, and enclosures. Laser cutting can create fine - pitched traces on circuit boards, while CNC milling is used to create complex shapes for heat sinks to improve their cooling efficiency.
CNC Cutting Service Providers
Finding the Right Provider
When looking for a CNC cutting service provider, several factors need to be considered. First, the provider's experience and reputation are crucial. A company with years of experience in the industry is more likely to have the knowledge and skills to handle complex projects. Reading customer reviews and testimonials can give you an idea of the provider's track record. For example, if a provider has a high number of positive reviews from customers in your industry, it's a good sign.
Second, the range of services offered is important. A good provider should be able to offer multiple CNC cutting technologies, such as laser, plasma, and water jet cutting, as well as post - processing services like finishing and assembly. This allows you to get all your manufacturing needs met in one place.
Comparing Service Providers
It's also essential to compare different service providers in terms of their capabilities, prices, and delivery times. Some providers may specialize in certain materials or industries. For instance, one company may be an expert in cutting aerospace - grade materials, while another may be more focused on consumer electronics. Get quotes from multiple providers and compare not only the prices but also the quality of their work, as sometimes a slightly higher price may be worth it for better quality and shorter lead times.
CNC Cutting Costs and Pricing
Cost Estimation Factors
CNC cutting costs are influenced by several factors. The most obvious one is the material cost. Different materials, such as high - grade stainless steel or exotic composites, can be significantly more expensive than common metals or plastics. The machine time is another major factor. Complex parts that require longer cutting times will cost more. For example, a part that takes 2 hours to cut on a CNC machine will cost more than one that takes 30 minutes.
Labor cost also plays a role. Skilled operators are needed to set up and monitor the CNC machines, and their wages are factored into the overall cost. The complexity of the project is another cost determinant. Parts with intricate designs and tight tolerances require more programming time and careful attention during the cutting process, increasing the cost.
Budget - Friendly Options
To find budget - friendly CNC cutting options, you can consider the following. First, optimize your design to reduce complexity without sacrificing functionality. A simpler design may require less machine time and programming effort. Second, choose a more common and cost - effective material if possible. For example, if your application allows, using mild steel instead of a high - end alloy can significantly reduce material costs. Third, look for service providers that offer competitive pricing and volume discounts. Some providers may offer lower per - unit prices for larger orders.
CNC Cutting Quality and Precision
High - Precision Cutting
Achieving high - precision cutting is crucial in many industries. The tolerance levels that can be achieved depend on the cutting technology and the machine's capabilities. As mentioned earlier, laser cutting can achieve tolerances as low as ±0.05 mm, while plasma cutting typically has tolerances around ±0.5 mm. High - precision cutting is essential in industries like aerospace and medical, where even the slightest deviation can have serious consequences.
Quality Control and Assurance
Quality control in CNC cutting involves several steps. First, the cutting process is closely monitored to ensure that the machine is operating within the specified parameters. This includes checking the cutting speed, power, and other variables. After the cutting is complete, the parts are inspected using precision measurement tools such as coordinate measuring machines (CMMs). CMMs can measure the dimensions of a part with extremely high accuracy, ensuring that it meets the design specifications. Service providers may also have quality assurance processes in place, such as multiple - stage inspections and certifications to demonstrate their commitment to quality.
CNC Cutting Equipment and Tools
Types of Equipment
The choice of CNC cutting equipment depends on the materials and applications. As described earlier, laser cutting machines are suitable for precision cutting of thin materials, plasma cutting equipment for thicker metals, and water jet cutting systems for heat - sensitive materials. CNC milling and routing machines are used for creating 3D shapes in various materials. Each type of equipment has its own advantages and limitations, and the right choice can significantly impact the quality and efficiency of the cutting process.
Tool Maintenance and Upgrades
Tool maintenance is essential for ensuring consistent cutting quality. For example, the cutting heads of laser and plasma cutters need to be regularly cleaned and inspected for wear. The cutting tools in CNC milling and routing machines, such as end mills, also need to be replaced when they become dull. Upgrading the equipment can also improve performance. Newer models of CNC machines often come with advanced features like better automation, higher cutting speeds, and improved precision, which can increase productivity and reduce costs in the long run.
CNC Cutting Software and Programming
CAD/CAM Software and CNC Programming
CAD/CAM software is the backbone of CNC cutting. CAD (Computer - Aided Design) software is used to create the 3D models of the parts to be cut. CAM (Computer - Aided Manufacturing) software then takes these models and generates the toolpaths for the CNC machine. CNC programming involves writing the code that controls the movement of the machine based on the toolpaths generated by the CAM software. The most common programming language for CNC machines is G - code. For example, a simple G - code command like "G01 X10 Y20 Z5 F100" tells the machine to move in a linear path to the coordinates (X = 10, Y = 20, Z = 5) at a feed rate of 100 mm/min.
Software Integration and Training
Integrating different software systems can streamline the CNC cutting process. For example, integrating the CAD/CAM software with the CNC machine's control system can reduce the chances of errors during the transfer of data. Training is also important for operators to effectively use the software and programming tools. Well - trained operators can optimize the cutting paths, resulting in faster cutting times and better - quality parts.
Yigu Technology, as a plastic metal parts custom manufacturing Supplier, believes that in the realm of CNC cutting services, a combination of advanced technology and a deep understanding of materials is key. Our experience has shown that by investing in state - of - the - art CNC machines and continuously training our staff on the latest software and programming techniques, we can provide high - quality custom parts. We also focus on material compatibility, ensuring that the right cutting method is chosen for each plastic or metal material. This approach allows us to meet the diverse needs of our clients, whether it's for small - scale prototypes or large - scale production runs.
FAQs
1. What is the difference between laser cutting and plasma cutting?
Laser cutting uses a high - power laser beam to melt, burn, or vaporize materials, offering high precision (tolerances as low as ±0.05 mm) and is suitable for a wide range of materials including metals, plastics, and wood. Plasma cutting, on the other hand, creates a high - temperature plasma arc to melt and expel the material. It is faster for thick metal sheets but has lower precision (tolerances around ±0.5 mm) compared to laser cutting.
2. How can I reduce the cost of CNC cutting services?
You can reduce costs by optimizing your design to be less complex, choosing a more cost - effective material, looking for service providers that offer volume discounts, and minimizing machine time by ensuring efficient programming and setup.
3. What kind of quality control measures are in place for CNC cutting?
Quality control measures include closely monitoring the cutting process to ensure the machine operates within specified parameters, using precision measurement tools like coordinate measuring machines (CMMs) to inspect the parts after cutting, and having multiple - stage inspection processes and quality certifications.