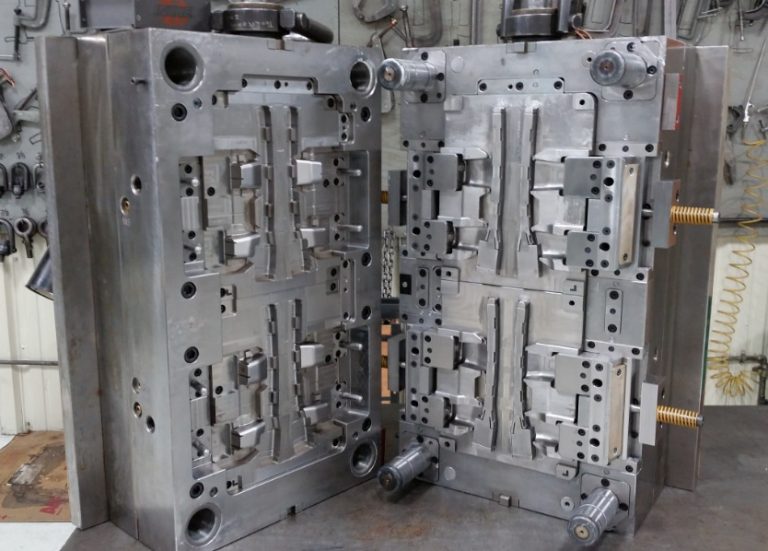
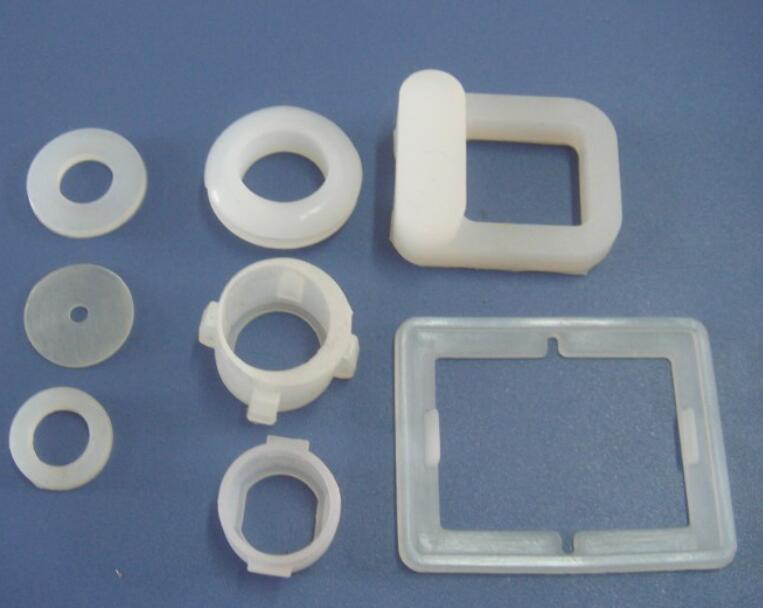
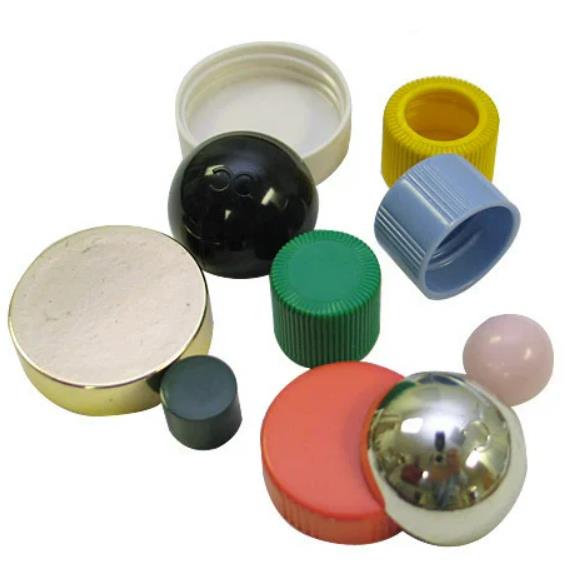
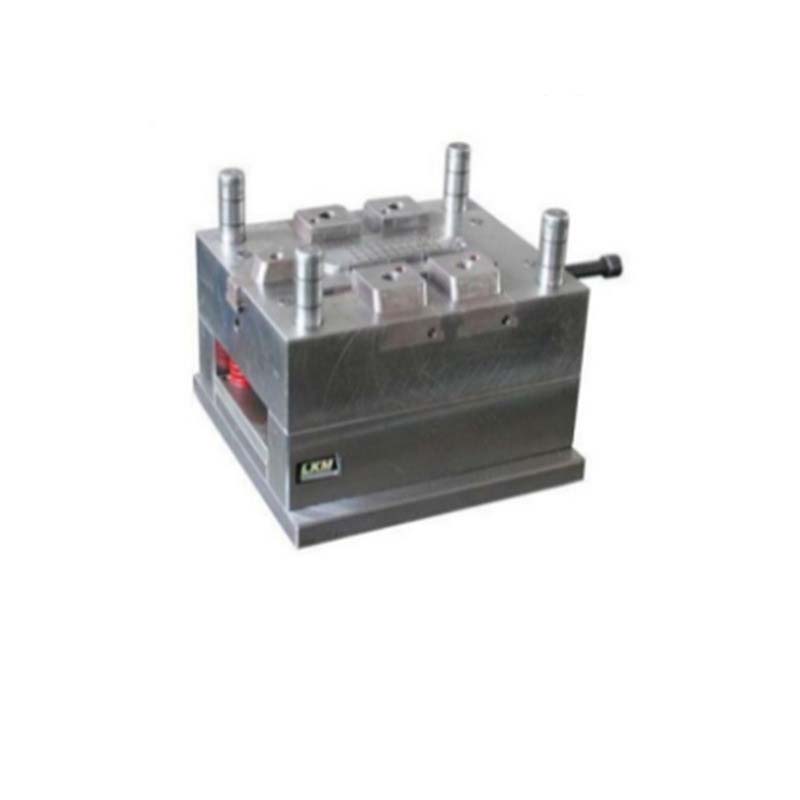
What is Injection Molding?
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process that involves injecting molten material, typically plastic, into a mold cavity. Once the material cools and solidifies within the mold, it takes on the shape of the cavity, creating a finished product. This method is highly efficient for producing high - volume, complex - shaped parts with consistent quality.
How It Works
- Material Preparation: The process begins with raw materials, usually in the form of pellets. These pellets are fed into the hopper of an injection molding machine. For example, if you're producing plastic toys, the plastic pellets are the starting point.
- Melting: Inside the machine, a heating unit melts the material. The temperature is carefully controlled based on the type of material. For common plastics like polyethylene (PE) or polypropylene (PP), the melting temperature ranges from approximately 130 - 170°C for PE and 160 - 170°C for PP.
- Injection: A reciprocating screw or a plunger then forces the molten material at high pressure into the closed mold cavity. The pressure can range from 10 - 100 MPa, depending on the complexity of the part and the material being used.
- Cooling and Solidification: Once the mold cavity is filled, the material cools down. This cooling process is crucial as it determines the final shape and quality of the product. Cooling times can vary from a few seconds to several minutes, depending on the size and thickness of the part.
- Ejection: After the material has solidified, the mold opens, and the finished part is ejected, often with the help of ejector pins.
Applications Across Industries
Injection molding has found its way into countless industries due to its versatility and efficiency:
- Automotive Industry: It is used to produce a wide range of components, such as dashboards, bumpers, and interior trim parts. For instance, the intricate design of a car's dashboard, with its various curves and features, can be precisely replicated through injection molding. In fact, about 50% of the parts in a modern car are made using injection molding.
- Electronics: Components like smartphone cases, computer housings, and keyboard keys are commonly injection - molded. The high precision of the process ensures a perfect fit for all the internal components of these devices. For example, the smooth and sleek design of an iPhone case is achieved through injection molding.
- Medical Field: Products such as syringes, medical device housings, and prosthetics are made using injection molding. In the case of syringes, the process allows for the production of parts with extremely tight tolerances, ensuring safety and functionality.
- Consumer Goods: From plastic toys to kitchen utensils, injection molding is the go - to process. For example, the colorful and detailed plastic toys that kids play with are often injection - molded, allowing for mass production at a relatively low cost.
Roles and Responsibilities in Injection Molding Jobs
1. Injection Molding Operator
The injection molding operator is the front - line worker in the injection molding process, and their tasks are crucial for the smooth running of production:
- Equipment Operation: They are responsible for the daily operation of the injection molding machine. This includes starting up the machine, ensuring that all components are in working order. For example, they need to check the hopper to ensure a continuous supply of raw material pellets, and start the heating units to melt the plastic to the correct temperature. According to industry statistics, about 70% of machine - related issues can be avoided with proper startup procedures.
- Parameter Monitoring: Operators must closely monitor the machine's parameters throughout the production process. These parameters include temperature, pressure, and injection speed. For instance, if the temperature is too low, the plastic may not flow properly into the mold, resulting in incomplete parts. On average, operators need to check and adjust parameters every 15 - 30 minutes during continuous production.
- Product Quality Inspection: They conduct regular quality checks on the molded products. This involves visually inspecting the parts for any defects such as warping, flash (excess material), or incomplete filling. In a high - volume production line, operators may inspect up to 100 - 200 parts per hour, depending on the complexity of the product.
- Simple Troubleshooting: When minor issues occur, such as a jam in the hopper or a small leak in the cooling system, operators are expected to perform simple troubleshooting. For example, they can clear a blocked hopper by gently removing the obstruction or tighten a loose connection in the cooling system to stop a minor leak.
2. Injection Molding Engineer
The injection molding engineer plays a more strategic and technical role in the injection molding process:
- New Product Development: Engineers are involved from the early stages of new product development. They work with designers to ensure that the product design is suitable for injection molding. For example, they analyze the part's geometry to determine the best gate location (the point where the molten plastic enters the mold), which can affect the flow of the plastic and the overall quality of the part.
- Process Optimization: They are responsible for optimizing the injection molding process to improve efficiency and product quality. This may involve adjusting the molding parameters based on the material being used and the product requirements. By optimizing the process, they can reduce cycle times (the time it takes to produce one part) by up to 20 - 30% in some cases.
- Solving Production Problems: When complex production problems arise, such as inconsistent part quality or mold failures, engineers are called in to find solutions. They use their knowledge of materials, mold design, and machine operation to diagnose the root cause. For example, if parts are coming out with internal voids, they may adjust the injection pressure and cooling rates to eliminate the problem.
- Equipment Selection and maintenance: Engineers are also involved in selecting the right injection molding equipment for a particular production need. They consider factors such as the size of the parts to be produced, the production volume, and the material being used. Additionally, they develop maintenance plans for the equipment to ensure its long - term reliability. A well - maintained machine can have a lifespan of 10 - 15 years in normal production environments.
Skills and Requirements for Injection Molding Jobs
1. Technical Skills
- In - depth Knowledge of Injection Molding Processes: A solid understanding of the injection molding process is fundamental. This includes knowledge of the different stages, such as filling, packing, cooling, and ejection. For example, understanding how the filling speed affects the formation of weld lines in the final product is crucial. An injection molding professional should know that a faster filling speed can sometimes reduce the visibility of weld lines but may also introduce other issues like air traps. According to industry research, about 80% of product defects can be traced back to improper process control during injection molding.
- Proficiency in Injection Molding Machine Operation and Maintenance: Operators and engineers need to be proficient in operating injection molding machines. This involves knowing how to set up the machine for different products, adjust parameters like temperature, pressure, and injection speed, and perform routine maintenance. For instance, regular cleaning of the machine's barrel and screw can prevent material buildup, which could affect the quality of the molded parts. A well - maintained machine can also reduce downtime. Studies show that machines with proper maintenance schedules have 30 - 40% less unplanned downtime compared to those with irregular maintenance.
- Understanding of Mold Structure and Debugging: Knowledge of mold structure is essential. This includes understanding the function of different mold components such as the cavity, core, runner system, and cooling channels. When a mold is not producing parts to the required quality standards, the ability to debug is crucial. For example, if parts are coming out with uneven cooling, it may be necessary to check and potentially modify the cooling channel design in the mold. Approximately 70% of mold - related issues can be resolved with proper understanding and debugging skills.
- Familiarity with Plastic Material Properties: Different plastic materials have unique properties, and professionals in injection molding must be familiar with them. This includes knowing the melting temperature, viscosity, shrinkage rate, and mechanical properties of various plastics. For example, when working with a high - shrinkage material like polypropylene, extra care needs to be taken in the mold design and process parameters to avoid dimensional inaccuracies in the final product.
2. Soft Skills
- Responsibility: Workers in injection molding jobs are responsible for the quality of the products they produce and the proper functioning of the equipment. A small oversight, such as not properly checking the raw materials for impurities, can lead to a large batch of defective products. For example, if a small piece of foreign matter is present in the plastic pellets and goes unnoticed, it can cause defects in the molded parts, resulting in significant losses for the company.
- Teamwork: Injection molding operations often involve multiple teams, such as production, engineering, and quality control. Teamwork is essential for smooth operations. For example, the production team needs to communicate effectively with the engineering team when there are issues with the injection molding process. The engineering team can then provide technical support to resolve the problem. A study found that companies with strong teamwork in injection molding operations have a 25% higher productivity rate.
- Communication Skills: Clear communication is necessary both within the injection molding team and with other departments. For instance, the injection molding operator needs to communicate any machine malfunctions or quality issues to the maintenance and quality control teams promptly. Good communication can prevent minor issues from escalating into major production problems.
- Problem - Solving Skills: Injection molding processes can encounter various problems, from equipment failures to product quality issues. Workers need to be able to analyze the problem, identify the root cause, and develop solutions. For example, if a part is not ejecting properly from the mold, the operator or engineer needs to troubleshoot whether the problem lies with the ejector pins, the mold design, or the injection process parameters.
- Learning Ability: The injection molding industry is constantly evolving, with new materials, technologies, and processes being introduced. Workers need to have the ability to learn and adapt to these changes. For example, the development of new biodegradable plastics requires injection molding professionals to learn about their unique processing requirements.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology plays a vital role in the injection molding ecosystem. We pride ourselves on our rapid response to customer needs. When clients come to us with unique injection molding project requirements, our team springs into action immediately. We understand that time is often of the essence in product development, so we work efficiently to translate their ideas into feasible production plans.
In terms of product quality, we have a rigorous quality - control system in place. From the selection of high - quality raw materials to the precision manufacturing of molds and the careful monitoring of the injection molding process, every step is strictly supervised. Our advanced inspection equipment allows us to detect even the slightest defects, ensuring that only products of the highest quality reach our customers.
Moreover, Yigu Technology is committed to innovation. We constantly invest in research and development to explore new materials and improve our injection molding techniques. This enables us to offer our customers more creative solutions, such as developing injection - molded products with enhanced functionality or unique aesthetic features. Whether it's creating a complex plastic part with improved strength - to - weight ratio or a metal - plastic composite product with excellent heat - dissipation properties, we strive to exceed customer expectations.