In the competitive world of manufacturing, scaling up plastic part production is a critical yet challenging leap. This comprehensive guide delves into the world of large scale injection molding, moving beyond basic concepts to provide a strategic roadmap for manufacturers. We will explore what truly defines large-scale production, its undeniable importance in modern manufacturing, and the pivotal decisions that determine success or failure. From navigating the complexities of material selection for durability and cost to mastering the nuances of high-cavitation mold design, and selecting heavy-duty machinery that ensures uptime, this article is built on industry expertise. It’s designed to give you the substantive, experience-driven knowledge needed to make informed decisions, optimize your process, and achieve reliability at volume.
Introduction
So, you've mastered prototyping and small batches, and now demand is surging. Transitioning to or optimizing large scale injection molding is the pivotal step that separates thriving manufacturers from the rest. It's a complex symphony of engineering, material science, and logistical precision, where mistakes are magnified and efficiency is king. This isn't just about using bigger machines; it's about a fundamental shift in mindset from making parts to sustaining a flawless, cost-effective manufacturing process. Whether you're producing millions of automotive components, consumer electronics housings, or industrial containers, understanding the core principles of scaling up is non-negotiable. This guide is crafted from the ground up to address the real-world challenges and critical considerations you face, providing actionable insights to build a robust, high-volume manufacturing operation.
What is Large Scale Injection Molding?
When we talk about large scale injection molding, what metrics truly define it? It’s less about the physical size of a single part and more about the sheer volume of output and the systematic, continuous production required to achieve it. We're typically discussing production runs in the hundreds of thousands to millions of identical parts. The focus shifts from flexibility to maximizing efficiency, consistency, and minimizing cost per unit.
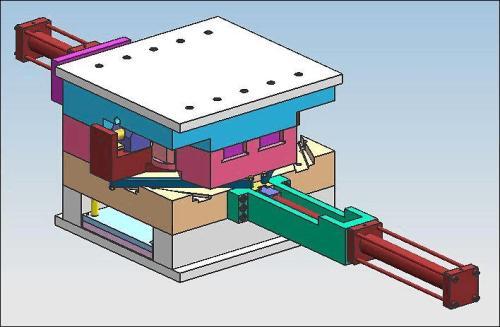
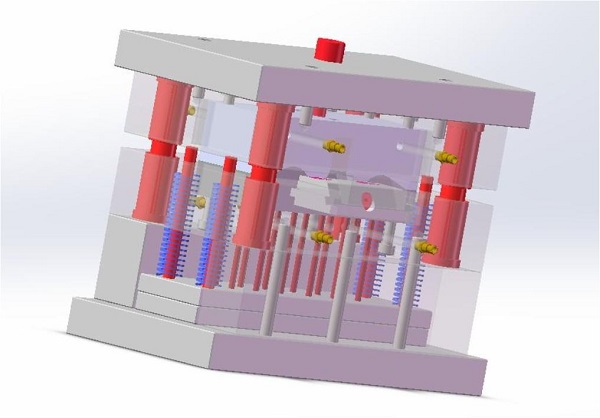
The core of this scale is built on three pillars: high-cavitation molds, specialized engineering resins, and dedicated, automated machinery. A mold for large-scale production isn't just a larger version of a prototype tool. It's a masterpiece of durability and precision, often with 32, 64, or even 128 cavities, engineered to withstand millions of cycles with minimal maintenance. The process runs not just for a shift, but often 24/7, with cycle times shaved down to seconds. The goal is a seamless, lights-out operation where automation—robotic part removal, conveyors, and vision inspection systems— is integral, not optional.
Why is Large Scale Injection Molding So Crucial in Modern Manufacturing?
The importance of large scale injection molding is woven into the fabric of global industry. It is the engine behind mass production, enabling the economies of scale that make everyday products affordable. Without it, the cost of a plastic water bottle, a smartphone case, or a car interior component would be prohibitive.
Beyond cost, it delivers the unmatched consistency and part quality demanded by sectors like automotive and medical. When you're producing a million taillight lenses, part #500,000 must be virtually identical to part #1. This repeatability is paramount. Furthermore, it allows for the use of advanced, high-performance materials that offer superior strength, heat resistance, or chemical stability—materials whose properties can only be fully realized and justified in high-volume applications. In today's on-demand economy, it also provides the supply chain reliability that large OEMs depend on, ensuring a steady, predictable flow of components. Simply put, it transforms a design into a ubiquitous product.
What Are the Key Considerations for Manufacturers?
Jumping into large-scale production without a strategy is a recipe for costly delays and quality issues. Success hinges on deliberate planning across several interdependent areas. It’s a holistic exercise where material selection, mold design, and equipment choice must be in perfect alignment with your production targets and quality standards. Overlooking one can compromise the entire operation. The following sections break down these critical pillars, providing a framework for your decision-making process.
How Do You Select the Right Material for High-Volume Production?
Material selection for large scale runs is a strategic decision balancing performance, cost, and processability. While a material might work for a prototype, it must be viable for millions of cycles.
- Performance & Specifications: The material must meet the part's functional requirements—** tensile strength, impact resistance, heat deflection temperature (HDT)**, and regulatory compliance (e.g., FDA, UL94).
- Cost-Per-Unit & Raw Material Stability: At scale, even fractions of a cent per part add up. You must evaluate resin cost per pound and material yield. Furthermore, you need a supplier capable of guaranteeing consistent material properties across enormous batch orders to prevent production variances.
- Processability & Cycle Time: Some engineering-grade resins like PEEK offer fantastic properties but are difficult to process and have longer cycle times. For high volume, you often need a material that balances performance with the ability to fill and cool rapidly. Flow additives can be critical here.
Case in Point: A client needed a million-plus automotive under-hood components. The initial choice was a standard nylon 6/6. Through testing, we recommended switching to a heat-stabilized, lubricated nylon 6/6 with a narrower molecular weight distribution. While slightly more expensive per kilogram, it filled the complex, 64-cavity mold more consistently and reduced cycle time by 15%. This change improved part quality and lowered the total production cost.
Quick-Reference: Common High-Volume Material Trade-Offs
| Material | Best For | Key Consideration for Scale |
|---|---|---|
| Polypropylene (PP) | Food containers, living hinges, low-cost parts | Excellent flow, low cost, but can have higher shrinkage. |
| ABS | Automotive trim, electronics housings | Good toughness & finish; watch for moisture sensitivity causing voids. |
| Polycarbonate (PC) | Transparent parts, impact-resistant covers | High clarity & strength; requires high drying temps and melt temps. |
| Nylon (PA 6/6) | Gears, under-hood components | Excellent strength & heat resistance; highly hygroscopic—must be dried meticulously. |
What Makes Mold Design and Engineering Different at Scale?
The mold is the heart of your operation. For large scale work, mold design transitions from art to predictive science. The primary objective is dubility, efficiency, and maintenance predictability.
- High-Cavitation Molds & Balanced Flow: Designing a 64-cavity mold isn't about duplicating a single cavity 64 times. It requires sophisticated mold flow analysis to ensure every cavity fills at exactly the same time and pressure. An unbalanced fill leads to inconsistent part quality and waste.
- Durability & Steel Selection: Molds must be built from pre-hardened or hardened tool steels (like H-13 or S-7) to resist wear, corrosion, and high clamping pressures over millions of cycles. Critical areas like gates and cores may require even harder materials or coatings.
- Hot Runner Systems: Essential for scale, hot runner systems eliminate sprue and runner waste, reducing material cost and cycle time. However, they are complex and require expert design to prevent heat degradation and ensure uniform thermal control across all nozzles.
- Predictive Maintenance & Cooling: A large-scale mold is a capital asset. Design must include easily accessible cooling channels and wear plates. Integrating sensor technology for pressure and temperature monitoring allows for predictive maintenance, preventing unplanned downtime.
How Do You Choose the Right Equipment and Machinery?
The press is the muscle. Selecting injection molding machinery for high-volume production means prioritizing reliability, precision, and integration over mere tonnage.
- Clamping Force & Shot Capacity: The machine must provide adequate clamping force (in tons) to keep the multi-cavity mold closed against injection pressure and have sufficient shot capacity to fill all cavities. Undersizing here causes flash; oversizing wastes energy.
- Repeatability & Control: Look for machines with closed-loop servo-hydraulic or all-electric systems. All-electric machines offer superior energy efficiency and shot-to-shot repeatability, which is critical for part consistency. Precision in injection speed, pressure control, and temperature zones is non-negotiable.
- Integration & Automation Readiness: The press must be designed for a lights-out manufacturing environment. This includes standard interfaces for robotic sprue pickers, conveyor systems, and the ability to feed data into a Manufacturing Execution System (MES) for real-time monitoring and process control.
Data Point: A 2022 study by Plastics Today found that in large-scale operations switching from traditional hydraulic to all-electric presses, manufacturers reported an average 30% reduction in energy consumption and a 15% improvement in process consistency, leading to a significant reduction in scrap rates.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
What is the minimum order quantity (MOQ) for large scale injection molding?
While it varies by project complexity, true large-scale MOQs typically start at 50,000 to 100,000 parts, as this volume is needed to justify the high cost of multi-cavity mold tooling and production setup.
How long does it take to build a mold for large-scale production?
Lead times are significantly longer than for prototype tools. For a complex, high-cavitation mold with a hot runner system, expect 14 to 20 weeks for design, machining, hardening, polishing, and testing.
What is the biggest risk when scaling up injection molding production?
The single biggest risk is inadequate mold design and engineering. A poorly designed mold will lead to chronic issues—short shots, flash, inconsistent part dimensions—that are extremely costly and time-consuming to fix once in production. Investing upfront in expert design and mold flow analysis is critical.
Can you use recycled materials in large-scale molding?
Yes, but it requires rigorous planning. Post-industrial recycled (PIR) content with a known and consistent source is often viable. Using post-consumer recycled (PCR) resin adds complexity due to potential contamination and variability, which can affect processing and part properties. It must be carefully evaluated and potentially blended with virgin material.
How do you control quality across millions of parts?
Quality control shifts from inspecting every part to statistical process control (SPC). This involves automated in-machine vision systems for critical features and periodic manual checks against key dimensions. The focus is on monitoring process parameters (pressure, temperature, time) – if the process is in control, the parts will be consistent.
Contact Yigu Technology for Custom Manufacturing.
Navigating the complexities of large scale injection molding requires a partner with proven expertise and a commitment to precision. At Yigu Technology, we combine decades of engineering experience with state-of-the-art facilities to turn your high-volume production goals into a reliable, cost-effective reality. From design-for-manufacturability (DFM) analysis and precision mold making to fully automated production and integrated quality assurance, we manage the entire process.
Let's discuss how to optimize your next project for scale, durability, and total value. Contact our engineering team today for a confidential consultation and quote.