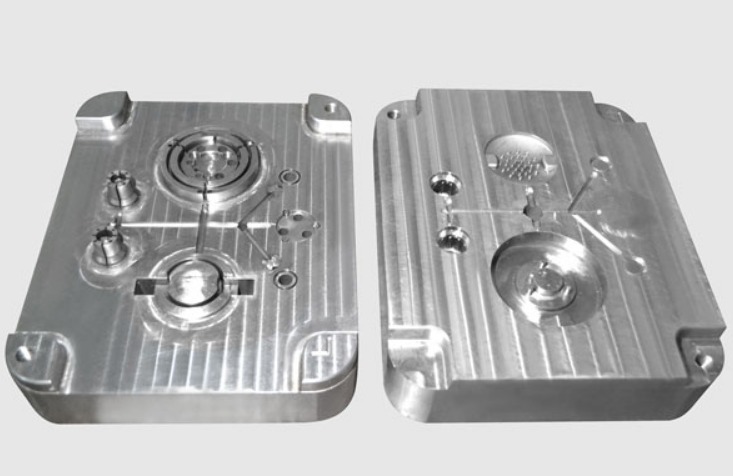
In the fast-paced world of product development, China Rapid Tooling has emerged as a strategic game-changer, enabling companies to iterate designs, validate markets, and launch low-volume products with unprecedented speed and cost efficiency. This process involves creating injection molds quickly using materials like aluminum or soft steel, bypassing the long lead times and high costs of traditional hardened steel tooling. For product managers, engineers, and entrepreneurs, understanding how to effectively leverage China Rapid Tooling is crucial. This guide provides a comprehensive overview, from the core process and material choices to navigating supplier selection and quality assurance, equipping you to make informed decisions and accelerate your product journey from concept to customer.
What is Rapid Tooling?
Rapid Tooling is a subset of rapid prototyping/manufacturing focused on producing functional injection molds in a significantly shortened timeframe. Unlike conventional tooling that uses hardened steel (H13, P20) machined over weeks or months, rapid tooling typically employs softer metals like aluminum alloy (7075-T6) or pre-hardened steels (e.g., NAK80). These materials can be machined much faster on high-speed CNC equipment. The trade-off is mold life—an aluminum mold may be good for 1,000 to 50,000 shots versus 1,000,000+ for hardened steel—making it perfect for prototyping, pilot runs, bridge tooling, and low-to-medium volume production.
Why Choose China for Rapid Tooling Services?
China’s dominance in this sector is built on a powerful combination of factors that deliver unmatched value:
- Cost Competitiveness: The most significant advantage. Lower operational and labor costs translate into dramatically lower tooling prices, often 60-80% less than Western counterparts, without necessarily sacrificing quality.
- Unparalleled Speed & Scale: China’s vast manufacturing ecosystem, with deeply integrated supply chains for mold bases, materials, and machining, enables incredibly fast turnarounds. The sheer volume of specialized shops drives competition and efficiency.
- Technical Expertise & Specialization: Many Chinese manufacturers have refined rapid tooling into a core competency, with over a decade of experience optimizing processes for speed, cost, and reliability.
- Material & Process Flexibility: Suppliers offer a wide range of rapid tooling materials (from basic aluminum to hybrid steel inserts) and are familiar with processing most commercial thermoplastics.
The Rapid Tooling Process Workflow
A streamlined, digital-forward process is key to achieving "rapid" results.
- Design for Manufacturability (DFM) Analysis: The supplier’s engineers review your 3D CAD model (STEP/IGES format) to identify potential molding issues (undercuts, wall thickness, draft) and suggest modifications. This collaborative step is critical for success.
- Quotation & Agreement: Based on DFM, you receive a detailed quote outlining tooling cost, part cost, and lead time.
- Mold Design & CNC Machining: Simplified, single-cavity mold designs are created. Cavity and core blocks are machined directly from aluminum or pre-hardened steel billet using high-speed CNC mills, avoiding slower EDM processes where possible.
- Mold Assembly & First Shot Trial: Components are fitted into a standard mold base, and the mold is tested on an injection press. T1 samples are produced.
- Sample Approval & Minor Revisions: Samples are shipped to you for evaluation. Most reputable suppliers include one round of minor revisions (e.g., polishing, gate adjustment) in the tooling cost.
- Production & Delivery: Upon your approval, the production run begins, and finished parts are shipped.
What Materials are Available?
The choice of mold material is the primary decision, balancing cost, lead time, durability, and final part material.
- Aluminum (7075-T6): The most common and cost-effective option. Excellent for prototyping and short runs (up to ~10,000 cycles) with unfilled plastics like ABS, PP, PC. It machines very quickly but wears faster and is not suitable for abrasive filled materials.
- Pre-Hardened Steels (e.g., NAK80, P20): A step up in durability. Offers better wear resistance and polishability, suitable for higher volumes (10k-50k+ shots) and lightly filled materials. Lead time and cost are higher than aluminum but lower than fully hardened steels.
- Hybrid/Insert Molds: A cost-effective strategy where hardened steel inserts are used for high-wear areas (like gates) within an aluminum mold base. This extends mold life for abrasive materials.
- Part Materials: Virtually all standard thermoplastics (ABS, Nylon, PC, PP, TPU) are available. For engineering resins, discuss compatibility with your chosen mold material.
Quality Control Measures
Ensuring quality in a fast-paced, remote environment requires clear protocols.
- In-House QC: A reliable partner will have a First Article Inspection (FAI) process, using CMMs or precision measuring tools to verify T1 samples against your drawings. In-process checks during production are also standard.
- Documentation: Expect FAI reports, material certifications (C of C), and photos/videos of parts and packaging.
- Third-Party Inspection (Highly Recommended): For critical projects, hiring a local third-party quality inspection company to conduct a pre-shipment inspection is a best practice. They check dimensions, appearance, and function, providing an unbiased report.
What are Typical Lead Times and Costs?
Setting realistic expectations is crucial for project planning.
- Lead Times: Total project lead time typically ranges from 2 to 5 weeks.
- Quotation & DFM: 1-2 days.
- Tool Fabrication: 10-15 working days.
- Sampling & Production: 5-10 working days.
- Cost Structure:
- Tooling (NRE): $1,000 to $10,000+, driven by part size, complexity, and chosen mold material (Aluminum at the low end, steel inserts at the high end).
- Per-Part Cost: Varies widely based on part size, material, and quantity. Unit cost decreases significantly with higher volumes, even within a "low-volume" run of a few thousand pieces.
How to Select a Manufacturing Partner?
Choosing the right supplier is the most critical step to mitigate risk.
- Specialization & Portfolio: Look for a supplier whose main business is Rapid Tooling and Low-Volume Molding. Review their online portfolio and request physical samples of their work.
- Communication & Transparency: Gauge their responsiveness and clarity during quoting. They should provide detailed DFM feedback and a clear, itemized breakdown of costs. Effective English communication is a strong positive indicator.
- Ask Specific Technical Questions: “What mold material do you recommend for my part in PA6+30%GF?” “What is your process for validating mold cooling?” “Can you share a sample FAI report?”
- Start with a Pilot Project: For new partnerships, begin with a smaller, less critical project to evaluate their performance, quality, and reliability.
Conclusion
China Rapid Tooling is an indispensable strategy for compressing development cycles and reducing upfront investment. It empowers innovators to move beyond 3D-printed prototypes to obtain functional, end-use material parts for testing and low-volume launch. Success hinges on a clear understanding of the trade-offs (mold life vs. speed/cost), a strategic choice of tooling material, and, most importantly, partnering with a communicative and specialized supplier with robust quality processes. By following the framework outlined in this guide, you can confidently navigate the China Rapid Tooling landscape and turn your designs into tangible products faster than ever before.
FAQ on China Rapid Tooling
What is the main difference between rapid tooling and conventional tooling?
Rapid Tooling uses softer metals (Aluminum, Pre-hardened Steel) for fast, low-cost molds suitable for prototypes and low volumes. Conventional Tooling uses hardened tool steels for high-cost, long-lead-time molds designed for mass production (millions of cycles).
Can a rapid tool be used for production-grade materials like PEEK or glass-filled nylon?
It is possible but requires careful planning. Abrasive or high-temperature materials drastically reduce aluminum mold life. For such materials, a pre-hardened steel mold or a hybrid mold with steel inserts is strongly recommended to achieve a viable production run.
Who owns the intellectual property (IP) and the physical mold?
You (the client) typically own the IP and the physical mold as you are paying for its fabrication. This must be explicitly stated in the agreement. The supplier usually stores the mold for a limited time (e.g., 12 months) after project completion.
How many design revisions are typically included?
Most reputable suppliers include one round of minor revisions (e.g., adjusting gate size, venting, polishing) after the first sample. Major design changes that require re-machining the core or cavity are billed as an Engineering Change Order (ECO).
Is it safe to send my CAD files to a Chinese supplier?
While legitimate suppliers protect client IP to maintain their business reputation, it is a valid concern. To mitigate risk:
- Work with established companies with a strong track record.
- Start with non-critical projects.
- Consider filing for patents or design protection before sharing files.
- Use a Non-Disclosure Agreement (NDA), though enforcement can be challenging internationally.
Contact Yigu technology for custom manufacturing.
At Yigu Technology, we specialize in providing reliable, high-value China Rapid Tooling solutions. Our expertise lies in guiding clients through the optimal choice between aluminum and pre-hardened steel molds to balance speed, cost, and part performance. With a transparent process, clear communication, and a commitment to quality documentation, we help you de-risk development and bring functional prototypes and low-volume products to market efficiently.
Partner with us to experience a streamlined rapid tooling workflow.
Contact Yigu technology today for a fast, detailed quote and expert DFM analysis of your project.