1. What exactly is CNC prototyping service? Core concept analysis
Many product developers are confused at the beginning of a project: What is the difference between CNC prototyping and ordinary machining? Simply put, CNC prototyping service is a professional service that quickly converts design drawings into physical prototypes through computer numerical control (CNC) technology, and its core value lies in "quickly verifying design feasibility". The working principle is not complicated: the 3D model is first imported into the programming software to generate the machining path, and then the CNC machine cuts the material according to the instructions, resulting in a high-precision prototype.
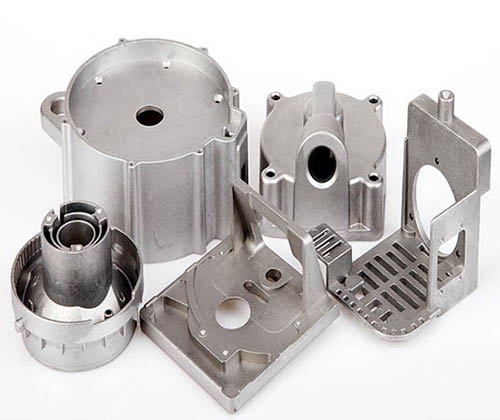
As the mainstream form of CNC machining prototypes, the biggest difference between them and traditional manual prototypes is that they have a high degree of automation, controllable precision, and repeatable production. A medical device company once shared a case study where they first used CNC technology to create three prototypes and completed the assembly test in just 5 days, which is 80% shorter than manual manufacturing. The core advantage of rapid prototype CNC machining is that it allows R&D teams to detect design flaws before mass production, avoiding large-scale rework later.
The complete CNC machining process typically includes: drawing review→ material selection→ programming→ on-machining→ post-processing→ and quality inspection, each of which directly impacts the accuracy and delivery efficiency of the prototype. For startups, the value of prototyping services is even greater – samples close to production standards can be obtained quickly without the need for expensive equipment.
2. Core Advantages of CNC Prototype Services, Which Industries Will Benefit the Most?
1. Three irreplaceable advantages
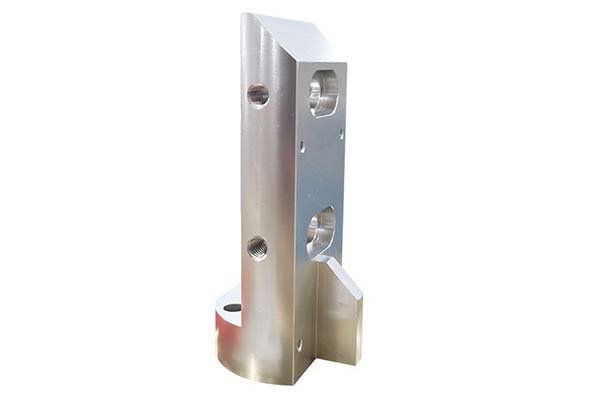
- High-Precision Prototyping: This is the core competence of CNC prototypes. Through five-axis parallel machining, the tolerance can be controlled within ±0.05mm, and the surface finish is below Ra0.8μm, which far exceeds the prototype accuracy of 3D printing.
- Multifunctional Material CNC Machining: Whether it's metal materials like aluminum alloys and stainless steel, or engineering plastics like ABS and PEEK, it can be stably processed to meet the performance needs of different scenarios.
- Compatible with small batch production: From 1 prototype to 500 small batch production, CNC machining does not require additional mold opening, and the cost advantage is obvious, especially suitable for the product trial production stage.
2. Four core application areas
- Automotive prototype CNC service: For functional testing of engine parts and interior parts, a car company used CNC prototypes to verify the gearbox gear design, shortening the R&D cycle by 3 months.
- Aerospace Prototyping: Prototypes of difficult-to-machine materials such as titanium alloys and superalloys must rely on CNC precision machining and meet AS9100 industry certification standards.
- Consumer electronics prototypes: Structural parts such as mobile phone frames and drone shells can be quickly iterated through CNC machining to match the market rhythm.
- Medical Device CNC Prototypes: Surgical instruments and implant prototypes require ISO13485 certification, and CNC machining's biocompatible material handling capabilities are key.
3. How to choose materials and processes? Professional selection guide
1. Comparison table of mainstream materials
| Material type | Representative material | Applicable scenarios | Processing difficulty | Cost tier |
| Metallic materials | 6061 Aluminum Alloy | Structural parts, shell | ★★☆☆☆ | medium |
| 304 stainless steel | High-strength parts | ★★★☆☆ | Middle and high | |
| Titanium alloy | aviation, medical | ★★★★★ | high | |
| Plastic material | ABS | Universal case | ★☆☆☆☆ | low |
| PEEK | High temperature resistant parts | ★★★☆☆ | high | |
| Nylon 30% GF | Structural supports | ★★☆☆☆ | medium |
2. Analysis of core processing processes
- 5-axis CNC machining: Suitable for complex surfaces, polyhedral prototypes, such as aero engine blades, with more than 40% higher machining efficiency than 3-axis machines.
- Precision Milling Prototypes: For flat and grooved structures, the minimum feature size can reach 1mm, making it the preferred process for consumer electronics prototypes.
- CNC Turning Services: Specialized in handling cylindrical parts, such as shaft and sleeve prototypes, with machining tolerances as low as ±0.01mm.
The case of a new energy company is very informative: when they developed charging pile connectors, they initially chose 3D printing prototypes, but the strength was insufficient; After switching to aluminum alloy CNC prototypes, it not only passed the plug-and-remove test but also reduced the machining time by 20%. This shows that the selection of CNC machining materials must be based on product function requirements, rather than simply pursuing low cost.
4. Complete process and time period, avoid stepping on pit guidelines
1. Standard service process
- Requirements Communication: Clarify the prototype's purpose, precision requirements, materials, and delivery time
- Drawing optimization: The service provider provides prototype design optimization suggestions (DFM analysis) to reduce the difficulty of processing
- Quick Quote for CNC Services: The professional service provider should provide a detailed quotation within 24 hours, detailing the material cost, machine time, etc
- Processing and production: Arrange equipment according to complexity, small batch orders can be processed in parallel
- Post-treatment: including surface treatments such as deburring, anodizing, and painting
- Quality inspection and delivery: Provide coordinate measurement reports to ensure compliance with drawing requirements
2. Time period reference
| Project type | Typical cycle | Fastest delivery | Influencing factors |
| Simple parts (single process) | 3-5 days | 2 days | Material inventory, equipment load |
| Complex Parts (Multi-Process) | 7-12 days | 5 days | process complexity and post-processing requirements |
| Low-Volume CNC Prototypes (within 100 pieces) | 10-20 days | 8 days | Batch size, whether mold assistance is required |
It's important to note that faster CNC prototype delivery is not always better, and excessive compression cycles can lead to reduced accuracy. It's recommended to allow a buffer period of 1-2 days for unexpected issues.
5. How to Choose a Reliable CNC Prototype Supplier? 5 Evaluation Dimensions
1. Technical hard power
Focus on equipment configuration (whether there is a five-axis machine tool, coordinate measuring instrument), processing capacity (maximum processing size, minimum tolerance) and industry certification (ISO9001, IATF16949, etc.). An auto parts company once delayed the project schedule by 3 months due to the deviation of the prototype size due to the selection of an uncertified service provider.
2. Quality control system
A reliable service provider should have an independent quality inspection department and be able to provide a complete shipment inspection report. Ask "whether it supports full-size testing" and "non-conforming product handling process" to quickly judge its professionalism.
3. Responsiveness and delivery capabilities
The advantages of local CNC machining services are convenient communication, fast logistics, and suitable for urgent orders; while international CNC prototype suppliers may have more advantages in material selection and mass production. It is recommended to give preference to service providers with quotation response times ≤ 24 hours and on-time delivery rates ≥ 95%.
4. Service support level
A high-quality service provider is not only a processor but also a technical partner. For example, DFM analysis is provided during the design stage to help optimize the structure to reduce costs. A startup shared that the initial processing cost of their product prototype was high, and the service provider suggested adjusting the rounded corner design, which directly reduced the cost by 30%.
5. Cost transparency
Beware of low price traps! Formal quotations should include material costs, machine time costs, labor post-processing fees and reasonable profits, rather than just quoting a single price. It is recommended to choose a service provider that can provide tiered quotations (the larger the batch, the lower the unit price).
6. How to choose a CNC prototype compared to other technologies?
| Types of technology | Accuracy level | Material compatibility | Cost (Small Batch) | Applicable scenarios |
| CNC machining | ★★★★★ | ★★★★★ | ★★★☆☆ | High-precision, high-strength prototypes for low-volume production |
| 3D printing | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★☆☆☆ | Proof of concept, complex structures (no strength requirements) |
| Fast injection molding | ★★★★☆ | ★★★☆☆ | ★★★★☆ | High-volume prototypes (500 pieces or more) |
In simple terms: if high-intensity prototype selection or near-mass production samples are required, CNC is preferred; If it's an initial proof-of-concept, 3D printing is more cost-effective; With larger batches, the cost gap between CNC vs rapid injection molding narrows and can be decided based on the lead time. The practice of a home appliance company shows that 3D printing for proof of concept in the early stage of product development, CNC for functional testing in the middle stage, and rapid injection molding for small-batch trial production in the later stage can minimize R&D costs.
Yigu Technology Perspective
The core value of CNC prototyping services lies in "rapid iteration + precise verification", which is the key bridge between design and mass production. With the acceleration of the digital transformation of the manufacturing industry, technologies such as five-axis machining and intelligent programming will further improve service efficiency, while material innovation will continue to expand application scenarios. For enterprises, choosing a service provider should not only look at price, but also pay attention to technology matching, quality stability and service response speed - high-quality partners can help you shorten the R&D cycle, reduce trial and error costs, and seize opportunities in market competition. It is recommended to combine their own product characteristics and give priority to service providers with industry certifications and can provide one-stop services, so that prototype development is more efficient and reliable.
FAQ
- What is the difference between CNC prototypes and mass-produced products?
A: The core difference is in production efficiency and cost structure, prototype processing does not need to open the mold, suitable for small batches; Mass production will optimize process parameters and use mold assistance to reduce unit cost, but the upfront investment is higher.
- How to Control CNC Machining Costs for Prototypes?
Answer: Optimizing design (reducing complex surfaces, unifying tolerance requirements), rational selection of materials (avoiding excessive pursuit of high performance), and batch combined processing can effectively reduce costs.
- How to choose between foreign service providers and local service providers?
Answer: Urgent orders and projects that require frequent communication and adjustment are selected locally; If the material is special, the batch size is large or there is a need for international certification, you can consider an international service provider and pay attention to reserving logistics time.
- What is the maximum machining size limit for CNC prototypes?
A: The maximum processing size of conventional three-axis machine tools is about 1800×1000×500mm, and five-axis machine tools are about 1000×900×600mm.
- What Situations Are Not Appropriate with CNC Prototypes?
A: CNC is not recommended for ultra-complex internal structures (which cannot be machined by tools), very small-scale proof-of-concept (3D printing is more cost-effective), and prototypes that require special materials (such as ceramics).