Understanding 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a revolutionary technology that has been transforming various industries in recent years. At its core, 3D printing works by building three - dimensional objects layer by layer from a digital file. This is in contrast to traditional manufacturing methods, which often rely on subtractive processes like cutting, milling, or casting.
The Working Principle of 3D Printing
The process starts with creating a 3D model using computer - aided design (CAD) software or by scanning an existing object. This digital model serves as the blueprint for the final product. Once the model is ready, it is sliced into thin cross - sectional layers by specialized software. These layers are then fed into the 3D printer, which deposits materials such as plastics, metals, ceramics, or even biological materials in precise patterns according to the layer information. As the layers are stacked one on top of another, the 3D object gradually takes shape.
Comparison with Traditional Manufacturing
| Comparison Items | Traditional Manufacturing | 3D Printing |
| Production Method | Subtractive (removing material from a larger block) | Additive (building up material layer by layer) |
| Complexity of Design | Limited by manufacturing processes, complex designs are often difficult and costly to produce | Allows for highly complex geometries without significant additional cost |
| Material Waste | High, as a large amount of material is removed during the manufacturing process | Low, as material is only used where needed |
| Production Volume Suitability | More suitable for mass production with lower unit costs | Ideal for small - batch production, rapid prototyping, and customized products |
| Tooling and Setup | Requires extensive tooling and setup, which can be time - consuming and expensive | Little to no tooling required, reducing setup time and cost |
For example, in traditional injection molding, creating a mold for a complex part can take weeks and cost thousands of dollars. In contrast, a 3D printer can start producing a similar complex part within hours, with no need for a mold. The ability to create complex internal structures and lattice patterns in 3D printing is also a game - changer. These structures can reduce the weight of a component while maintaining its strength, something that is nearly impossible to achieve with traditional manufacturing techniques. In the aerospace industry, for instance, 3D - printed parts with optimized internal structures have helped to reduce the weight of aircraft components, leading to better fuel efficiency.
Different Ways to Get 3D Printed Parts
Now that you have a basic understanding of 3D printing technology, let's explore the different ways to obtain 3D printed parts.
DIY with Your Own 3D Printer
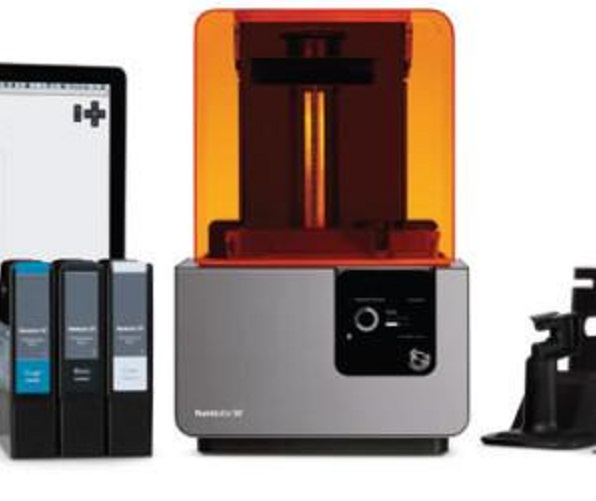
Investing in your own 3D printer can be a great option if you have regular 3D printing needs or want to experiment with the technology. There are several types of 3D printers available on the market, each with its own characteristics, suitable scenarios, and costs.
Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM) Printers
- Characteristics: FDM printers are the most common type for home and small - business use. They work by melting a thermoplastic filament, such as PLA (polylactic acid) or ABS (acrylonitrile butadiene styrene), and extruding it layer by layer to build the 3D object. They are relatively easy to use and have a wide range of available filaments in different colors and materials.
- Suitable Scenarios: Ideal for creating prototypes, small - scale production of simple parts, and educational purposes. For example, if you are a hobbyist who wants to print small figurines or a teacher demonstrating 3D printing concepts in a classroom, an FDM printer would be a good choice.
- Cost:
- Purchase: The price of FDM printers can range from as low as \(200 for entry - level models to over \)1000 for more advanced, high - precision ones.
- Maintenance: Maintenance costs are relatively low. You may need to replace parts like the nozzle occasionally, which usually costs around \(10 - \)50 depending on the quality and type.
- Consumables: Filaments typically cost between \(20 - \)50 per kilogram, depending on the material.
Stereolithography (SLA) Printers
- Characteristics: SLA printers use a laser to cure a photosensitive resin layer by layer, resulting in high - precision prints with smooth surfaces. They can produce more detailed and complex models compared to FDM printers.
- Suitable Scenarios: SLA printers are popular in jewelry making, dental applications, and the production of highly detailed prototypes. For instance, jewelry designers can use SLA printers to create intricate wax - like models for casting.
- Cost:
- Purchase: SLA printers are generally more expensive, with prices starting from around $1000 and going up to several thousand dollars for professional - grade models.
- Maintenance: Maintenance may involve replacing the resin tank and the laser module over time. The resin tank can cost around \(50 - \)200, and the laser module replacement can be more costly, up to several hundred dollars.
- Consumables: Resin is more expensive than FDM filaments, usually costing around \(50 - \)150 per liter.
Outsourcing to Professional 3D Printing Services
Outsourcing your 3D printing tasks to professional services can offer several advantages. These services often have a wide range of high - end 3D printers, access to various materials, and professional technical support.
| Service Provider | Price Range per Cubic Centimeter (Approx.) | Service Quality | Delivery Time |
| Service A | \(0.5 - \)2 | High - quality prints, with strict quality control and good post - processing options | 3 - 7 working days for standard orders, 1 - 3 days for expedited |
| Service B | \(0.3 - \)1.5 | Average quality, with basic post - processing. Good for simple and cost - effective prints | 5 - 10 working days |
| Service C | \(1 - \)3 | High - end quality, specialized in complex and high - precision prints. Offers a wide range of materials | 2 - 6 working days, depending on the complexity |
They can provide a broader selection of materials, including high - performance plastics, metals, and ceramics, which may not be accessible to individual users. For example, if you need a 3D - printed part made of titanium for an aerospace application, a professional service is more likely to have the equipment and expertise to handle the job. Professional 3D printing services also have the advantage of high - precision equipment. Their printers are often calibrated and maintained to ensure consistent and accurate results, which is crucial for industrial and engineering applications.
Buying Pre - Printed 3D Parts
Buying pre - printed 3D parts can be a convenient option, especially if you need a part quickly or don't have the time or resources to print it yourself. There are various types of pre - printed 3D parts available in the market, such as replacement parts for electronics, toys, and hobbyist items. For example, some companies sell pre - printed replacement gears for 3D printers or small robotic components.
However, the quality of pre - printed 3D parts can vary greatly. This is mainly due to differences in the 3D printers used, the materials, and the post - processing techniques. To 辨别 the quality of pre - printed parts, you can look at the surface finish. A smooth surface without visible layer lines usually indicates a higher - quality print. You can also check for any signs of warping or distortion in the part. Additionally, reading reviews from other customers who have purchased the same part can give you an idea of its quality and performance.
.
Yigu Technology's View
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom Supplier, Yigu Technology deeply understands the significance of 3D printed parts in modern manufacturing. We have a rich - experience in handling various materials for non - standard products, which also benefits our understanding of 3D printing materials.
When it comes to getting 3D printed parts, we emphasize the importance of precise material handling. For plastics and metals used in 3D printing, we have strict quality - control processes. We know that different applications demand specific material properties, and we can guide customers to make the right material choices.
In terms of the manufacturing process, our team of experts pays close attention to every detail in 3D printing. We ensure that the printing parameters are optimized to achieve high - quality and precise parts. Whether it's a complex plastic part or a high - strength metal component, we strive to meet and exceed customer expectations.
We also focus on understanding our customers' needs comprehensively. By working closely with clients, we can provide customized solutions for getting 3D printed parts, whether it's through in - house 3D printing capabilities or outsourcing to reliable partners. Our goal is to offer cost - effective, high - quality, and timely solutions to help our customers succeed in their projects.