Introduction to 3D Printing in Automotive
The automotive industry has always been quick to adopt cutting-edge technologies, and 3D printing is no exception. This transformative manufacturing process has significantly impacted how car models are designed and produced, from rapid prototyping to creating customized parts and end-use components. By utilizing 3D printing, manufacturers can create complex parts with high precision, reduce material waste, and shorten development cycles. This article explores the history, benefits, applications, and challenges of 3D printing in the automotive sector, showcasing its potential to revolutionize the industry.
Overview of 3D Printing Technology
3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, is a process where objects are created by building up layers of material based on digital files. Unlike traditional subtractive manufacturing, which involves cutting away material from a larger block, 3D printing creates parts layer by layer. This allows for the production of intricate designs and geometries that would be difficult or prohibitively expensive with conventional techniques.
Several types of 3D printing technologies are used in automotive applications, including:
- Fused Deposition Modeling (FDM): Popular for prototyping and low-volume production, FDM works by extruding thermoplastic material.
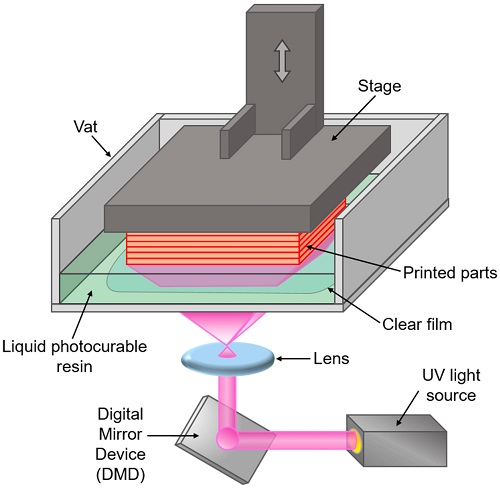
- Stereolithography (SLA): Known for its high precision and smooth surface finish, SLA uses a UV laser to cure liquid resin.
- Selective Laser Sintering (SLS): Suitable for producing durable parts, SLS uses a laser to fuse powdered material.
- Metal 3D Printing: A growing technology for producing strong, functional metal parts for the automotive industry.
Each of these methods offers unique advantages, depending on the type of part being produced and the material requirements.
History of 3D Printing in Cars
3D printing's integration into the automotive industry began in the late 20th century, when it was primarily used for rapid prototyping. Early adopters recognized the ability of additive manufacturing to reduce lead times and costs associated with traditional prototype creation. Over the years, this technology evolved, leading to its broader adoption in both prototyping and manufacturing processes.
A key milestone in the automotive use of 3D printing occurred in 2014, when Local Motors introduced the Strati, the world's first 3D-printed car. This full-scale prototype demonstrated that 3D printing could be used for the production of entire vehicles, signaling a significant shift toward more innovative, efficient, and customizable car manufacturing processes.
Benefits of 3D Printed Car Models
Cost Efficiency
One of the most significant advantages of 3D printing in the automotive industry is its cost efficiency. Traditional manufacturing methods often require expensive molds and tooling, which can be cost-prohibitive for small production runs. 3D printing eliminates these costs by directly producing parts from digital files. This capability makes it ideal for prototyping, custom components, and low-volume production.
Additionally, 3D printing reduces material waste by using only the amount of material needed to create each part, unlike subtractive methods where excess material is discarded. This leads to reduced overall production costs.
Time Reduction in Prototyping
Time is a critical factor in the automotive industry, where getting products to market quickly is essential for staying competitive. 3D printing accelerates the prototyping process by enabling rapid creation of parts that can be quickly tested and iterated upon. This ability to quickly produce and refine prototypes significantly shortens development cycles, helping manufacturers respond more quickly to market demands and consumer preferences.
Material Efficiency
3D printing optimizes material usage by building parts layer by layer, which minimizes waste. This is particularly important in the automotive industry, where reducing vehicle weight is crucial for improving fuel efficiency and meeting sustainability goals. By using lightweight materials and optimizing designs through 3D printing, manufacturers can enhance vehicle performance and contribute to lower emissions.
Applications of 3D Printing in Car Manufacturing
Prototyping Complex Components
Prototyping remains one of the most common uses for 3D printing in the automotive industry. Designers can create highly detailed prototypes of complex components, such as engine parts, interior elements, and body panels. These prototypes allow for functional testing, design validation, and the ability to showcase new features to customers before full-scale production.
Customization of Car Models
Customization is another key area where 3D printing excels. Traditional manufacturing methods make car customization a costly and time-consuming process. However, with 3D printing, manufacturers can easily produce bespoke parts and components tailored to individual customer preferences. This allows for highly personalized vehicles, from aesthetic customizations like personalized dashboards to functional modifications, such as performance-enhancing components.
Production of End-Use Parts
While 3D printing is traditionally associated with prototyping, it is increasingly being used for end-use parts production. Advances in 3D printing technology and materials have made it possible to create functional components that meet the rigorous standards of the automotive industry. Components such as interior trims, brackets, structural elements, and even entire body panels are now being produced using 3D printing, particularly for low-volume production runs or for cars with highly specialized parts.
Challenges and Limitations
Material Strength and Durability
One of the major challenges of using 3D printing in the automotive industry is ensuring that printed parts have the necessary strength and durability. While there have been significant advancements in the development of strong materials for 3D printing, many additively manufactured parts still don't match the mechanical properties of parts made with traditional methods, particularly for components that must withstand heavy loads or extreme conditions.
Scalability of 3D Printing Processes
While 3D printing is excellent for prototyping and small-batch production, scaling the process for large-scale manufacturing remains a challenge. The logistics and economics of using 3D printers for mass production are complex, especially when high volumes of parts are required. To address this, some manufacturers are exploring hybrid manufacturing models that combine 3D printing with traditional production methods, taking advantage of the benefits of both approaches.
Regulatory and Safety Standards
Safety and regulatory compliance are critical in the automotive industry. For 3D-printed parts to be used in vehicles, they must meet stringent safety standards. This requires extensive testing and certification, which can be time-consuming and costly. The industry is working to establish standardized protocols for 3D-printed parts to ensure they meet the required safety and performance criteria.
Conclusion
3D printing is revolutionizing the creation of car models by providing unprecedented levels of customization, cost efficiency, and rapid prototyping capabilities. While there are challenges, such as material strength, scalability, and regulatory compliance, ongoing advancements in technology and materials science are enabling more widespread use of 3D printing in the automotive industry. As manufacturers continue to explore the potential of this technology, we can expect to see even more innovative and efficient vehicles in the future.
FAQs
What are the primary benefits of 3D printing in car model creation?
The main benefits of 3D printing in car model creation include cost efficiency, reduced prototyping time, material efficiency, and enhanced customization options. 3D printing allows for faster iteration, reducing the need for expensive molds and tooling, while minimizing material waste.
How does 3D printing impact the development cycle of car models?
3D printing accelerates the development cycle by enabling faster prototyping and iteration. Designers can quickly test multiple design variations, leading to faster refinement and faster market entry. This helps manufacturers stay competitive by responding to market demands more swiftly.
Are there any limitations to using 3D printing for car model creation?
Yes, there are limitations. These include challenges related to material strength and durability, scalability for mass production, and ensuring that parts comply with safety and regulatory standards. Despite these challenges, the potential of 3D printing to revolutionize automotive manufacturing remains significant.