Introduction
What is Medical Device Plastic Injection Moulding?
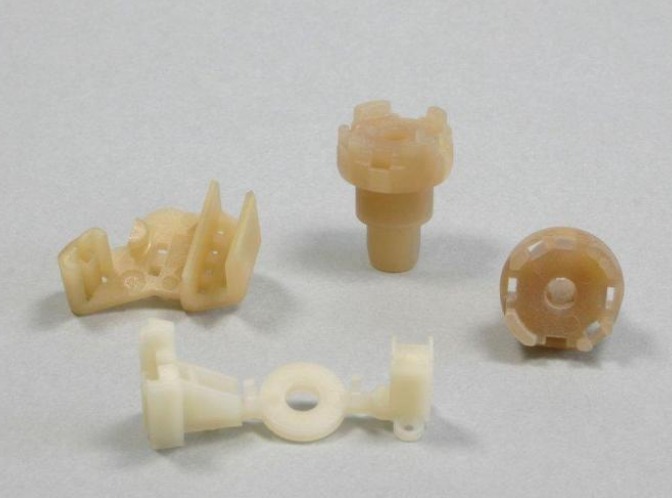
Medical Device Plastic Injection Moulding is a manufacturing process that plays a pivotal role in the production of various medical components. At its core, it involves injecting molten plastic material into a precisely designed metal mold cavity. The process begins with the selection of the appropriate plastic resin, which is carefully chosen based on its compatibility with medical applications, considering factors such as biocompatibility, chemical resistance, and mechanical properties. For example, materials like polycarbonate (PC) and acrylonitrile butadiene styrene (ABS) are popular choices due to their excellent strength - to - weight ratio and resistance to sterilization methods such as autoclaving and gamma irradiation.
Once the plastic resin is selected, it is fed into an injection molding machine. The machine heats the resin until it reaches a molten state. A high - pressure screw then forces this molten plastic into the closed mold cavity, which has been intricately designed to match the exact shape of the desired medical device part. The plastic fills every nook and cranny of the mold, taking on its form. After the cavity is filled, the plastic is allowed to cool and solidify under controlled conditions. Once solid, the mold opens, and the newly formed plastic part is ejected. This process allows for the production of highly complex and precise medical components with tight tolerances, often in the range of ±0.05mm or even less, depending on the requirements of the medical device.
The Process Unveiled
Step - by - Step Guide
- Material Preparation:
- First and foremost, the selection of the plastic material is crucial. As mentioned before, materials like PC, ABS, and polypropylene (PP) are commonly used in medical device production. The plastic comes in pellet form. These pellets are then often pre - dried to remove any moisture. Moisture in the plastic can cause defects such as bubbles and voids in the final product. For example, if a medical device component is being made from ABS, it may need to be dried at around 80 - 90°C for 2 - 4 hours in a desiccant dryer.
- Mold Manufacturing:
- The mold is the heart of the injection molding process. High - quality steel is typically used to manufacture molds for medical device components due to its durability and ability to maintain precision. The mold is designed using computer - aided design (CAD) software, which allows for highly detailed and accurate design. For instance, if creating a mold for a complex catheter tip, the CAD design can precisely define the intricate shape, including any channels or grooves required for fluid flow. After the design is complete, the mold is machined using computer - numerically controlled (CNC) machines. These machines can achieve extremely tight tolerances, often within the range of ±0.01mm for medical - grade molds.
- Injection:
- The dried plastic pellets are fed into the hopper of the injection molding machine. Inside the machine, a heated barrel melts the plastic to a molten state. The temperature of the barrel is carefully controlled based on the type of plastic. For example, PP has a melting temperature range of 160 - 170°C, while PC melts at around 220 - 240°C. Once molten, a screw - type plunger injects the plastic into the closed mold cavity at high pressure. The injection pressure can range from 50 - 200 MPa, depending on the complexity of the part and the plastic material used. High - pressure injection ensures that the molten plastic fills every detail of the mold cavity.
- Cooling:
- After the mold cavity is filled, the plastic needs to cool and solidify. Cooling channels are integrated into the mold design. These channels carry a coolant, usually water or a water - glycol mixture, to remove heat from the plastic. The cooling time is a critical factor as it affects the cycle time of the injection molding process and the quality of the final product. For small medical device components, the cooling time can be as short as 10 - 30 seconds, while larger or more complex parts may require several minutes to cool properly.
- Ejection:
- Once the plastic has cooled and solidified, the mold opens. Ejector pins, which are part of the mold, push the finished part out of the mold cavity. The ejector pins are strategically placed to ensure that the part is ejected smoothly without causing any damage. For example, in the case of a syringe barrel, the ejector pins may be placed evenly around the perimeter of the barrel to ensure uniform ejection.
Key Equipment and Their Roles
- Injection Molding Machine:
- The injection molding machine is the primary piece of equipment in the process. It has several key functions. First, it melts the plastic pellets through the heated barrel. The heating system in the barrel can be precisely controlled to maintain the optimal temperature for the plastic material. Second, it injects the molten plastic into the mold cavity with high pressure. The injection system, which includes the screw - type plunger, can adjust the injection speed and pressure according to the requirements of the part. For example, for a thin - walled medical device component, a faster injection speed may be required to ensure proper filling of the mold cavity.
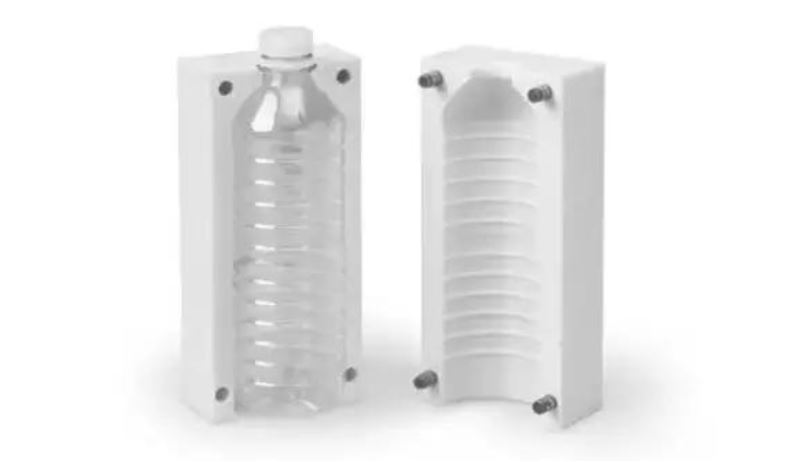
- Mold:
- As previously stated, the mold determines the shape of the final product. It consists of two halves, the stationary half (which is attached to the fixed platen of the injection molding machine) and the moving half (attached to the movable platen). The mold cavities and cores are the parts that define the shape of the medical device component. For example, in a mold for a medical connector, the cavities and cores will be designed to create the exact shape of the connector, including any mating features and internal channels. The mold also contains the cooling channels and the ejection system, which are essential for the successful production of the part.
- Auxiliary Equipment:
- Dryers: As mentioned, dryers are used to remove moisture from the plastic pellets before they are fed into the injection molding machine. This helps to prevent defects in the final product.
- Chillers: Chillers are used to cool the coolant that flows through the cooling channels in the mold. They ensure that the coolant remains at a consistent temperature, which is crucial for uniform cooling of the plastic part. For example, in a high - volume production of medical device components, a chiller can maintain the coolant temperature within ±1°C.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
Yigu Technology, as a non - standard plastic metal products custom supplier, has a unique perspective on Medical Device Plastic Injection Moulding. With our professional technical expertise and rich experience in the field, we understand the critical requirements of the medical device industry.
We are committed to providing one - stop services, starting from the initial design stage. Our design team, equipped with advanced CAD/CAM software, can work closely with clients to create customized mold designs that meet the most intricate requirements of medical devices. For example, when designing molds for complex surgical instrument components, we take into account factors such as ergonomics and sterilization - friendliness.
During the production process, we use high - quality materials and state - of - the - art injection molding equipment. Our strict quality control system ensures that every product we produce adheres to the strict medical standards, such as ISO 13485. We also offer post - production services like surface treatment and assembly, which can help our clients save time and resources. In a nutshell, we strive to be a reliable partner for medical device manufacturers, contributing to the development of the healthcare industry through our high - quality products and services.
FAQ
What types of plastics are most suitable for medical device injection moulding?
Several plastics are highly suitable for medical device injection moulding. ABS (Acrylonitrile Butadiene Styrene) offers good impact resistance, dimensional stability, and is easy to color, making it useful for medical device housings and some non - critical components. PC (Polycarbonate) has excellent strength, high heat resistance, and optical clarity, which is ideal for applications like medical lenses and transparent parts of diagnostic equipment. PP (Polypropylene) is lightweight, has good chemical resistance, and is biocompatible, often used in syringes, medical containers, and disposable medical products. PEEK (Polyether Ether Ketone) is a high - performance polymer with outstanding mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and can withstand high - temperature sterilization, making it suitable for implantable devices and high - stress medical components.
How can I ensure the quality of injection - moulded medical devices?
To ensure the quality of injection - moulded medical devices, several steps can be taken. First, follow relevant standards such as ISO 13485, which is the international standard for quality management systems in the medical device industry. This standard helps in maintaining a systematic approach to quality. Second, implement a strict detection process, including regular visual inspections for surface defects like scratches or cracks, dimensional measurements to ensure the parts meet the design specifications (using tools like coordinate measuring machines), and material testing to verify the properties of the plastic used. Third, optimize the process control by carefully monitoring and adjusting parameters such as injection pressure, temperature, and cooling time during the injection moulding process.
What is the typical lead time for custom medical device plastic injection moulding?
The lead time for custom medical device plastic injection moulding is influenced by several factors. Mold making is a significant factor. If a new mold needs to be designed and fabricated, it can take anywhere from 4 - 8 weeks, depending on the complexity of the mold. Production quantity also matters. For small - batch production (less than 1000 units), the production time might be around 1 - 2 weeks. For large - scale production (10,000 units or more), it could take 3 - 6 weeks or longer. Overall, the typical lead time for custom medical device plastic injection moulding, from the initial order to delivery, can range from 6 - 12 weeks.