Introduction
In the vast and dynamic realm of the food industry, Food Packaging Moulds stand as the unsung heroes, playing a pivotal role that goes far beyond mere containment. These moulds are the architects behind the physical form of food packaging, dictating not only how our favorite edibles are presented but also safeguarding their quality, freshness, and safety from the production line to our tables.
Think about the last time you picked up a yogurt cup, a cereal box, or a chocolate wrapper. The shape, size, and functionality of these packages were all meticulously crafted through the use of specialized moulds. From the simple yet efficient design of a plastic food container to the intricate and eye - catching contours of a premium confectionery package, food packaging moulds are the tools that translate the concepts of food manufacturers and designers into tangible, market - ready products.
This article delves deep into the fascinating world of food packaging moulds, exploring the intricate balance between art and science that defines their creation and application. We will journey through the technological advancements that have revolutionized their production, the design principles that make them both functional and aesthetically appealing, and the crucial role they play in ensuring food safety and shelf - life extension. Whether you're a food industry professional looking to enhance your packaging game, an entrepreneur exploring new product packaging ideas, or simply a curious consumer interested in the behind - the - scenes of food packaging, this exploration will provide valuable insights into the molding future of the food packaging landscape.
The Scientific Side of Food Packaging Moulds
Material Selection
The choice of materials for food packaging moulds is a critical decision that can significantly impact the performance, cost, and environmental footprint of the final product. Common materials used in mould manufacturing include steel, aluminum, and various types of plastics. Each material comes with its own set of properties, as shown in the table below:
| Material | Strength | Durability | Cost | Thermal Conductivity | Machinability |
| Steel | High | High, resistant to wear and tear | High | Moderate | Good, but requires specialized tools |
| Aluminum | Moderate | Good, resistant to corrosion | Moderate | High | Excellent, easy to machine |
| Plastic (e.g., ABS, Polypropylene) | Varies (low - moderate) | Varies (depends on type) | Low | Low | Good, can be easily molded |
When selecting a material for food packaging moulds, several factors need to be considered. For high - volume production of simple - shaped packages, such as plastic bottles for beverages, plastic moulds might be a cost - effective choice due to their lower initial investment and ease of molding. However, if the packaging requires high precision and long - term durability, like moulds for metal cans used in the food canning industry, steel or aluminum would be more suitable. Additionally, the type of food being packaged also plays a role. For example, acidic foods may require materials that are highly resistant to corrosion, such as certain grades of stainless steel or corrosion - resistant plastics.
Precision Engineering
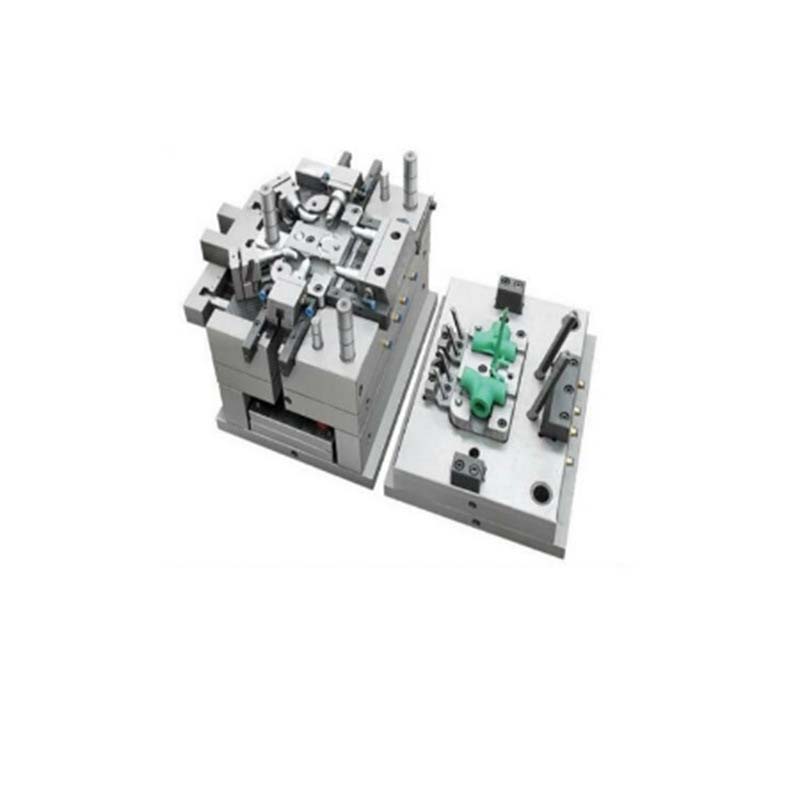
Precision is the name of the game when it comes to food packaging moulds. The manufacturing process demands extremely tight tolerances to ensure that each package produced is consistent in size, shape, and functionality. Even the slightest deviation in the mould's dimensions can lead to significant issues in the packaging process and the quality of the final product.
Tolerance control is crucial for several reasons. In terms of production efficiency, precise moulds minimize waste. If a mould has inconsistent dimensions, packages may not seal properly, leading to product spoilage or leakage. This not only results in financial losses but also potential damage to the brand's reputation. For example, in the production of blister packs for pharmaceutical products (which can be considered a form of food - adjacent packaging in terms of precision requirements), a deviation of just a few millimeters in the mould can prevent the tablets from fitting correctly, causing production delays and increased costs.
In the case of food packaging, precision also contributes to the overall aesthetics of the product. A well - crafted mould can create packaging with smooth edges, sharp corners, and consistent wall thickness, enhancing the visual appeal of the food item on the store shelves.
Functionality and Food Safety
Food packaging moulds are designed with multiple functions in mind, all of which are essential for protecting the food product, maintaining its freshness, and ensuring consumer convenience. One of the primary functions is protection. Moulds are designed to create packages that can withstand physical impacts during transportation and handling. For instance, the thick - walled plastic containers used for packaging yogurt are moulded in a way that they can resist being crushed, preventing leaks and spills.
Freshness preservation is another key function. Moulds can be designed to create packages with features like air - tight seals and moisture - resistant barriers. For example, the moulds used to make vacuum - sealed food bags ensure that oxygen is kept out, extending the shelf - life of products such as coffee beans or cured meats.
Ease of use is also a consideration in mould design. Moulds are crafted to create packages with features like easy - open tabs, pour spouts, or resealable closures. Think of the mould - made plastic containers with snap - on lids that are so commonly used for storing leftovers at home.
Food safety is non - negotiable in the design and production of food packaging moulds. The materials used in the moulds must comply with strict food - contact safety standards. For example, plastics used in food packaging moulds should be free from harmful chemicals such as bisphenol A (BPA), which has been linked to various health concerns. Additionally, the surface finish of the mould is important. A smooth surface finish on the mould helps prevent the accumulation of bacteria or food residues, which could potentially contaminate the food product. Special coatings or treatments may be applied to the mould surface to further enhance its food - safety properties, such as antimicrobial coatings in some moulds used for packaging fresh produce.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic and metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology deeply understands the significance of Food Packaging Moulds in the food industry. We take pride in our expertise in the design and manufacturing of moulds, which enables us to offer tailored solutions to meet the unique requirements of our clients.
Our team of experienced engineers and designers is well - versed in the latest technologies and trends in mould manufacturing. When it comes to food packaging moulds, we first focus on a comprehensive understanding of the client's product. Whether it's a new food product with specific shape and size requirements or a need to upgrade an existing packaging design, we collaborate closely with our clients from the initial concept stage.
We use advanced CAD/CAM software to create detailed 3D models of the moulds, allowing our clients to visualize the final product before production begins. This not only helps in ensuring that the design meets all the functional and aesthetic requirements but also minimizes the risk of errors during the manufacturing process.
In terms of materials, we have an in - depth knowledge of a wide range of options. We can recommend the most suitable materials based on factors such as the type of food, production volume, and cost - effectiveness. For example, if a client is packaging a high - end, heat - sensitive food product, we might suggest using a special grade of stainless steel for the mould due to its excellent heat resistance and food - contact safety properties.
Quality control is at the heart of our manufacturing process. We have a strict quality management system in place, with multiple inspection points throughout the production cycle. From the raw material inspection to the final mould testing, every step is carefully monitored to ensure that the moulds meet the highest quality standards. This attention to detail ensures that our clients receive moulds that are durable, precise, and capable of producing high - quality food packaging consistently.
In addition, we keep a close eye on emerging trends in the food packaging industry, such as the increasing demand for sustainable and eco - friendly packaging. We are constantly exploring new materials and manufacturing processes to help our clients meet these evolving market demands. Whether it's developing moulds for biodegradable plastic packaging or implementing energy - efficient manufacturing techniques, Yigu Technology is committed to providing innovative and sustainable solutions for food packaging moulds.
FAQ
What factors should be considered when choosing food packaging moulds?
When choosing food packaging moulds, several crucial factors need to be taken into account. Material is a primary consideration. You need to assess the strength, durability, cost, and thermal conductivity of materials like steel, aluminum, and plastics. For example, if you're producing large - volume, simple - shaped packages, plastics may be cost - effective, while high - precision and durable applications might require steel or aluminum. The design of the mould should match the functionality of the packaging, such as creating air - tight seals for freshness preservation or easy - open features for consumer convenience. Production scale also matters. High - volume production may benefit from more durable and efficient moulds, while small - scale production can be more flexible with cost - effective options. Cost includes not only the initial purchase price of the mould but also long - term costs like maintenance and replacement. Finally, food safety standards must be strictly adhered to. Ensure that the materials used in the moulds are non - toxic and comply with relevant food - contact regulations.
How can I ensure the quality of food packaging moulds?
To ensure the quality of food packaging moulds, first, choose a reliable supplier with a good reputation and experience in the industry. Check if the supplier has relevant certifications and qualifications, such as ISO certifications, which can indicate their commitment to quality management systems. Request sample testing and inspection before placing a large order. Examine the sample moulds for any defects, check the precision of the dimensions, and test their functionality. For example, if it's a mould for a plastic food container, test the seal tightness of the container produced by the sample mould. Additionally, establish a quality control system in your own production process. Conduct regular inspections during the production run using the moulds to detect any signs of wear, deformation, or other issues that could affect the quality of the packaging products.
Are there any environmental - friendly options for food packaging moulds?
Yes, there are several environmentally - friendly options for food packaging moulds. One option is to use biodegradable materials for moulds. For instance, moulds made from polylactic acid (PLA), which is derived from renewable resources like corn starch or sugarcane, can break down naturally over time. Another biodegradable material is polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), which also offers good performance in food packaging applications. Recyclable materials are also a great choice. Moulds made from metal, such as aluminum, are highly recyclable. Some plastics, like high - density polyethylene (HDPE) and polypropylene (PP), can also be recycled. In addition, consider the production process of the moulds. Look for suppliers that use energy - efficient production techniques to reduce the overall environmental impact. This can include using advanced manufacturing technologies that minimize waste and energy consumption during the mould - making process.