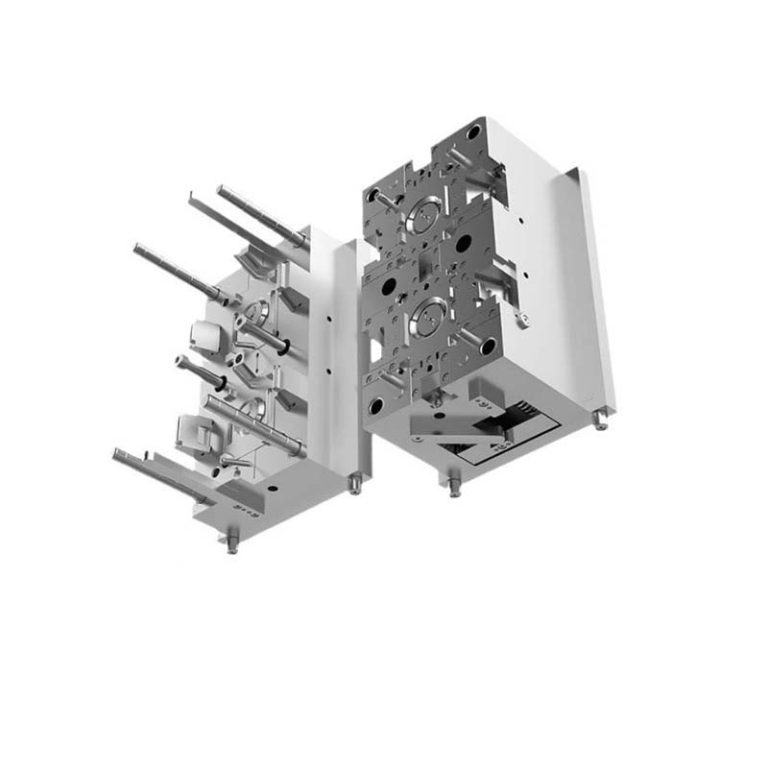
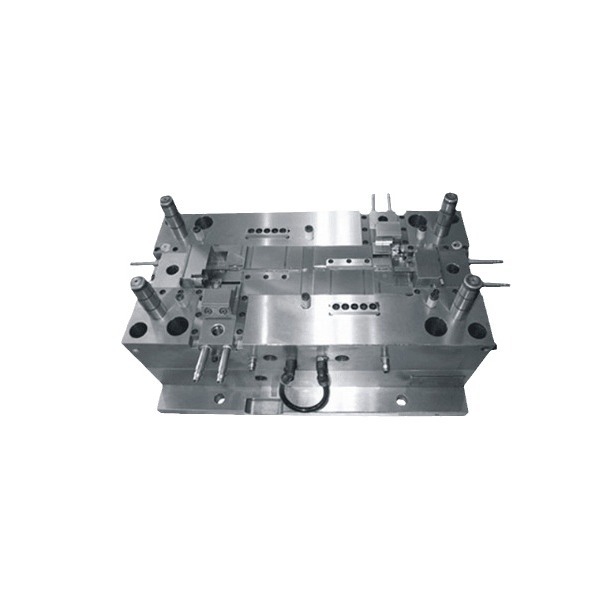
Understanding the Basics of Plastic Moulds
Plastic moulds are the unsung heroes of modern manufacturing, playing a pivotal role in shaping countless products we use in our daily lives. A plastic mould is a specialized tool used to form plastic materials into specific shapes and sizes through processes like injection moulding, blow moulding, and compression moulding.
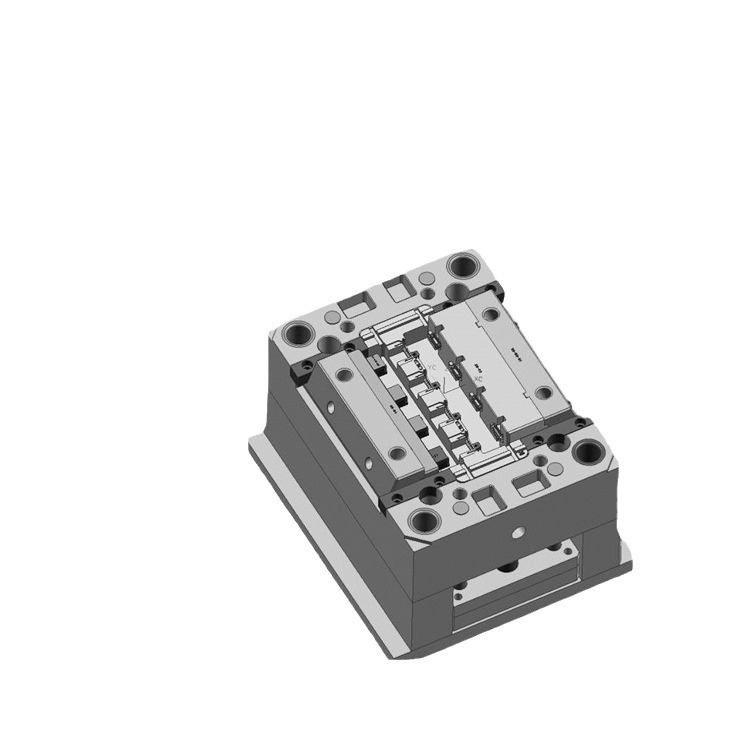
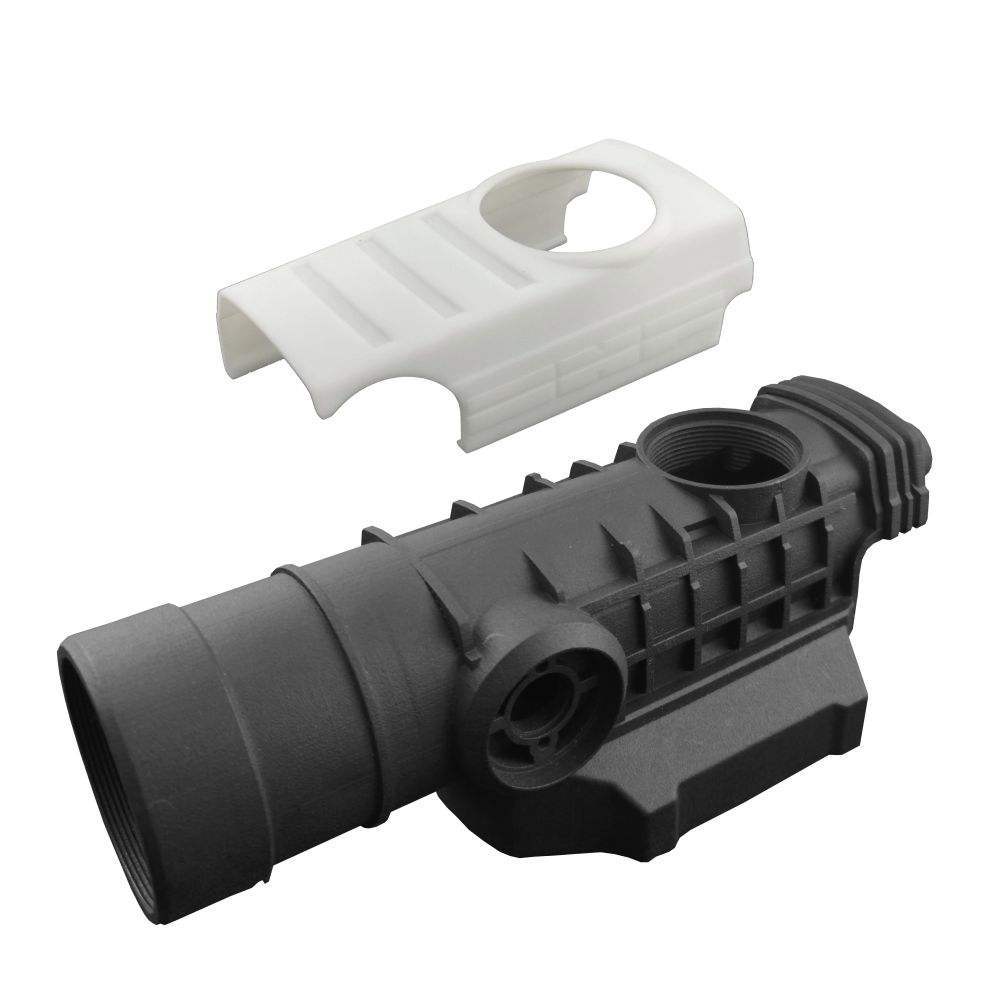
In injection moulding, molten plastic is injected into a mould cavity under high pressure. Once cooled, the plastic solidifies, taking on the precise shape of the mould. This process is incredibly efficient for producing high - volume, intricate plastic parts, such as those found in electronic devices, automotive interiors, and household appliances. For example, the outer casing of your smartphone is likely produced through injection moulding using a highly precise plastic mould.
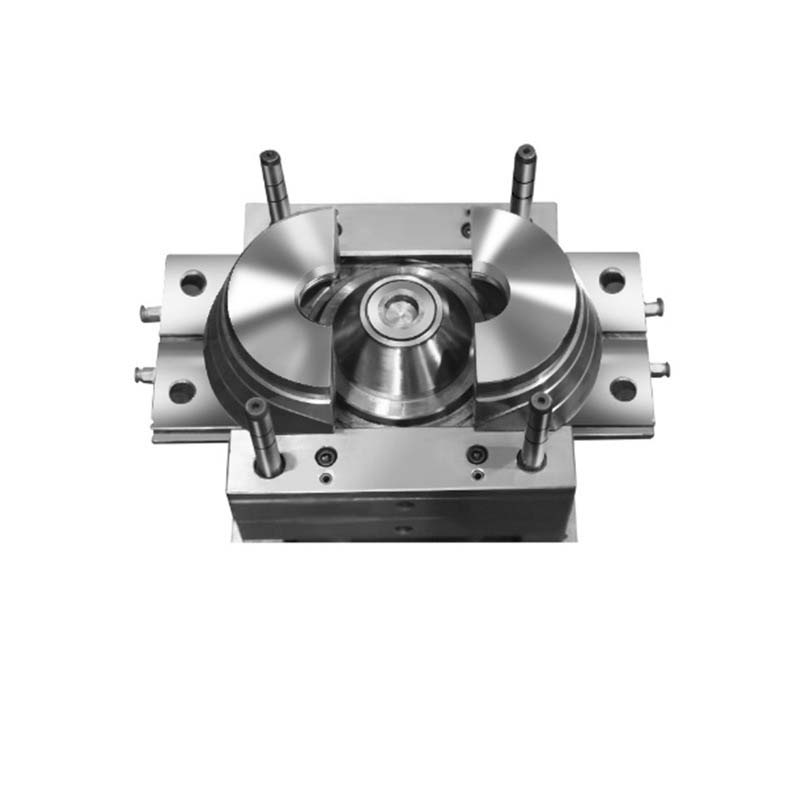
Blow moulding, on the other hand, is commonly used to create hollow plastic products like plastic bottles. A parison (a tube - like piece of molten plastic) is placed in a mould, and air is blown into it, forcing the plastic to expand and conform to the mould's shape. This method is ideal for producing containers with consistent wall thickness and smooth finishes.
Compression moulding involves placing pre - formed plastic material into a heated mould. Pressure is then applied, causing the plastic to flow and fill the mould cavity. This process is often used for manufacturing larger, more robust plastic components, such as the body panels of some furniture pieces.
The importance of plastic moulds in manufacturing cannot be overstated. They enable mass production with high precision and repeatability. A well - designed plastic mould can produce thousands, if not millions, of identical plastic parts with minimal variation. This not only ensures product quality but also reduces production costs per unit. In fact, in high - volume manufacturing, the cost savings achieved through efficient mould - based production can be in the tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars over the product's lifecycle. Additionally, plastic moulds allow for the creation of complex geometries that would be extremely difficult and costly to achieve through other manufacturing methods.
Types of Plastic Moulds and Their Advantages/Disadvantages
Injection Moulds
Injection moulds are among the most widely used types in the plastic manufacturing industry. One of the primary advantages of injection moulds is their high production efficiency. They can produce a large number of plastic parts in a relatively short time. For instance, in a typical injection - moulding factory, a well - maintained injection moulding machine equipped with a high - quality injection mould can produce hundreds of parts per hour. This makes them ideal for mass - production scenarios, such as manufacturing plastic toys, where millions of units may be required.
Injection moulds also offer high precision. The tolerance levels achievable with injection moulding are extremely tight, often within ±0.05mm. This high precision ensures that each plastic part produced is nearly identical, which is crucial for products that require a perfect fit, like the components of a complex electronic device.
However, injection moulds come with some significant disadvantages. The initial cost of an injection mould is relatively high. Designing and manufacturing a high - quality injection mould can cost anywhere from a few thousand to hundreds of thousands of dollars, depending on the complexity of the part and the materials used for the mould. Additionally, the tooling time for injection moulds can be long. It may take several weeks to months to design, test, and finalize an injection mould, which can delay the product launch if not planned properly.
Compression Moulds
Compression moulds are well - suited for working with thermosetting plastics. One of their main advantages is the relatively low cost of the mould itself. Compared to injection moulds, compression moulds generally require less complex tooling and manufacturing processes, which results in lower production costs. This makes them an attractive option for small - scale manufacturers or for products with lower production volume requirements.
Another benefit is that they can produce parts with good mechanical properties. Since the plastic material is compressed and cured in the mould, the resulting parts often have high density and strength, which is suitable for applications like manufacturing electrical insulators.
Nevertheless, compression moulds have their drawbacks. The production cycle for compression moulding is relatively long. Each cycle can take several minutes to complete, much longer than the cycle times in injection moulding. This slower production rate can limit the overall output, making it less suitable for high - volume production demands. Additionally, the surface finish of parts produced by compression moulding may not be as smooth as those made by injection moulding, which can be a concern for products where aesthetics are important.
Blow Moulds
Blow moulds are specifically designed for creating hollow plastic products, such as plastic bottles, containers, and toys. One of the key advantages of blow moulding is its ability to produce products with a consistent wall thickness. This is essential for ensuring the structural integrity and durability of the final product. For example, in the production of water bottles, a uniform wall thickness ensures that the bottle can withstand the internal pressure without bursting.
Blow moulding also allows for the creation of products with complex shapes and designs. With the right mould design, it is possible to produce unique - shaped containers that stand out on the shelves.
However, the equipment required for blow moulding, including the blow moulds themselves, can be quite costly. Setting up a blow - moulding production line involves a significant investment in machinery, moulds, and associated equipment. Additionally, the process has some limitations in terms of the materials that can be used compared to injection moulding and compression moulding, which may restrict its application in certain industries.
Key Factors to Consider When Buying Plastic Moulds
Material Quality
The quality of the materials used in plastic moulds is of utmost importance. The choice of steel for the mould can significantly impact its lifespan and the quality of the products it produces. For instance, high - quality alloy steels like P20, 718, and NAK80 are popular choices for plastic moulds. P20 steel, which contains chromium, nickel, and molybdenum, offers good machinability and polishing properties. It is suitable for moulds with a relatively short lifespan of around 300,000 - 500,000 shots. 718 steel, an upgraded version of P20, has better hardness and wear - resistance, making it ideal for moulds with a higher production volume, often used for up to 500,000 - 1,000,000 shots. NAK80 is a precipitation - hardening steel known for its excellent mirror polishing performance and dimensional stability. It is commonly used in moulds for products with high - gloss surface requirements, such as cosmetic packaging. Using low - quality materials can lead to premature wear and tear of the mould, resulting in frequent replacements. This not only increases costs but also disrupts the production schedule.
Precision and Tolerance
High - precision plastic moulds are crucial for manufacturing products with tight tolerances. The precision of a mould determines how accurately the final plastic product will match its design specifications. In industries like electronics, where components need to fit together perfectly, the tolerance levels can be as low as ±0.01mm. A high - precision mould ensures that each part produced has consistent dimensions. This is vital for the proper functioning of the final product. For example, in the production of connectors for electronic devices, a small deviation in the mould's precision can lead to a poor fit between the connector and the device, causing issues such as signal loss or connection failures. High - precision moulds also contribute to better product aesthetics. When producing items like plastic furniture or decorative items, the smooth and accurate surfaces achieved through high - precision moulds enhance the overall appearance and marketability of the product.
Durability
Durability is another key factor when purchasing plastic moulds. A durable mould can withstand the rigors of continuous production over an extended period, reducing the need for frequent replacements. Moulds that are made from high - quality materials and have a sound design are more likely to be durable. For example, moulds with proper heat - treatment and surface - hardening processes can resist wear and tear better. The durability of a mould is directly related to maintenance costs and production efficiency. A non - durable mould may require frequent repairs, which can be time - consuming and costly. Each time a mould is taken out of production for repair, it results in downtime, reducing the overall production output. In contrast, a durable mould can operate continuously with minimal maintenance, ensuring high - volume production and lower production costs per unit over the long term.
Cost - Initial and Long - Term
When buying plastic moulds, it's essential to consider both the initial purchase cost and the long - term costs. The initial cost of a plastic mould can vary widely depending on factors such as its complexity, size, and the materials used. For example, a simple two - plate injection mould for a small plastic part may cost a few thousand dollars, while a complex multi - cavity mould with intricate features and high - precision requirements can cost hundreds of thousands of dollars.
However, focusing solely on the initial cost can be a costly mistake. Long - term costs include maintenance, repairs, and replacements. A cheaper mould may require more frequent maintenance and replacement, which can add up significantly over time. On the other hand, a higher - quality mould with a higher initial investment may have lower long - term costs due to its durability and reliability. Consider a production run of one million plastic parts. A lower - cost mould that needs to be replaced every 100,000 parts will result in multiple replacement costs, as well as the associated downtime costs. In contrast, a more expensive but durable mould that can produce the entire one - million - part run without major issues will prove to be more cost - effective in the long run.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic and metal products custom supplier, Yigu Technology has rich experience in the procurement and customization of plastic moulds. When it comes to material selection, we are extremely strict. We work closely with reliable material suppliers to ensure that only the highest - quality raw materials are used in our moulds. For example, for moulds with high - wear requirements, we prefer to use premium alloy steels that can withstand the test of long - term production.
In terms of the manufacturing process, our team of skilled engineers and technicians is proficient in various advanced techniques. We use state - of - the - art CNC machining, EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining), and other precision - manufacturing methods to guarantee the high precision and quality of our plastic moulds.
Moreover, we understand that every customer has unique needs. Whether it's a special product shape, a specific tolerance requirement, or an urgent delivery time, we are committed to providing customized solutions. We communicate closely with customers from the initial design stage, listening to their ideas and requirements, and then optimize the design and manufacturing process accordingly. This customer - centric approach has enabled us to build long - term partnerships with many clients in different industries.
FAQ about Plastic Moulds
Q1: How can I determine the right type of plastic mould for my product?
The choice of plastic mould depends on several factors. First, consider the shape and size of your product. Complex - shaped products with fine details are often better suited for injection moulds due to their high - precision capabilities. For example, if you are manufacturing small, intricate plastic gears, injection moulding would be an ideal choice. Second, think about the production volume. For high - volume production, injection moulds are more cost - effective in the long run despite their high initial cost. However, if you are producing a small number of parts, compression moulds might be a more affordable option. Additionally, the type of plastic material you plan to use also matters. Some plastics are more suitable for certain moulding processes. For instance, thermosetting plastics are typically processed using compression moulds.
Q2: What is the typical lifespan of a plastic mould?
The lifespan of a plastic mould can vary widely. It depends on factors such as the material of the mould, the frequency of use, and the maintenance it receives. Generally, a well - made plastic mould can last from several thousand to millions of injection cycles. For example, a mould made from lower - quality steel might have a lifespan of around 10,000 - 50,000 cycles, while a high - quality mould made from premium alloy steel like NAK80 can endure up to 1,000,000 cycles or more in some cases. Moulds used in high - volume production environments with proper maintenance can often achieve the higher end of the cycle range, while those in less - ideal conditions or with poor maintenance may have a shorter lifespan.
Q3: How do I maintain my plastic moulds to ensure their longevity?
Regular maintenance is crucial for extending the lifespan of plastic moulds. Firstly, clean the mould regularly. After each production cycle, remove any plastic residue, dust, and debris from the mould's surface and cavities. You can use a soft brush and a suitable cleaning agent that is compatible with the mould material. For example, a mild detergent solution can be used for most steel moulds. Secondly, lubricate the moving parts of the mould, such as the ejector pins and slides. This reduces friction and wear, ensuring smooth operation. Thirdly, check the mould for signs of wear, such as scratches, dents, or cracks, on a regular basis. Early detection of these issues allows for timely repairs, preventing further damage. Finally, when the mould is not in use, store it in a clean, dry environment to prevent rust and corrosion. You can also apply a protective coating or rust inhibitor to the mould's surface for added protection.