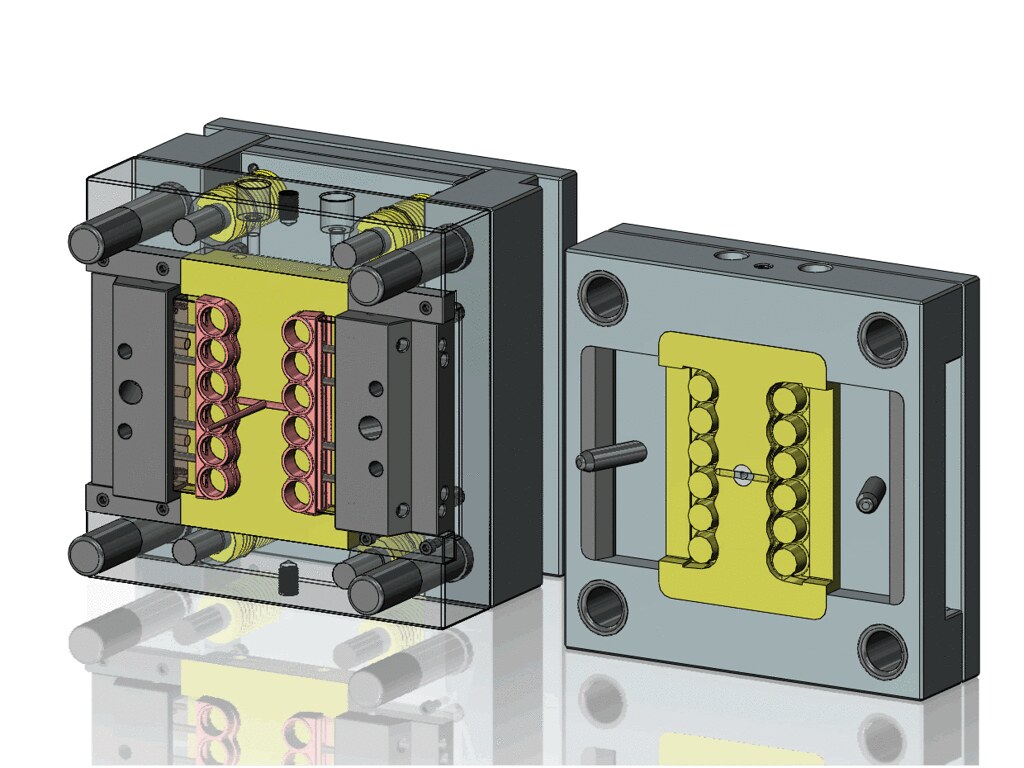
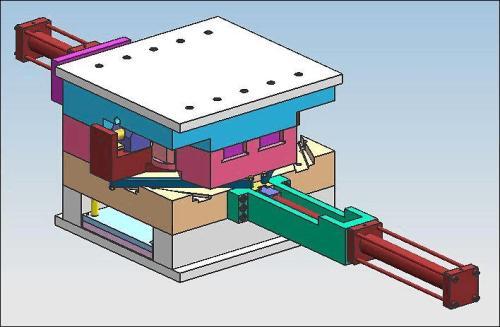
Introduction
Injection molding is a widely used manufacturing process in the plastics industry. It involves melting plastic material and injecting it into a mold cavity under high pressure. Once the plastic cools and solidifies, the mold is opened, and the finished part is ejected. This process allows for the production of complex - shaped plastic parts with high precision and in large quantities.
The choice of mold material plays a crucial role in the injection - molding process. Among various mold materials, aluminum molds have emerged as an ideal option for many applications. In this article, we will explore what makes aluminum molds so suitable for injection molding from multiple aspects, including their physical properties, cost - effectiveness, and production - related advantages.
1. Exceptional Thermal Conductivity
1.1 Fast Cooling Cycles
One of the most remarkable features of aluminum molds in injection molding is their exceptional thermal conductivity. Aluminum has a much higher thermal conductivity compared to many other mold materials, such as steel. For instance, the thermal conductivity of aluminum alloys commonly used in mold - making can be around 150 - 200 W/(m·K), while that of some tool steels is only about 30 - 50 W/(m·K).
This high thermal conductivity allows aluminum molds to transfer heat away from the injected plastic much more rapidly. As a result, the cooling cycles in the injection - molding process are significantly shortened. In a typical injection - molding production of small plastic components, if a steel mold is used, the cooling time might be around 30 seconds per cycle. However, when an aluminum mold is employed, the cooling time can be reduced to as little as 10 - 15 seconds per cycle. This reduction in cooling time directly translates into a higher production output. With shorter cooling cycles, more parts can be produced within the same time frame, increasing the overall productivity of the injection - molding operation.
1.2 Consistent Product Quality
The fast and uniform cooling provided by aluminum molds is crucial for ensuring consistent product quality. When the plastic in the mold cools evenly, it solidifies uniformly, minimizing the occurrence of internal stresses and defects within the final product.
Uneven cooling can lead to several product defects. For example, it can cause warping, where the part twists or bends out of its intended shape. In the case of plastic boxes produced through injection molding, if the cooling is uneven, one side of the box may cool faster than the other, causing the box to warp, which can affect its functionality and aesthetics. Another common defect is sink marks. When a thick - walled section of a plastic part cools more slowly than the surrounding areas, the material shrinks unevenly, creating small depressions or sink marks on the surface of the part.
Aluminum molds, with their excellent thermal conductivity, help to prevent these issues. The heat is dissipated quickly and evenly across the mold cavity, ensuring that all parts of the plastic cool at a similar rate. This results in products with consistent wall thicknesses, uniform mechanical properties, and a high - quality surface finish. For products like plastic gears, which require precise dimensions and uniform material properties for smooth operation, the use of aluminum molds can significantly improve the manufacturing quality, reducing the number of defective products and improving the overall yield of the production process.
2. Lightweight and Easy to Handle
2.1 Reduced Setup Time
Aluminum molds are significantly lighter than molds made from materials like steel. The density of aluminum is approximately one - third that of steel. For example, if a steel mold of a certain size weighs 300 kilograms, an aluminum mold of the same dimensions might weigh only around 100 kilograms. This substantial difference in weight makes aluminum molds much easier to handle during the setup process in injection - molding operations.
When setting up a new mold for production, workers need to move the mold into place on the injection - molding machine, align it correctly, and make the necessary connections. With a lighter aluminum mold, fewer workers are required for this task, and the time taken to complete the setup is reduced. In a large - scale injection - molding factory where multiple mold setups are carried out daily, this reduction in setup time can accumulate to a significant amount over a month or a year. For instance, if a steel - mold setup takes 2 hours on average, an aluminum - mold setup might only take 30 minutes to 1 hour, depending on the complexity of the mold and the injection - molding machine. This shorter setup time not only increases the overall productivity of the factory but also allows for more frequent mold changes, enabling the production of a wider variety of plastic parts without significant time losses between production runs.
2.2 Lower Equipment Wear
The reduced weight of aluminum molds also has a positive impact on the injection - molding equipment. When a heavy mold is mounted on an injection - molding machine, the machine's moving parts, such as the tie bars, hydraulic cylinders, and the mold - mounting plates, are subjected to greater stress during the opening and closing of the mold, as well as during the injection and ejection processes.
Over time, this continuous stress can lead to premature wear and tear of these components. For example, the tie bars of an injection - molding machine might experience fatigue and elongation if they are constantly under the load of a heavy steel mold. This can result in inaccurate mold clamping, which in turn can cause issues such as flash (excess plastic around the edges of the molded part) and inconsistent part quality.
In contrast, the lighter aluminum molds place less stress on the injection - molding machine. The machine's components experience less wear, which means they can operate for longer periods without the need for replacement or major repairs. A study on injection - molding machine maintenance costs showed that when using aluminum molds, the annual maintenance cost related to the mold - handling components of the machine was reduced by approximately 30 - 40% compared to when using steel molds. This not only saves on the cost of replacement parts but also reduces the downtime of the injection - molding machine, keeping the production line running more smoothly and efficiently.
3. High Machinability
3.1 Complex Geometries with Ease
Aluminum is highly malleable and has excellent machinability, making it an ideal material for creating molds with complex geometries. In the injection - molding process, many products require molds with intricate shapes, such as those for electronic device housings with curved surfaces, thin - walled sections, and multiple internal features.
For example, in the production of smartphone cases, the molds need to have precise details to replicate the logo, camera cut - outs, and speaker grilles accurately. Aluminum molds can be machined using various techniques, including computer - numerical - control (CNC) machining, to achieve these complex shapes with high precision. The ability to create such detailed molds allows manufacturers to produce plastic parts that meet the aesthetic and functional requirements of modern products.
In contrast, some other mold materials, like certain types of cast iron, are more difficult to machine into complex shapes. Their brittleness and lower machinability make it challenging to achieve the same level of detail and precision without the risk of cracking or chipping during the machining process. This makes aluminum a clear choice when the injection - molding mold needs to have a complex design.
3.2 Quick Turnaround for Prototyping
During the product - development phase, rapid prototyping is crucial. Aluminum molds can be fabricated much faster than molds made from other materials, such as steel. This is because aluminum has a relatively low hardness, which allows for faster cutting speeds and reduced machining time.
For instance, when developing a new medical device prototype, time is of the essence. A company might need to quickly test different design concepts to ensure the device's functionality, ergonomics, and compatibility with other components. With an aluminum mold, the machining process for creating the prototype mold can be completed in a matter of days or even hours, depending on the complexity of the design. This allows for multiple design iterations within a short period.
If a steel mold were used instead, the machining process would be much slower due to the higher hardness of steel. The longer machining time would not only delay the prototyping process but also increase the cost associated with the development, as more machine - hours would be required. The quick turnaround time provided by aluminum molds enables companies to get their products to market faster, gain a competitive edge, and make informed decisions about the final product design based on early prototype testing.
4. Cost - effectiveness
4.1 Initial Investment
When considering the initial investment for molds in injection - molding projects, aluminum molds often present a more cost - friendly option compared to some other mold materials, especially steel. The cost of raw materials is a significant factor in mold manufacturing. Aluminum is generally less expensive per unit mass than high - quality tool steels. For example, in the current market, the price of aluminum alloy materials suitable for mold - making is relatively lower. A typical aluminum alloy used in mold production might cost around \(2 - \)3 per pound, while certain high - performance tool steels can cost \(5 - \)10 per pound or even more.
This price difference in raw materials directly affects the overall cost of the mold. For small - to medium - sized injection - molding businesses with limited budgets, the lower initial cost of aluminum molds can be a major advantage. It allows these companies to start production with a smaller capital outlay, reducing the financial burden in the early stages of a project. Additionally, the machining cost of aluminum is also relatively lower. As mentioned before, aluminum has excellent machinability, which means it requires less machining time and fewer cutting tools compared to steel during the mold - making process. This further contributes to the lower initial investment in aluminum molds.
4.2 Long - term Savings
Aluminum molds offer substantial long - term savings in the injection - molding production process. Firstly, as we discussed in the thermal conductivity section, the fast cooling cycles of aluminum molds lead to increased production output. With more parts being produced per unit of time, the cost per part is effectively reduced. For instance, if a factory is producing plastic toys, and by using aluminum molds, it can increase the daily production quantity from 1000 to 1500 units. Assuming the total daily production cost (including labor, energy, etc.) remains relatively stable, the cost per toy will decrease, resulting in higher profit margins in the long run.
Secondly, the reduced weight of aluminum molds, which is beneficial for handling and equipment wear, also brings cost savings. Since aluminum molds cause less wear and tear on the injection - molding equipment, the maintenance and replacement costs of the equipment are significantly reduced. For example, the replacement frequency of tie bars in an injection - molding machine can be extended from once every two years when using steel molds to once every three to four years when using aluminum molds. Considering the high cost of replacing these key components of the injection - molding machine, this can lead to substantial savings over the years of operation.
Moreover, the high machinability of aluminum molds means that they can be repaired and modified more easily and inexpensively. If there are any design changes or minor damages during the production process, aluminum molds can be quickly adjusted, minimizing the downtime of the production line. In contrast, making the same modifications to a steel mold might be more time - consuming and costly, as steel is more difficult to machine and requires more advanced techniques and tools for repair. Overall, the long - term savings associated with aluminum molds make them an economically attractive choice for injection - molding operations.
5. Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic metal custom products Supplier, Yigu Technology highly values the advantages of aluminum molds in injection molding. We believe that aluminum molds have unique strengths, especially when it comes to small - batch production and high - precision injection - molding requirements.
For small - batch production, the relatively low initial investment of aluminum molds allows customers to start production with less capital. This is a great advantage for startups or projects with limited budgets. The quick turnaround time for prototyping with aluminum molds also enables us to respond rapidly to customers' design changes and new product development needs.
In terms of high - precision requirements, the excellent machinability of aluminum molds ensures that we can create molds with complex and accurate geometries, meeting the strict quality standards of our customers. We have witnessed how aluminum molds have helped us provide more flexible and customized solutions to our clients, satisfying their diverse needs in the market.
6. FAQ
6.1 Are aluminum molds suitable for high - volume production?
Aluminum molds can be suitable for high - volume production to a certain extent. Their fast cooling cycles enable higher production rates, which is beneficial for high - volume scenarios. However, compared to steel molds, aluminum molds may experience more significant wear and tear over a large number of production cycles due to their relatively lower hardness. For very high - volume production runs of hundreds of thousands or millions of parts, steel molds might be a more durable option in the long run. But if the production volume is in the tens of thousands or if the production cycle needs to be completed in a short time, aluminum molds can still be a great choice. It's important to consider factors like the part design, production schedule, and budget when determining if aluminum molds are suitable for high - volume production.
6.2 How does the cost of aluminum molds compare to steel molds?
In terms of the initial cost, aluminum molds are generally more cost - effective. The raw material cost of aluminum is lower than that of high - quality tool steels, and its better machinability also reduces the machining cost during mold manufacturing. However, steel molds usually have a longer lifespan. In high - volume, long - term production, although the initial investment in steel molds is higher, their longer - term use can spread the cost over more production cycles. Aluminum molds, on the other hand, may need to be replaced more frequently in high - volume production, but their advantages in shorter production cycles and lower equipment wear can also bring long - term savings. For example, for a small - batch production of 5000 parts, an aluminum mold might cost \(5000, while a steel mold could cost \)8000. But if the production volume increases to 500,000 parts, the steel mold, with its longer lifespan, may end up being more cost - effective overall considering replacement costs.
6.3 Can aluminum molds be used for all types of plastics?
Aluminum molds can be used for most common plastics in injection molding, such as polyethylene (PE), polypropylene (PP), and acrylonitrile - butadiene - styrene (ABS). These plastics have relatively low processing temperatures and do not cause significant chemical reactions with aluminum. However, for some high - temperature plastics like polyetheretherketone (PEEK) or plastics with strong chemical reactivity, the use of aluminum molds may be challenging. High - temperature plastics can cause rapid wear and degradation of aluminum molds due to the high processing temperatures involved. Additionally, some plastics may have chemical components that can corrode aluminum over time. So, while aluminum molds are versatile, it's essential to consider the compatibility between the plastic material and the aluminum mold, especially when dealing with special - purpose plastics, to ensure mold life and product quality.
Conclusion
In conclusion, aluminum molds offer a wide range of advantages that make them an ideal choice for injection molding in many applications. Their high thermal conductivity leads to fast cooling cycles and consistent product quality, while their lightweight nature reduces setup time and equipment wear. The high machinability of aluminum allows for the creation of complex geometries and quick prototyping, and they are cost - effective both in terms of initial investment and long - term savings.
However, it's important to note that aluminum molds may not be suitable for every injection - molding scenario. For example, in cases where extremely high - volume production with millions of parts is required or when dealing with plastics that have very high processing temperatures, other mold materials like steel might be more appropriate.
When choosing a mold material for your injection - molding project, carefully consider your specific requirements, such as production volume, part complexity, plastic material type, and budget. By weighing the pros and cons of different mold materials, you can make an informed decision and select the mold that best suits your needs, ensuring efficient production and high - quality end products.