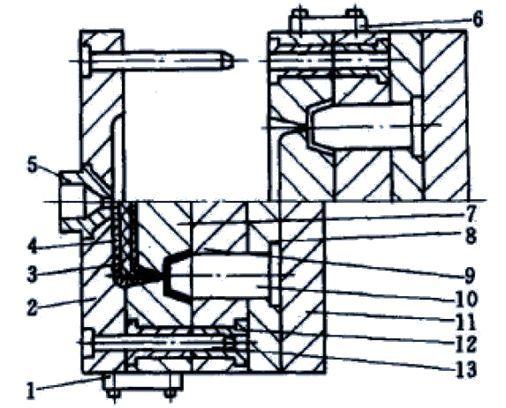
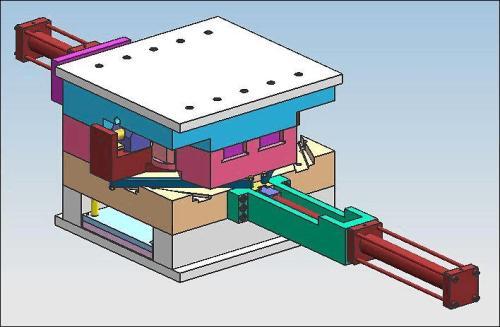
What is an Injection Mold Sprue?
In the world of injection molding, the injection mold sprue is a fundamental and crucial component. It serves as the primary channel through which the molten plastic enters the mold cavity. Think of it as the "gateway" for the plastic material to start its transformative journey into the desired final product.
When the injection molding process begins, plastic pellets are first melted in the injection unit of the molding machine. This molten plastic, which is now in a highly fluid state, needs a clear path to reach the mold where it will take on the shape of the product. The sprue provides exactly that path. It is typically a cylindrical or conical - shaped passageway that connects the nozzle of the injection machine to the mold cavity.
The sprue's design is carefully engineered to ensure smooth and efficient flow of the molten plastic. A well - designed sprue minimizes pressure drops during the injection process. If the sprue has an improper diameter or shape, it can cause issues such as uneven filling of the mold cavity, premature solidification of the plastic, or even result in defects in the final product. For example, if the sprue is too narrow, the high - pressure flow of the molten plastic can create excessive shear stress, which may lead to material degradation or inconsistent part quality.
In a standard two - plate injection mold, the sprue is usually located at the center of the mold's stationary half. As the injection machine injects the molten plastic, it passes through the sprue bushing, which is a hardened steel insert that lines the sprue. The sprue bushing helps to maintain the integrity of the sprue, resist wear and tear from the high - velocity plastic flow, and also aids in heat transfer, ensuring that the plastic remains in a molten state as it travels through the sprue.
Understanding the basic concept of the injection mold sprue is the first step in grasping the complexity of the injection molding process. Without a properly functioning sprue, the entire injection molding operation can be compromised, leading to increased production costs, lower - quality products, and potential production delays.
The Structure and Components of the Sprue
Sprue Bushing
The sprue bushing is an essential part of the injection mold sprue system. It is typically made of high - quality, wear - resistant materials such as hardened steel. The reason for using such materials is that during the injection molding process, the molten plastic rushes through the sprue at a very high speed. This high - velocity flow can cause significant abrasion to the inner surface of the sprue passage.
A sprue bushing with excellent wear - resistance can effectively withstand this high - speed plastic flow. For example, in a high - volume production of small plastic components like smartphone cases, the injection molding machine may cycle hundreds of times a day. Over time, without a proper sprue bushing, the sprue would quickly wear out, leading to an irregular inner surface. This irregularity could cause plastic flow disruptions, such as turbulence in the plastic stream, which in turn may result in inconsistent wall thicknesses in the final product.
Moreover, the sprue bushing also plays a role in heat transfer. It helps to keep the molten plastic at the right temperature as it travels through the sprue. If the plastic cools down prematurely in the sprue, it can cause blockages or incomplete filling of the mold cavity. By maintaining good heat - transfer properties, the sprue bushing ensures the stability of the injection molding process, which is crucial for the overall mold life and the quality of the products being produced.
Nozzle Bushing Connection
The connection between the nozzle bushing (also known as the sprue bushing in some contexts, but here we refer to its function of connecting the injection nozzle) and the injection machine nozzle is of utmost importance. This connection must be both tight and smooth.
A tight connection is necessary to prevent any leakage of the molten plastic. When the injection machine injects the plastic at high pressure, even a tiny gap at the connection point can lead to plastic seepage. For instance, in a study of a medium - sized injection molding factory, it was found that a 0.1 - mm gap at the nozzle - bushing connection could cause a leakage rate of about 5 - 10 grams of plastic per injection cycle in a high - pressure injection process. This not only results in material waste but can also cause problems such as messy machine work areas and potential damage to the injection machine components due to the hardened leaked plastic.
A smooth connection is equally vital for the unobstructed flow of the molten plastic. If there are any misalignments or rough surfaces at the connection, it can create flow resistance. Research has shown that a surface roughness of more than Ra 0.8μm at the connection can increase the injection pressure required by about 10 - 15%. Higher injection pressures mean more energy consumption, and it can also put additional stress on the mold and the injection machine, reducing their service life. In some cases, the rough connection can even cause the plastic to solidify prematurely at the connection point, halting the injection process.
Common Issues with Injection Mold Sprue and Solutions
Blockage Problems
One of the most prevalent issues with the injection mold sprue is blockage. There are several reasons for this problem. Firstly, impurities can mix into the molten plastic during the material - handling process. For example, dust particles or small pieces of foreign matter from the storage environment might enter the plastic pellets. Once these impurities reach the sprue, they can accumulate over time and gradually block the flow path. In a production environment where raw materials are not properly stored in sealed containers, the probability of impurity - induced blockages can increase by about 30 - 40%.
Secondly, plastic 碳化 (carbonization) can occur. This usually happens when the plastic stays in the heating barrel of the injection machine for too long at high temperatures. The over - heated plastic decomposes and forms charred particles. These carbonized plastic pieces are then carried along with the molten plastic stream into the sprue, where they can cause blockages. In cases where the injection molding machine's temperature control system malfunctions, the risk of plastic carbonization and subsequent sprue blockage rises significantly.
To solve these blockage problems, several measures can be taken. Installing a filter at the entrance of the injection unit can effectively prevent impurities from entering the sprue. A fine - mesh filter with a pore size of around 0.1 - 0.3 mm can capture most of the common impurities. Regularly cleaning the mold, especially the sprue area, is also crucial. A cleaning cycle of every 500 - 1000 injection cycles can help keep the sprue free from accumulated debris. Additionally, optimizing the injection process parameters, such as adjusting the temperature profile and reducing the residence time of the plastic in the heating barrel, can prevent plastic carbonization.
Erosion and Wear
The sprue bushing, which is in direct contact with the high - velocity molten plastic flow, is prone to erosion and wear. The continuous abrasion by the flowing plastic gradually wears down the inner surface of the sprue bushing. This wear is mainly caused by the mechanical friction between the plastic and the bushing material. In high - volume production scenarios where the injection molding machine runs continuously for long hours, the wear rate of the sprue bushing can be quite significant. For instance, in a factory that produces plastic toys, after 10,000 injection cycles, the inner diameter of the sprue bushing may increase by 0.1 - 0.2 mm due to wear.
The consequences of erosion and wear are significant. As the sprue bushing wears out, the inner surface becomes rough, which increases the flow resistance of the molten plastic. This, in turn, can lead to higher injection pressures being required to fill the mold cavity. Higher injection pressures can cause more stress on the mold components, potentially leading to premature mold failure. Moreover, the uneven wear of the sprue bushing can result in an uneven plastic flow, which may cause defects in the final product, such as inconsistent wall thicknesses or surface irregularities.
To prevent erosion and wear, choosing the right material for the sprue bushing is essential. High - quality, wear - resistant steels, such as those with high chromium content, can offer better resistance to the abrasive action of the plastic. Surface treatment techniques, like nitriding or hard chrome plating, can also enhance the wear - resistance of the sprue bushing. Regularly checking the condition of the sprue bushing and replacing it when necessary is a must. A visual inspection every 2000 - 3000 injection cycles, along with dimensional measurements using precision tools like calipers, can help determine when the bushing needs to be replaced. If signs of excessive wear, such as a roughness value of more than Ra 1.6μm or a significant increase in the inner diameter, are detected, it's time to replace the sprue bushing to ensure the smooth operation of the injection molding process.
Yigu Technology's Perspective
As a non - standard plastic metal products custom Supplier, Yigu Technology deeply understands the significance of the injection mold sprue. In our custom - service process, the design of the sprue is always a top priority. A well - designed sprue can ensure that the molten plastic flows smoothly into the custom - designed mold cavity, which is crucial for achieving the high - precision and unique shape requirements of non - standard products.
We also pay great attention to the maintenance of the sprue. Regular inspections and timely replacement of worn - out sprue bushings are carried out to prevent issues like blockages and inconsistent plastic flow. By doing so, we can maintain the stability of the injection molding process, reduce production errors, and ultimately provide our customers with high - quality non - standard plastic metal products that meet their specific needs.
FAQ about Injection Mold Sprue
Q1: How to choose the right diameter for the injection mold sprue?
When choosing the diameter of the injection mold sprue, several factors need to be considered. First, the flowability of the plastic material is crucial. For highly viscous plastics like some engineering plastics, a larger - diameter sprue is required to reduce the flow resistance. For example, if you are using polycarbonate, the sprue diameter might need to be 6 - 8 mm for a medium - sized product. Second, the size of the product matters. Larger products generally need a larger - diameter sprue to ensure sufficient plastic flow to fill the entire mold cavity. If the product has a large volume, say above 100 cubic centimeters, a sprue diameter of 8 - 12 mm could be appropriate. Additionally, the injection volume of the injection machine should also be taken into account. A machine with a higher injection volume can support a larger - diameter sprue.
Q2: What should I do if the sprue bushing is worn out?
If you find that the sprue bushing is worn out, the first step is to stop the injection molding process immediately to prevent further issues with the product quality. Then, carefully remove the mold from the injection machine. To replace the sprue bushing, you need to first loosen the retaining screws or bolts that hold the bushing in place. After removing the old bushing, clean the sprue area thoroughly to remove any debris or plastic residues. When installing the new sprue bushing, make sure it is properly aligned with the injection nozzle and the mold cavity. Tighten the retaining screws or bolts evenly to ensure a secure fit. It's also important to check the connection between the new bushing and the injection nozzle for any gaps or misalignments before restarting the injection molding process.
Q3: Can the shape of the injection mold sprue affect the quality of the final product?
Yes, the shape of the injection mold sprue can significantly affect the quality of the final product. A conical - shaped sprue is commonly used because it helps to gradually reduce the cross - sectional area of the plastic flow, which can improve the filling efficiency and reduce the risk of air traps. If the sprue has an irregular or non - optimal shape, it can lead to uneven plastic flow. For example, a sprue with sharp corners can cause turbulence in the plastic stream, resulting in inconsistent filling of the mold cavity. This can lead to defects such as short shots (incomplete filling), weld lines (where two streams of plastic meet), and variations in product thickness. A well - designed sprue shape ensures that the plastic fills the mold cavity evenly, which is essential for achieving a high - quality product with consistent strength and dimensions.